IT Asset Lifecycle Management Best Practices
Discover IT asset lifecycle management best practices to optimize costs, ensure compliance, and enhance cybersecurity.
Effective management of IT assets is vital for organizations aiming to reduce costs, ensure compliance, and enhance cybersecurity. Adopting IT asset lifecycle management best practices enables businesses to streamline processes and maximize the value of hardware and software assets. This article outlines detailed best practices for each stage of the IT asset lifecycle, helping organizations achieve efficiency, compliance, and security.
What is IT Asset Lifecycle Management?
IT asset lifecycle management (ITALM) involves overseeing hardware and software assets throughout their lifespan. The lifecycle consists of five stages: Planning and Inventory, Acquisition, Deployment, Maintenance and Monitoring, and Retirement and Disposal. By following IT asset lifecycle management best practices, organizations ensure assets are used efficiently, remain compliant with regulations, and are protected against security risks. This systematic process supports cost savings and operational success.
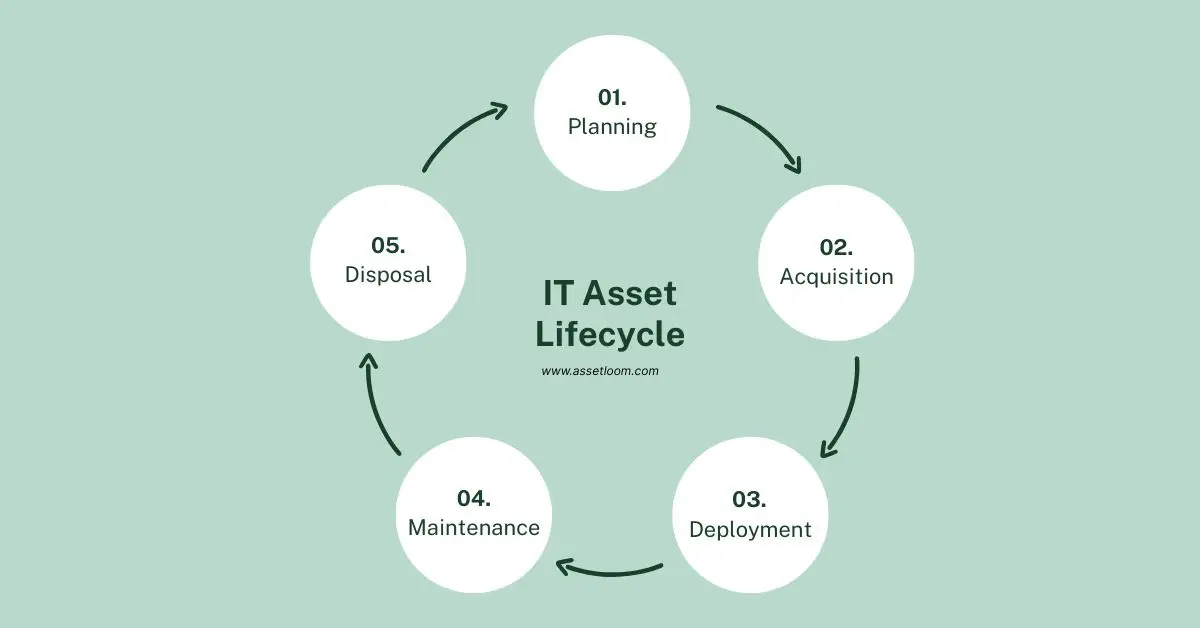
Related article: What Is IT Asset Lifecycle Management?
Why IT Asset Lifecycle Management Matters
Proper ITALM minimizes costs, strengthens security, and ensures regulatory compliance. Mismanaged assets can result in overspending, security vulnerabilities, or penalties from non-compliance. A 2024 Gartner report indicates organizations with effective ITALM practices can reduce IT costs by up to 30%. Implementing IT asset lifecycle management best practices helps businesses avoid these pitfalls, optimize asset performance, and maintain a secure IT environment, making it a critical strategy for modern organizations.
