What is Inventory Tracking? How It Works, Methods, Benefits
Inventory tracking helps businesses monitor stock levels, reduce waste, and improve efficiency. Learn how it works, different methods, and key benefits.
Imagine running a business where stock levels are unpredictable, orders are delayed, and valuable products go missing. Many businesses struggle with inaccurate inventory records, stock shortages, and excess inventory that ties up cash flow.
For retailers, this can mean lost sales when a high-demand product is unavailable. Manufacturers may face production delays due to missing raw materials, while healthcare facilities risk running low on essential medical supplies. These issues arise when there’s limited visibility into stock levels, locations, and movement making it difficult to plan effectively.
Inventory tracking helps businesses solve these challenges by ensuring stock is monitored, accounted for, and optimized. It allows companies to improve efficiency, reduce losses, and make informed decisions. In this guide, we’ll explore what inventory tracking is, how it works, different tracking methods, its benefits, and the challenges businesses face when managing inventory.
What is inventory tracking?
Inventory tracking is the process of monitoring stock levels, locations, and movement within a business. It helps ensure that every product or material is accounted for, from the moment it is received to when it is sold, used, or discarded.
Tracking inventory is essential for maintaining stock accuracy, preventing losses, and optimizing supply chain operations. Whether a company is dealing with raw materials, finished goods, office supplies, or digital assets, knowing what is in stock, where it is located, and how it moves is key to efficient business operations.
How Inventory Tracking Differs from Inventory Management
While inventory tracking focuses on monitoring and recording stock movement, IT inventory management is a broader process that includes forecasting demand, purchasing stock, and optimizing storage and distribution.
![]()
For example:
- Inventory tracking ensures that a warehouse knows exactly how many units of a product are available at any given time.
- Inventory management ensures that the right amount of stock is ordered and stored efficiently to meet demand.
Key Aspects of Inventory Tracking
- Stock Levels: Keeping an accurate count of available inventory.
- Location Tracking: Knowing where each item is stored or moved.
