Agent vs Agentless ITAM: What’s the Difference?
Discover the differences between agent vs agentless ITAM, their pros and cons, and how to pick the right approach for your business.
Businesses manage IT assets in different ways depending on their environment. A company with remote employees may need to monitor laptops that are often offline, while another with all devices inside one office network may focus on scanning what’s connected in real time. Both approaches fall under IT Asset Management (ITAM), but they use different methods: agent-based and agentless.
Each method comes with unique strengths and challenges. In this article, we’ll break down what agent vs agentless ITAM means, how they work, and how to decide which approach makes the most sense for your organization.
What Is Agent-Based ITAM?
Agent-based IT Asset Management relies on small software programs, known as agents, that are installed on each device. Once installed, the agent runs quietly in the background and collects information such as hardware specifications, operating system details, installed applications, software usage, patch status, and security settings.
Because the agent lives on the device, it can continue to track activity even when the device is offline or outside the corporate network. When the device reconnects, the data is sent back to the ITAM system for analysis and reporting.
This method gives IT teams strong visibility into their assets. They can see changes in real time, spot compliance issues, and identify potential risks quickly. Agent-based ITAM is often preferred in organizations that have remote or hybrid workforces, strict regulatory requirements, or a need for detailed tracking of devices across multiple locations.
Pros of Agent-Based ITAM
- Collects rich and detailed data from each device.
- Enables real-time monitoring and faster issue detection.
- Works for remote or offline devices.
- Helps ensure compliance with software and security policies.
Cons of Agent-Based ITAM
- Requires installation and updates on every device.
- Adds extra workload for IT teams to maintain agents.
- Can slightly affect device performance in some cases.
What Is Agentless ITAM?
