What is a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) and Why It Matters in ITAM?
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a centralized system that stores and manages IT assets and their relationships.
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a centralized system that stores and manages IT assets and their relationships.
In IT Asset Management (ITAM), a well-structured CMDB plays a critical role by ensuring accurate asset tracking, optimizing resource allocation, and improving decision making. By integrating with IT Service Management (ITSM) and other business processes, CMDB enhances change management, incident resolution, and compliance efforts.
In this article, we’ll uncover the fundamentals of Configuration Management Database (CMDB), explore how it works, and its key benefits for ITAM
What is a Configuration Management Database (CMDB)?
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a centralized system used to store information about an organization’s IT assets, also known as configuration items (CIs). These assets can include hardware, software, networks, cloud resources, and relationships between them.
Unlike a simple asset inventory that only lists IT assets, a CMDB tracks how assets interact within the IT environment. It provides a centralized and comprehensive view of the entire IT infrastructure, helping to manage and operate the system more efficiently. As a result, businesses can better understand dependencies, optimize IT operations, and improve decision-making.
The relationship between CMDB and IT Asset Management (ITAM) is a symbiotic and mutually beneficial one in effectively managing an organization's IT systems. The CMDB provides detailed and accurate information about assets to ITAM, enabling ITAM to perform its functions more effectively. Conversely, ITAM helps ensure that the information in the CMDB is consistently updated and accurate, making the CMDB a reliable data source.
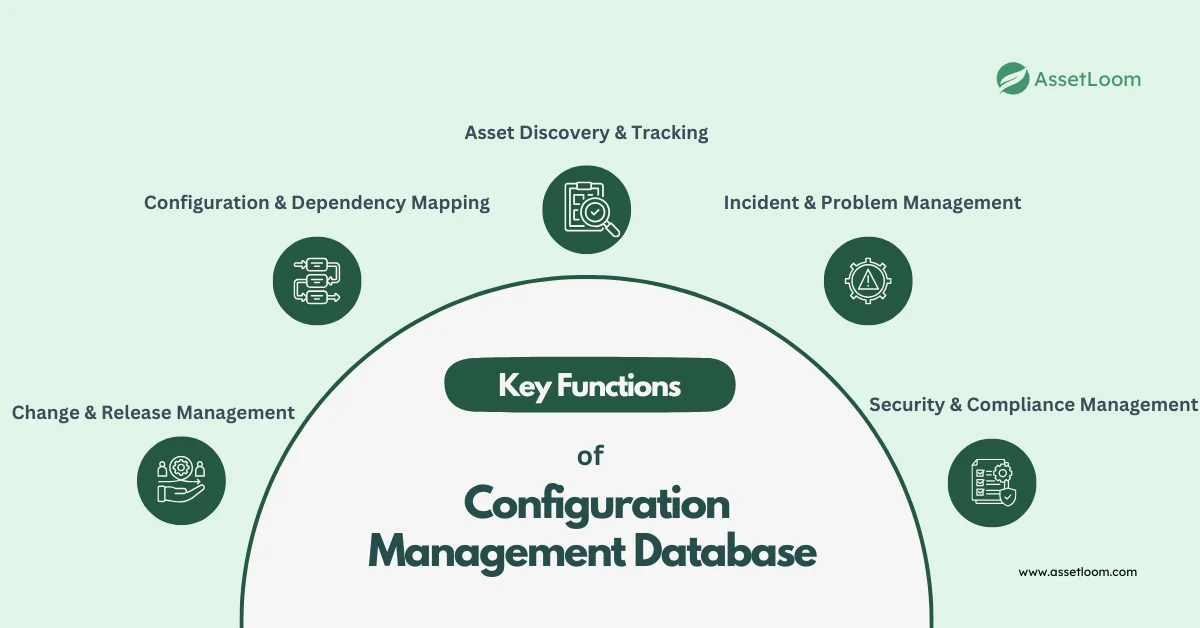
Features & Functions of Configuration Management Database (CMDB)
A CMDB acts as a digital blueprint of an organization's IT environment, offering a structured system to store and manage IT asset data. Its purpose is to provide accurate, real-time visibility into IT infrastructure, enabling businesses to track assets, manage dependencies, and reduce operational risks.