- Stock Movement Monitoring: Recording when inventory is received, transferred, or sold.
- Valuation & Auditing: Ensuring stock records match physical inventory.
Businesses across industries from retail and manufacturing to healthcare and IT rely on inventory tracking to reduce waste, improve efficiency, and enhance customer service.
What is being tracked?
Inventory tracking involves monitoring various types of stock and assets within a business. The type of inventory being tracked depends on the industry and business model, but it generally falls into the following categories:
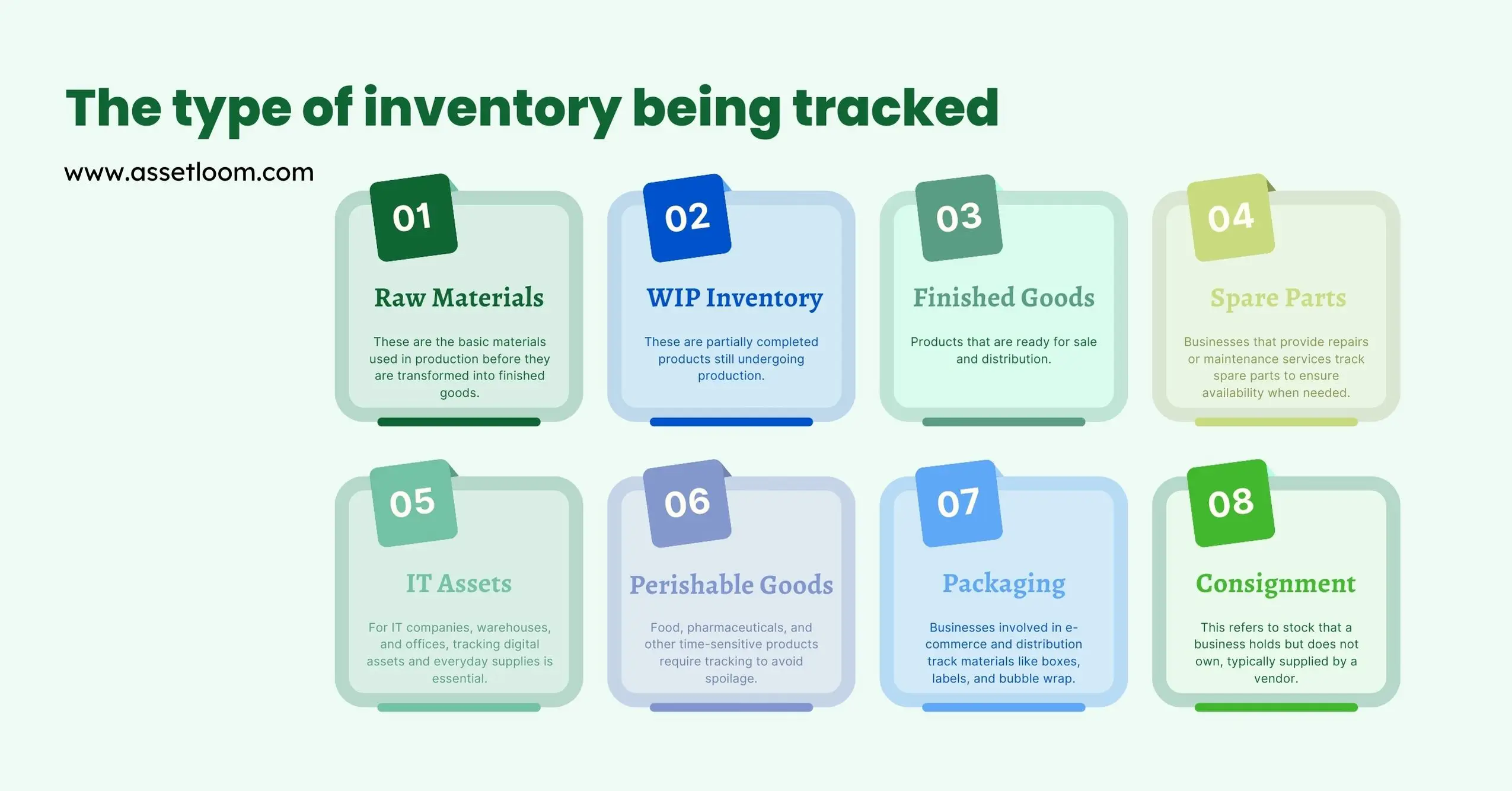
1. Raw Materials
These are the basic materials used in production before they are transformed into finished goods.
Example: A furniture manufacturer tracks wood, metal, and fabric used to produce tables and chairs.
2. Work-in-Progress (WIP) Inventory
These are partially completed products still undergoing production.
Example: A car manufacturing plant tracks vehicle frames before they are fully assembled.
3. Finished Goods
Products that are ready for sale and distribution.
Example: A retailer tracks smartphones in stock before they are sold to customers.
4. Spare Parts and Components
Businesses that provide repairs or maintenance services track spare parts to ensure availability when needed.
Example: An auto repair shop tracks engine parts, tires, and brake pads.
5. IT Assets and Office Supplies
For IT companies, warehouses, and offices, tracking digital assets and everyday supplies is essential.
Example: A corporate office tracks laptops, printers, and security keycards.
6. Perishable Goods
Food, pharmaceuticals, and other time-sensitive products require tracking to avoid spoilage.
Example: A grocery store tracks dairy products and fresh produce to reduce waste.
7. Packaging and Shipping Materials
Businesses involved in e-commerce and distribution track materials like boxes, labels, and bubble wrap.
Example: An online retailer tracks shipping supplies to ensure timely order fulfillment.
8. Consignment Inventory
This refers to stock that a business holds but does not own, typically supplied by a vendor.
Example: A bookstore tracks books provided by publishers on a consignment basis.
How Inventory Tracking Works
Inventory tracking involves a series of steps that ensure businesses have a clear understanding of what stock they have, where it is located, and how it moves through the supply chain. Whether done manually or with automated systems, the goal is to maintain accurate records and optimize inventory flow.