Agentless IT Asset Management does not require software to be installed on individual devices. Instead, it uses methods like network scanning, credentials, or integrations with existing systems such as Active Directory or cloud platforms to discover and collect asset information. This makes deployment faster, since IT teams do not need to touch each device individually.
The data gathered usually covers hardware details, installed applications, system configurations, and usage while the device is connected to the network. However, if a device is offline or not visible on the network, it may not be captured until it reconnects. Because of this, agentless ITAM works best in environments where most assets are consistently on the same network, such as office-based organizations or data centers.
Pros of Agentless ITAM
- Faster to deploy since no software installation is needed.
- Easier to maintain with fewer updates or patches.
- No impact on device performance.
- Ideal for organizations with centralized, network-connected assets.
Cons of Agentless ITAM
- Provides less detailed data compared to agents.
- Dependent on network availability and visibility.
- May miss assets that are offline, remote, or not properly connected.
- Limited ability to track real-time changes.
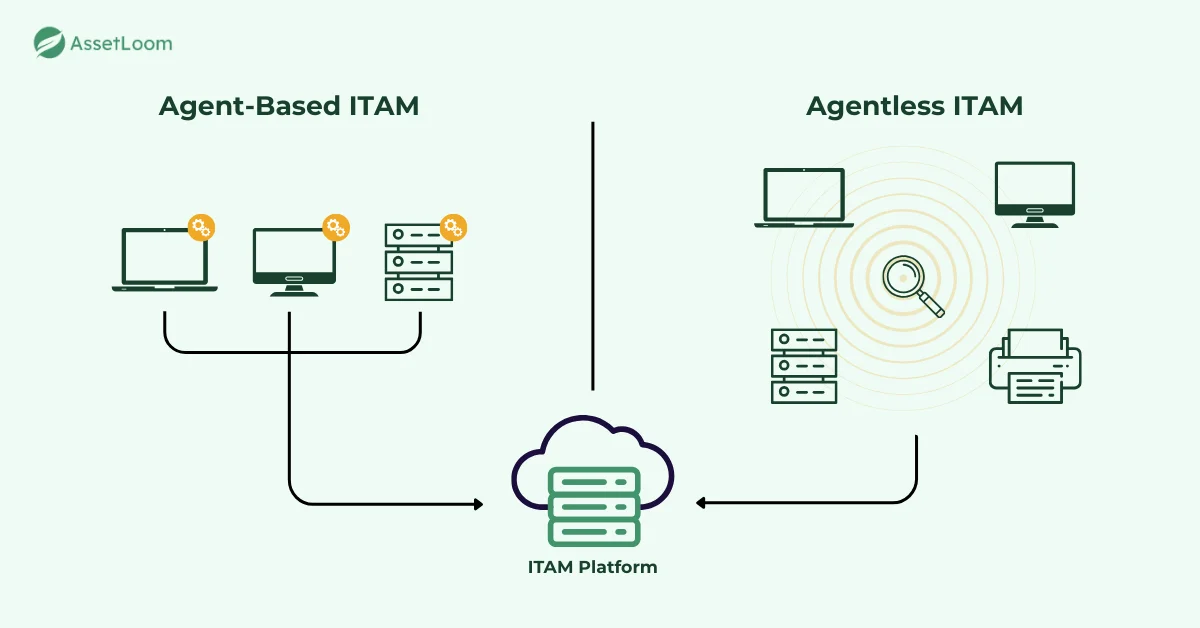
Key Differences Between Agent and Agentless ITAM
Both agent-based and agentless ITAM aim to give organizations better control over their assets, but they work in different ways. Understanding the differences helps businesses decide which method, or combination, best suits their needs.
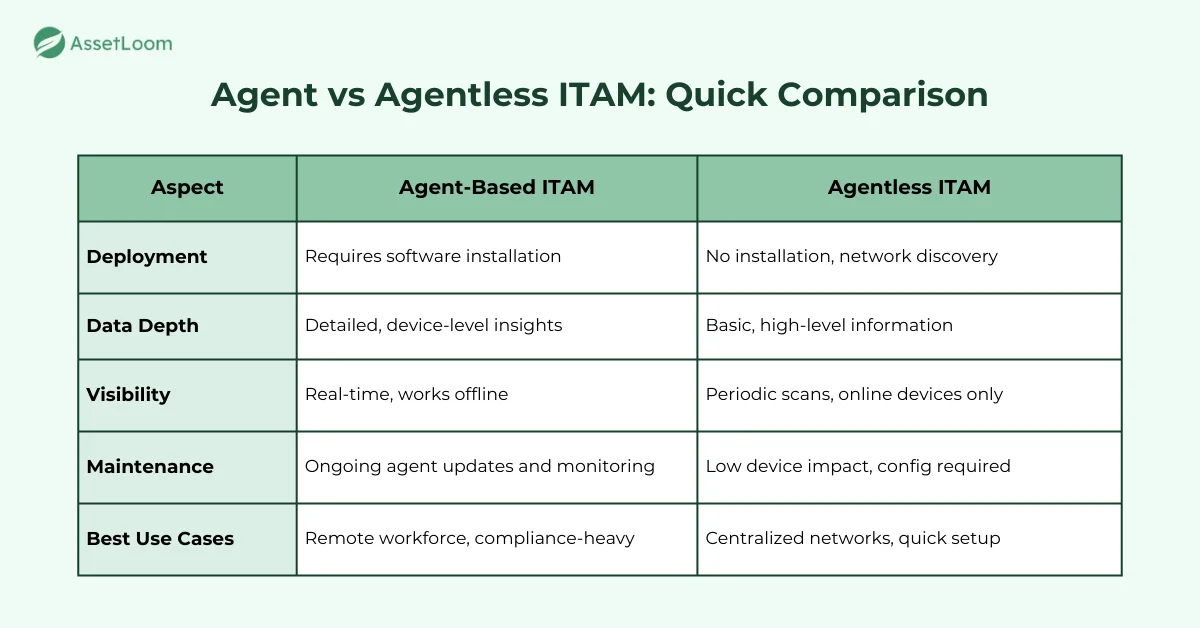
Deployment and Setup
Deployment is often the first factor organizations consider. Installing agents on every device requires planning, but once installed, they continue to run quietly in the background. This approach is more hands-on at the start but provides consistency once in place.
Agentless ITAM, by comparison, is easier to deploy because it does not require touching individual devices. Network scanning, system credentials, and platform integrations make it possible to get a broad view quickly. This is particularly helpful in large environments where time and resources are limited. The trade-off is that visibility depends on the strength and configuration of the discovery tools.