By centralizing this information, businesses can improve decision-making, streamline IT operations, and enhance system reliability. As a result, a well-structured CMDB serves several key functions:
- Asset Discovery & Tracking – Automatically detects and catalogs assets, keeping records updated.
- Configuration & Dependency Mapping – Shows how IT components interact, helping IT teams plan changes effectively.
- Incident & Problem Management – Identifies affected assets for faster issue resolution, reducing downtime.
- Change & Release Management – Assesses the impact of IT changes to minimize disruptions and improve stability.
- Security & Compliance Management – Helps maintain security policies and regulatory compliance, reducing risks.
How Does CMDB Work?
A CMDB functions through a structured approach that ensures IT assets are accurately documented and managed. Here’s how it works:
1. Data Collection & Discovery
To begin with, CMDB gathers asset data using automated discovery tools or manual entry. These tools scan networks, detect devices, and log configurations in real time, ensuring IT teams have up-to-date records.
2. Relationship Mapping
CMDB tracks how IT assets are connected. For example, if a database runs on a specific server, CMDB documents the relationship. This helps IT teams understand dependencies, troubleshoot faster, and prevent
3. Data Updates & Maintenance
Since IT environments constantly evolve, CMDB data must be regularly updated. IT teams ensure that newly added assets, updates, and retired devices are accurately recorded to maintain data integrity and reliability.
4. Integration with ITSM & ITAM Systems
Additionally, CMDB integrates with IT Service Management (ITSM) and IT Asset Management (ITAM) tools. This enables seamless incident management, asset tracking, and change control. For example, when a service request is logged, CMDB provides insights into the affected asset’s history.
5. Query & Reporting
Businesses rely on CMDB to generate reports for audits, compliance checks, and performance tracking. IT teams can run queries to assess system health, track software usage, and predict future IT needs. This capability makes CMDB a valuable tool for IT strategy and decision-making.
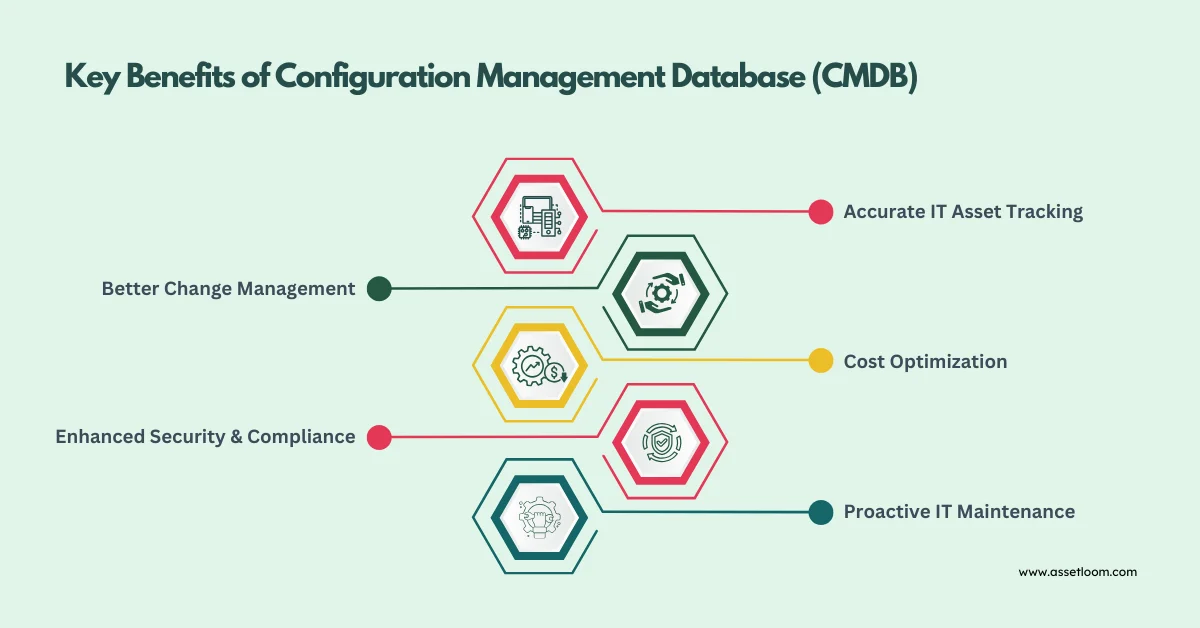
Key Benefits of Configuration Management Database (CMDB)
Implementing a CMDB brings numerous advantages. By maintaining a structured database of IT assets and their relationships, organizations gain better control over their infrastructure. This leads to improved decision-making, optimized costs, and reduced risks. Below are the key benefits:
- Accurate IT Asset Tracking
A CMDB eliminates guesswork by providing a real-time, detailed inventory of IT assets. It ensures accurate tracking of asset configurations, locations, and dependencies, reducing the risk of lost or mismanaged assets.