Best Practices for IT Asset Lifecycle Management
Each stage of the IT asset lifecycle requires careful management to achieve optimal results. Below, we describe IT asset lifecycle management best practices for each stage, providing detailed guidance to ensure efficiency, compliance, and cybersecurity.
1. Planning and Inventory: Establish a Solid Foundation
The planning and inventory stage is the starting point for effective ITALM. Begin by defining specific objectives, such as reducing costs, ensuring compliance, or enhancing security, to align asset management with organizational goals. Conduct a thorough inventory of all hardware and software assets, capturing details like versions, locations, and license agreements. This involves scanning networks to identify every device and application, ensuring no assets are missed. Assess potential risks, such as outdated hardware or unsupported software, to prioritize cybersecurity measures. Engage stakeholders from IT, finance, and compliance teams to ensure the inventory reflects business needs.
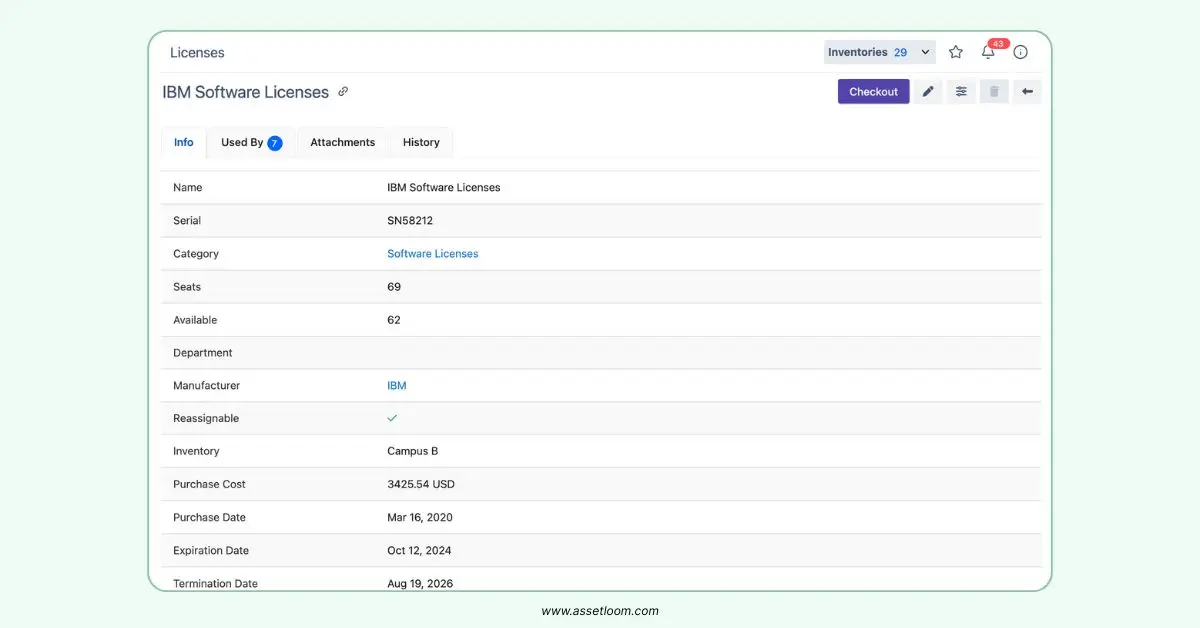
AssetLoom captures details like license seats, expiration dates, and license agreements
2. Acquisition: Procure Assets Strategically
The acquisition stage focuses on purchasing IT assets that meet organizational needs while maintaining security and compliance. Negotiate contracts with vendors to secure favorable terms, such as discounts for bulk purchases or flexible licensing options, to maximize cost efficiency. Verify that all assets comply with licensing agreements and adhere to security standards, such as ISO 27001, to prevent risks from unauthorized or insecure purchases. Evaluate assets for scalability to ensure they support future growth and integrate seamlessly with existing systems. Compare offerings from multiple vendors to select those with proven security practices. Document all procurement details, including contract terms and compliance requirements, to prepare for audits.