Data Depth and Accuracy
Data quality differs between the two approaches. Agent-based ITAM gathers detailed information directly from devices, often including hardware status, software versions, user activity, and security posture. This level of insight can be valuable for compliance or audit needs.
Agentless ITAM focuses on what is visible over the network. It captures enough information to build an inventory, but the details may not go as deep as agent-based tracking. For many organizations, especially those that only need a high-level view of their assets, this is sufficient. The choice depends on whether the business values depth of insight or prefers simplicity.
Real-Time Visibility
How often data is updated can also affect IT asset tracking. Agents run continuously, so they provide real-time or near-real-time updates. Devices that are offline can still be monitored, with the data syncing once they reconnect.
Agentless ITAM works differently. Data is collected during scheduled scans or discovery cycles, which means updates may not be instant. If a device is disconnected, it may not appear until it is back online. For businesses that do not require constant updates, this approach may be enough, while others may prefer the immediacy offered by agents.
Maintenance and Management
Maintenance is another key consideration. Agent-based ITAM requires updates to keep agents functioning properly. This adds a layer of responsibility for IT teams, although most modern agents are lightweight and designed to have minimal impact on performance.
Agentless ITAM reduces the need for device-level maintenance since no agents are installed. However, it does require strong network management. IT teams must ensure discovery scans are accurate and that access to systems is configured securely. Each approach shifts the management workload in different ways, one to device upkeep, the other to network and configuration oversight.
Best Use Cases
The decision often comes down to environment and priorities. Organizations with remote workers, mobile devices, or strict compliance needs often benefit from the detail and consistency that agent-based ITAM offers.
On the other hand, companies with centralized, always-connected devices may prefer the speed and simplicity of agentless ITAM. It provides visibility without adding overhead to devices or requiring installations.
Some organizations combine both. For example, they may use agents for remote laptops and mission-critical systems while using agentless scans to cover servers and office-based devices. This hybrid approach provides flexibility and balances depth with ease of management.
Which ITAM Approach Is Right for Your Business?
There isn’t a single answer that works for every organization. The right ITAM approach depends on how your business operates, what type of assets you manage, and what level of detail you need. Below are some key factors to consider.
Workforce Location
If your employees are remote or travel frequently, agent-based ITAM often makes sense. Agents continue collecting data even when devices are offline and sync updates once they reconnect. This prevents visibility gaps.
In contrast, if most devices are fixed in offices, campuses, or data centers, agentless ITAM may be a better fit. It can quickly discover assets on the network without adding software to each device.
Compliance and Reporting Needs
Industries with strict regulations, such as healthcare or finance, often benefit from agent-based ITAM. The richer, more detailed reporting helps satisfy audits and compliance checks.
For organizations where compliance demands are lighter, agentless ITAM provides enough information to build inventories and keep track of active assets without adding extra management tasks.
IT Resources and Maintenance
Agent-based ITAM requires time to deploy and maintain agents across devices. Larger teams may have the resources to manage this overhead, while smaller IT departments may prefer to avoid it.
Agentless ITAM reduces the device-level workload but shifts the responsibility to network and system management. IT teams must ensure discovery scans are configured correctly and network visibility remains strong.
Hybrid Approaches
Many organizations choose not to rely on just one method. A hybrid approach can use agents for critical or mobile assets while applying agentless discovery across stable, always-connected systems.
This balances the depth of agent-based monitoring with the simplicity of agentless scanning.
Conclusion
Agent-based and agentless ITAM both serve the same goal: giving organizations visibility into their assets. The difference lies in how they collect information, how detailed the data is, and how much effort is required to maintain them.
Agent-based ITAM offers depth and real-time visibility, making it valuable for businesses with remote workforces or strict compliance needs. Agentless ITAM delivers speed and simplicity, which can be enough for organizations with centralized assets and lighter reporting demands.
For many businesses, the right choice is not about picking one over the other. A hybrid approach that combines both methods often provides the best balance of coverage, detail, and efficiency.

Related Blogs
Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom. right in your inbox