- Better Change Management
With CMDB, IT teams can assess the impact of changes before implementation. By visualizing dependencies, businesses can reduce downtime, prevent disruptions, and make informed decisions when upgrading or replacing assets.
- Cost Optimization
A well-maintained CMDB prevents unnecessary IT spending by identifying underutilized assets, eliminating redundant purchases, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Enhanced Security & Compliance
CMDB helps organizations meet regulatory and security requirements by ensuring assets are documented, updated, and properly managed. This reduces the risk of compliance violations and security vulnerabilities.
- Proactive IT Maintenance
By tracking asset health and lifecycle, CMDB enables IT teams to predict failures before they occur. This proactive approach reduces downtime, enhances system performance, and extends asset lifespan.
Ultimately, CMDB is more than just a storage system. Instead, it serves as the foundation of IT Service Management (ITSM) and IT Asset Management (ITAM), providing a clear view of IT infrastructure to reduce risks and improve efficiency.
Best Practices for Implementing a CMDB in ITAM
Successfully implementing a CMDB requires a strategic approach. Following these best practices ensures that businesses maximize their CMDB's value and maintain accurate, useful data.
1. Define Clear Objectives
Start by establishing what the CMDB should track and why. Clearly define its role in ITAM, whether for asset tracking, compliance, or change management. This ensures alignment with business goals and avoids unnecessary data overload.
2. Automate Data Collection
Manual data entry is prone to errors. Using automated discovery tools helps reduce human mistakes, keep asset records accurate, and maintain real-time updates. Automation ensures that all newly added, modified, or retired assets are properly recorded.
3. Keep Data Clean & Updated
A CMDB is only valuable if its data is accurate and current. Regular audits, routine checks, and updates prevent outdated or duplicate records from compromising system reliability.
4. Integrate with ITAM & ITSM Systems
For maximum efficiency, the CMDB should be seamlessly connected to IT Asset Management (ITAM) and IT Service Management (ITSM) tools. This integration allows IT teams to track asset lifecycles, manage incidents, and enforce compliance policies more effectively.
5. Assign Ownership & Governance
Maintaining a CMDB requires clear roles and responsibilities. Designate a team or individual responsible for data accuracy, updates, and governance policies. This ensures long-term reliability and prevents inconsistencies in asset records.
By following these best practices, organizations can build and maintain an effective CMDB that enhances IT asset management, improves decision-making, and reduces operational risks.
Conclusion
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a vital component of IT Asset Management (ITAM), providing organizations with accurate, real-time visibility into their IT infrastructure. By tracking assets, mapping dependencies, and supporting ITSM processes, CMDB helps businesses optimize resource utilization, improve decision-making, and enhance overall IT efficiency.
However, the true value of CMDB lies in the accuracy and maintenance of its data. Without consistent updates, automation, and governance, CMDB can become unreliable, leading to poor asset tracking and ineffective IT management.
To fully leverage CMDB, businesses must follow best practices; define clear objectives, automate data collection, integrate with ITAM and ITSM tools, and assign ownership for data governance. By doing so, organizations can ensure a well-maintained CMDB that strengthens IT operations, reduces risks, and drives smarter decision-making.
Take your IT asset management to the next level with AssetLoom, a powerful platform designed to optimize and streamline your CMDB and ITAM processes.

Related Blogs
Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom, right in your inbox.