1. Recording Inventory Data
The first step in inventory tracking is collecting detailed information about each item in stock. This includes:
- Product name, description, and category
- Stock-keeping unit (SKU) or barcode for identification
- Quantity available
- Storage location
- Cost and valuation details
Businesses can record this information manually using spreadsheets or use inventory tracking software to automate data entry.
2. Categorizing Inventory
To improve efficiency, inventory is organized based on its characteristics, demand, and movement. Common categorization methods include:
- ABC Analysis – Classifying inventory based on value and importance (A = high-value, C = low-value).
- FIFO (First In, First Out) – Ensuring that older stock is used or sold first to prevent waste.
- LIFO (Last In, First Out) – Commonly used for non-perishable items, where newer stock is sold before older inventory.
Proper categorization helps businesses optimize stock usage and reduce financial losses.
3. Monitoring Stock Levels
Once inventory is recorded and categorized, businesses must keep track of stock levels in real-time to ensure they meet demand. There are several ways to do this:
- Periodic Tracking – Conducting manual stock counts at regular intervals.
- Perpetual Tracking – Using inventory management software that updates stock levels as sales or usage occur.
- Cycle Counting – Regularly checking specific items instead of conducting a full stock audit.
4. Tracking Inventory Movement
Inventory tracking also involves monitoring how stock moves throughout the supply chain. This includes:
- Receiving new inventory from suppliers.
- Storing stock in warehouses, retail locations, or fulfillment centers.
- Transferring stock between different locations.
- Fulfilling orders and shipping products to customers.
Businesses use barcodes, RFID tags, or cloud-based tracking systems to record every stock movement in real-time. This reduces the risk of misplacement, theft, or incorrect stock levels.
5. Updating and Auditing Inventory Records
To ensure accuracy, businesses regularly review and update inventory records. This includes:
- Conducting physical stock audits to match records with actual inventory.
- Identifying discrepancies, such as missing or damaged goods.
- Adjusting records to reflect real-time stock levels.
Regular inventory audits help businesses reduce errors, improve stock forecasting, and maintain financial accuracy.
Inventory tracking methods
Businesses use different methods to track inventory, depending on their size, industry, and operational needs. Some rely on traditional manual tracking, while others use technology-driven solutions for greater accuracy and efficiency. Below are the most common inventory tracking methods and their advantages.
1. Manual Inventory Tracking (Spreadsheets & Paper Logs)
How it works:
- Businesses record inventory transactions manually in notebooks, ledgers, or spreadsheets.
- When stock arrives, employees enter product details, including name, quantity, date received, and location.
- Every sale, return, or stock movement is manually logged to track usage and availability.
- Physical stock counts are conducted periodically (daily, weekly, or monthly) to compare recorded figures with actual inventory.
- Discrepancies must be manually adjusted, with missing or damaged stock accounted for in records.
Advantages:
✔ Low-cost and simple setup – No need for expensive software or special equipment.
✔ Flexible and customizable – Spreadsheets can be tailored with formulas and filters to track stock levels, reorder points, and stock valuation.
✔ Suitable for small businesses – Works well for companies with limited inventory and low transaction volumes.
✔ No reliance on technology – Can function without internet access or software, making it ideal for offline businesses.
Challenges:
❌ Prone to human errors – Miscounts, incorrect data entry, or forgetting to log transactions can lead to inaccurate stock records.
❌ Time-consuming and labor-intensive – Manually updating records takes time and increases administrative workload.
❌ Lack of real-time updates – Stock records are only updated after physical counts, leading to potential discrepancies.
❌ Difficult to scale – As inventory grows, tracking large stock volumes manually becomes impractical.
❌ Limited visibility – Cannot efficiently track stock across multiple locations or in fast-moving supply chains.