3. Deployment: Implement Assets Securely
Deploying IT assets requires precision to avoid errors and security vulnerabilities. Standardize installation processes across all devices to ensure consistency and prevent misconfigurations that could expose systems to threats. Apply security patches and firmware updates during deployment to address known vulnerabilities before assets are operational. Restrict installation permissions to authorized IT personnel to prevent unauthorized hardware or software from entering the environment, minimizing the risk of shadow IT. Test assets in a controlled environment before full deployment to confirm functionality and compatibility with existing systems. Document deployment procedures, including patch schedules and access controls, to maintain accountability and traceability.
4. Maintenance and Monitoring: Optimize Asset Performance
The maintenance and monitoring stage ensures assets remain functional, secure, and compliant throughout their use. Conduct regular audits of the asset inventory, ideally quarterly, to verify accuracy and identify discrepancies in hardware or software records. Monitor asset performance continuously to detect anomalies, such as unusual usage patterns that may indicate security threats. Apply patches and upgrades promptly to address vulnerabilities and maintain compatibility with evolving systems. Review assets regularly to identify those nearing end-of-life (EOL), planning replacements to avoid security risks from unsupported hardware or software. Engage IT teams to track usage data and ensure compliance with licensing agreements.
5. Retirement and Disposal: Close the Lifecycle Responsibly
Retiring and disposing of IT assets securely is critical to prevent data breaches and ensure compliance. Wipe sensitive data from hardware and software using certified tools to eliminate the risk of data leaks. Reallocate software licenses to other devices to optimize costs and avoid unnecessary purchases. Dispose of hardware in compliance with environmental regulations, such as WEEE or e-Stewards, to meet legal requirements and support sustainability goals. Document the retirement process, including data removal methods and disposal procedures, to maintain audit trails. Verify that no retired assets remain active in the network, as they could be exploited if left unmonitored.
FAQs About IT Asset Lifecycle Management Best Practices
Below are answers to common questions about IT asset lifecycle management best practices, designed to clarify key concepts and engage readers.
Why is ITALM important for cybersecurity?
ITALM identifies outdated or vulnerable assets, such as EOL hardware, and ensures timely updates. It also prevents unauthorized asset use, reducing security risks.
How often should I audit my IT asset inventory?
Audit your inventory every three months to account for new assets, updates, or retirements. Regular audits maintain accuracy and compliance.
How does automation improve ITALM?
Automation streamlines inventory tracking, compliance monitoring, and reporting. It reduces errors and saves time, improving overall efficiency.
What mistakes should I avoid in ITALM?
Avoid incomplete inventories, inconsistent deployment processes, and neglecting data security during disposal. Standardized procedures and automation prevent these issues.
How does ITALM reduce costs?
ITALM optimizes asset use by reallocating licenses and retiring redundant hardware. This can cut IT costs by up to 30%, according to Gartner.
Why is secure disposal important in ITALM?
Secure disposal prevents data leaks from retired assets and ensures compliance with environmental laws, protecting organizations from risks and penalties.
These FAQs, optimized for featured snippets, address user intent and boost engagement.
Common Challenges and Solutions
ITALM can face obstacles that hinder success. Incomplete inventories increase risks by leaving assets untracked, so use automated discovery to ensure full coverage. Complex processes can overwhelm teams, so simplify diagrams with clear labels and color-coded stages. Lack of expertise may slow progress, so invest in training or consult ITALM experts. These solutions keep your ITALM strategy effective and manageable.
Conclusion
Implementing IT asset lifecycle management best practices ensures organizations maximize asset value, reduce costs, and enhance cybersecurity. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, these practices deliver results.

Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom, right in your inbox.