Example:
A small bakery tracks ingredient stock using a spreadsheet. Each morning, an employee manually checks and records flour, sugar, and eggs in a logbook. When supplies run low, they place an order based on estimated usage. While this system works initially, as demand grows and the bakery starts offering catering services, the manual process becomes inefficient, leading to frequent shortages and excess stock. To improve accuracy and efficiency, they eventually switch to barcode-based tracking.
2. Barcode & QR Code Tracking
How it works:
- Each product is assigned a barcode or QR code that contains information like product name, SKU, and quantity.
- Businesses use barcode scanners or mobile devices to scan items when stock is received, sold, or transferred.
- Scanned data is automatically updated in an inventory management system to reflect real-time stock levels.
- Employees can instantly retrieve product details by scanning the barcode, reducing the need for manual data entry.
- Periodic audits and stock checks are streamlined as scanning provides instant access to inventory records.
Advantages:
✔ Faster and more accurate tracking – Scanning eliminates manual entry errors and speeds up inventory updates.
✔ Real-time stock visibility – Businesses can track stock movements as they happen, reducing discrepancies.
✔ Improves efficiency in warehouses and retail stores – Speeds up order fulfillment, stock audits, and restocking processes.
✔ Cost-effective for growing businesses – Barcode systems are relatively affordable compared to RFID or advanced tracking methods.
✔ Can integrate with inventory software – Allows for automated stock management and reporting.
Challenges:
❌ Requires barcode scanners or mobile devices – Businesses need to invest in scanning hardware or smartphone apps.
❌ Initial setup takes time – Products must be labeled with barcodes or QR codes, which can be labor-intensive at first.
❌ Dependent on technology – If scanners malfunction or software crashes, tracking can be temporarily disrupted.
❌ Not ideal for real-time location tracking – Unlike RFID, barcode scanning does not provide automatic movement tracking.
3. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
How it works:
- Each inventory item is fitted with an RFID tag containing a small microchip that stores product data.
- RFID readers automatically scan tags wirelessly without needing direct contact, unlike barcodes.
- Items can be tracked in real time as they move through warehouses, retail stores, or distribution centers.
- RFID tags can store detailed product information, including serial numbers, manufacturing dates, and batch details.
- Businesses use RFID software to monitor stock levels, detect missing items, and automate inventory updates.
Advantages:
✔ Fast, contactless scanning – RFID readers can scan multiple items simultaneously, improving efficiency.
✔ Real-time inventory visibility – Tracks stock movement without manual scanning, reducing errors.
✔ Enhanced security – RFID helps prevent theft and loss by detecting unauthorized stock movement.
✔ Ideal for large-scale inventory management – Used in industries like retail, logistics, and healthcare.
✔ Reduces human error – No need for manual entry, ensuring greater accuracy.
Challenges:
❌ Higher cost – RFID tags, readers, and software are more expensive than barcode systems.
❌ Requires infrastructure investment – Businesses need RFID scanners, antennas, and integrated software.
❌ Interference issues – Metal, liquids, or crowded environments can sometimes disrupt RFID signals.
❌ Not always necessary for small businesses – Best suited for large-scale operations handling high inventory volumes.
4. IoT-Based Smart Inventory Tracking
What is IoT-Based Smart Inventory Tracking?
IoT-based smart inventory tracking uses Internet of Things (IoT) technology to monitor and manage IT assets in real-time. IoT devices such as smart sensors, RFID tags, GPS trackers, and cloud-connected monitoring systems provide continuous data on an asset’s location, condition, and usage.
This method is particularly useful in large enterprises, data centers, logistics, and high-security environments where IT assets need to be continuously monitored for performance, security, and compliance.
How it works:
- IoT Sensors & RFID Tags – IT assets (laptops, servers, mobile devices) are equipped with IoT-enabled sensors or RFID tags that automatically track movement and usage.
- Automated Data Transmission – IoT devices send real-time updates on asset location, operational status, and temperature conditions to cloud-based ITAM software.
- Centralized Cloud Dashboard – IT managers can view asset data from multiple locations via a centralized dashboard, improving visibility and decision-making.
- Alerts & Automation – Smart inventory tracking systems trigger alerts for unauthorized asset movement, preventive maintenance schedules, and compliance checks.
Advantages:
✔ Real-Time IT Asset Monitoring – Provides instant visibility into asset status and location.
✔ Reduces Asset Loss & Theft – IoT-based alerts notify IT teams if an asset leaves a designated area or goes offline unexpectedly.
✔ Automates Maintenance & Compliance – Predictive analytics help schedule automatic updates, maintenance checks, and software license renewals.
✔ Improves Security & Remote Management – Allows remote tracking of IT assets across multiple locations, reducing unauthorized access risks.
✔ Enhances Inventory Forecasting – AI-powered IoT systems analyze asset usage trends to optimize purchasing and reduce unnecessary IT spending.
Challenges:
❌ High Implementation Costs – IoT-enabled tracking systems require RFID tags, GPS sensors, cloud-based ITAM software, and connectivity infrastructure, which can be costly.
❌ Network Dependency – Requires stable internet connectivity to ensure continuous data transmission.
❌ Integration Complexity – Needs seamless integration with existing IT security, finance, and asset management systems.
❌ Privacy & Data Security Risks – IoT devices collect vast amounts of data, making them a potential target for cyber threats.
IT Asset Management System (ITAM) and Inventory Tracking
An IT Asset Management (ITAM) System is designed to track, manage, and optimize IT assets throughout their lifecycle. Just like traditional inventory systems, ITAM relies on inventory tracking methods to monitor IT equipment, software licenses, and cloud resources.
1. Perpetual IT Asset Tracking System
A Perpetual IT Asset Tracking System functions similarly to a Perpetual Inventory System, where IT asset records update in real time as assets are deployed, moved, or retired.
How It Works in ITAM:
- IT assets (laptops, servers, software licenses) are assigned unique identifiers (barcodes, RFID tags, or serial numbers).
- Each time an IT asset is purchased, deployed, transferred, or disposed of, the system automatically updates records.
- IT asset tracking software integrates with network monitoring tools to detect active and inactive assets.
- Real-time tracking allows businesses to prevent asset loss, improve utilization, and manage compliance.
Advantages in ITAM:
✔ Real-time visibility – IT teams can instantly track asset locations and usage.
✔ Automated updates – Reduces manual data entry errors.
✔ Improves compliance – Helps track software licenses and ensure legal usage.
✔ Enhances security – Detects unauthorized IT assets or inactive devices.
Challenges in ITAM:
❌ Higher setup costs – Requires investment in RFID/barcode tracking or asset management software.
❌ Integration complexity – Needs seamless connection with IT security and procurement systems.
❌ Data accuracy depends on automation – If tracking tools fail, assets may be miscounted.
2. Periodic IT Asset Tracking System
A Periodic IT Asset Tracking System functions similarly to a Periodic Inventory System, where IT assets are only updated at scheduled intervals, instead of real-time tracking.
How It Works in ITAM:
- IT teams conduct scheduled physical audits (monthly, quarterly, or annually) to count and verify assets.
- Asset data is updated manually based on audit results.
- Missing or decommissioned IT assets are recorded after audits, leading to delayed updates.
- IT departments use spreadsheets or basic tracking tools rather than automated asset monitoring.
Advantages in ITAM:
✔ Lower cost – No need for automated asset tracking software.
✔ Simple implementation – Can be managed using spreadsheets or basic databases.
✔ Effective for static assets – Works well when IT assets rarely move or change.
Challenges in ITAM:
❌ Delayed asset visibility – IT teams may not know when an asset is lost or stolen until the next audit.
❌ Time-consuming manual tracking – Requires physical audits to maintain data accuracy.
❌ Limited efficiency for large organizations – Not suitable for businesses managing thousands of IT assets.
Choosing the Right Inventory Tracking Method
Selecting the right inventory tracking method depends on business size, budget, and operational complexity. Different businesses have different needs, so choosing the right system ensures efficient stock management, reduced losses, and streamlined operations.
- Small businesses may start with manual tracking or barcodes for cost efficiency and ease of implementation.
- Growing businesses benefit from barcode, QR code, or perpetual inventory systems, providing automation without high costs.
- Large enterprises and warehouses often use RFID, IoT, or smart tracking solutions for real-time accuracy and automation.
- IT-focused companies adopt IT asset management (ITAM) systems integrated with perpetual tracking, RFID, or IoT for better asset control and compliance.
Why do you need inventory tracking?
Inventory tracking is not just about knowing how much stock you have—it’s about ensuring efficiency, reducing costs, and improving overall business operations. Businesses that track their inventory accurately can avoid stock shortages, reduce waste, and streamline their supply chain. Here’s why inventory tracking is essential:
1. Prevents Overstocking and Stock Shortages
One of the biggest challenges businesses face is balancing supply and demand.
- Overstocking ties up cash in unsold goods, increases storage costs, and can lead to product waste, especially for perishable goods.
- Stock shortages result in missed sales, backorders, and dissatisfied customers.
Inventory tracking helps businesses maintain optimal stock levels, ensuring they have just the right amount of inventory to meet demand.
2. Improves Order Accuracy and Customer Satisfaction
Customers expect fast and accurate order fulfillment. If a business can’t track its stock properly, it risks selling items that are out of stock, leading to delays, cancellations, and unhappy customers.
With accurate inventory tracking, businesses can:
- Ensure real-time stock updates to avoid selling unavailable products.
- Process orders quickly and accurately to improve customer satisfaction.
- Provide better tracking and transparency on product availability.
3. Reduces Losses and Prevents Theft
Inventory loss due to theft, damage, or administrative errors can significantly impact a business’s bottom line. Inventory tracking helps businesses:
- Identify and reduce shrinkage caused by theft or misplacement.
- Detect discrepancies early through regular stock audits.
- Implement better security measures with real-time monitoring.
4. Enhances Financial Planning and Decision-Making
Inventory is one of the most valuable assets for many businesses, and tracking it accurately is critical for financial management. Proper inventory tracking allows businesses to:
- Assess inventory value for financial reporting.
- Plan purchases and budget effectively to avoid unnecessary expenses.
- Improve cash flow management by ensuring money isn’t tied up in excess stock.
5. Increases Operational Efficiency
A well-tracked inventory system reduces time wasted on manual stock checks and searching for misplaced items. Businesses can:
- Automate stock monitoring for real-time visibility.
- Optimize warehouse organization to speed up fulfillment and storage.
- Improve workflow efficiency, reducing labor costs and errors.
6. Helps Meet Regulatory Compliance
Many industries, such as food, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare, have strict regulatory requirements for tracking inventory. Businesses in these sectors must:
- Keep accurate records of stock movement for audits and safety compliance.
- Track product expiration dates to ensure quality control.
- Provide traceability reports in case of recalls or quality issues.
Inventory tracking challenges
While inventory tracking is essential for efficient operations, businesses often encounter challenges that can disrupt stock accuracy, delay order fulfillment, and increase costs. Below are some of the most common inventory tracking challenges and how they impact business operations.
1. Inconsistent Tracking and Human Errors
Many businesses still use manual inventory tracking methods, such as spreadsheets or paper logs. This can result in:
- Data entry mistakes, leading to inaccurate stock levels.
- Inconsistent record-keeping, causing discrepancies between actual and recorded inventory.
- Difficulty in maintaining updates, especially in fast-moving environments.
Impact: Poor inventory accuracy can lead to misplaced stock, fulfillment delays, and financial miscalculations.
Solution:
- Automate tracking with barcode or RFID systems to minimize human errors.
- Implement standardized inventory procedures across all departments.
- Regularly train employees on accurate inventory recording practices.
2. Supply Chain Disruptions
External factors such as supplier delays, transportation issues, or unexpected demand fluctuations can affect stock availability.
- Natural disasters, trade restrictions, or economic downturns can disrupt supply chains.
- Lead time variations make it difficult to maintain optimal stock levels.
Impact: Businesses may face stock shortages, backorders, or higher procurement costs, ultimately affecting sales and production.
Solution:
- Establish multiple supplier relationships to avoid over-reliance on a single source.
- Use demand forecasting tools to anticipate inventory needs.
- Maintain safety stock for critical items to buffer against supply chain delays.
3. Limited Real-Time Visibility
Without a real-time tracking system, businesses struggle to:
- Know exactly where products are located within warehouses or stores.
- Monitor stock movement across multiple locations.
- Track inventory levels accurately during peak seasons.
Impact: Lack of visibility leads to delays in order fulfillment, stock discrepancies, and inefficient warehouse management.
Solution:
- Implement cloud-based inventory tracking that updates stock levels in real time.
- Use RFID or barcode scanning systems to enhance visibility.
- Improve warehouse organization with inventory mapping and categorization.
4. Customer Expectations for Fast and Accurate Delivery
Consumers today expect businesses to provide:
- Accurate stock availability when shopping online.
- Fast and reliable order fulfillment with real-time tracking.
- Error-free deliveries with minimal delays.
Impact: If inventory tracking is inaccurate, businesses may:
- Sell out-of-stock products, leading to canceled orders and unhappy customers.
- Struggle to meet delivery promises, affecting brand reputation.
- Lose customers to competitors with better stock management.
Solution:
- Sync inventory tracking with e-commerce and order management systems.
- Implement automated stock updates to prevent overselling.
- Optimize warehouse operations for faster order processing and shipping.
5. Overstocking and Stockouts
Businesses often face challenges in balancing inventory levels:
- Overstocking ties up cash, increases storage costs, and leads to waste.
- Stockouts cause missed sales opportunities and dissatisfied customers.
Impact: Both scenarios harm business profitability and affect operational efficiency.
Solution:
- Use inventory forecasting tools to align stock levels with demand trends.
- Implement a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system to optimize stock replenishment.
- Set automated reorder points to prevent stock shortages.
6. High Costs of Implementing Advanced Tracking Systems
While automated inventory tracking offers accuracy and efficiency, many businesses hesitate due to:
- High initial costs for software, hardware, and training.
- Complex system integrations with existing workflows.
- Ongoing maintenance expenses for upgrades and troubleshooting.
Impact: Businesses may continue using outdated manual methods, leading to inefficiencies and higher operational costs in the long run.
Solution:
- Start with affordable solutions like barcode tracking before upgrading to RFID or IoT-based systems.
- Choose scalable inventory software with flexible pricing.
- Train employees gradually to maximize the return on investment in new tracking technologies.
7. Data Security and System Integration Issues
With the rise of cloud-based inventory management, businesses face concerns such as:
- Cybersecurity risks that could expose sensitive inventory data.
- Integration challenges when connecting inventory systems with accounting, sales, and supply chain tools.
Impact: Security breaches and system failures can lead to data loss, stock discrepancies, and disrupted operations.
Solution:
- Use secure, encrypted inventory software with access controls.
- Ensure seamless integration with ERP, POS, and accounting systems.
- Regularly back up inventory data to prevent loss in case of system failures.
How to Overcome Inventory Tracking Challenges
By identifying these challenges and implementing the right strategies, businesses can:
- Improve inventory accuracy and prevent costly errors.
- Optimize stock levels to avoid shortages and overstocking.
- Enhance customer satisfaction with reliable order fulfillment.
- Reduce financial losses and increase operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Inventory tracking is a fundamental part of efficient business operations, ensuring that stock levels are accurate, products are available when needed, and resources are used effectively. Businesses that fail to track inventory properly often face issues like stock discrepancies, missed sales opportunities, overstocking, and supply chain inefficiencies.
By understanding what inventory tracking is, how it works, the different tracking methods, and the benefits it provides, businesses can make informed decisions to improve their operations. However, challenges such as human errors, supply chain disruptions, and limited real-time visibility can make inventory tracking difficult without the right strategies in place.

Related Blogs
Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom, right in your inbox.


