What is Asset Recovery in IT Asset Management?
Learn how asset recovery in ITAM helps businesses recover value from old assets through resale, reuse, and recycling, ensuring data security and compliance.
What is Asset Recovery in ITAM?
Asset recovery in IT Asset Management (ITAM) is the process of getting value from old or unused IT equipment. This includes items like laptops, desktops, servers, smartphones, and more. Instead of throwing these assets away, asset recovery helps businesses reuse, resell, recycle, or dispose of them properly.
The goal of asset recovery is to get as much value as possible from old equipment. It also ensures that data is secure, laws are followed, and e-waste is reduced. In short, asset recovery helps businesses get the most out of their IT assets. Reselling them, reusing them internally, or recycling them helps save money and reduce waste.
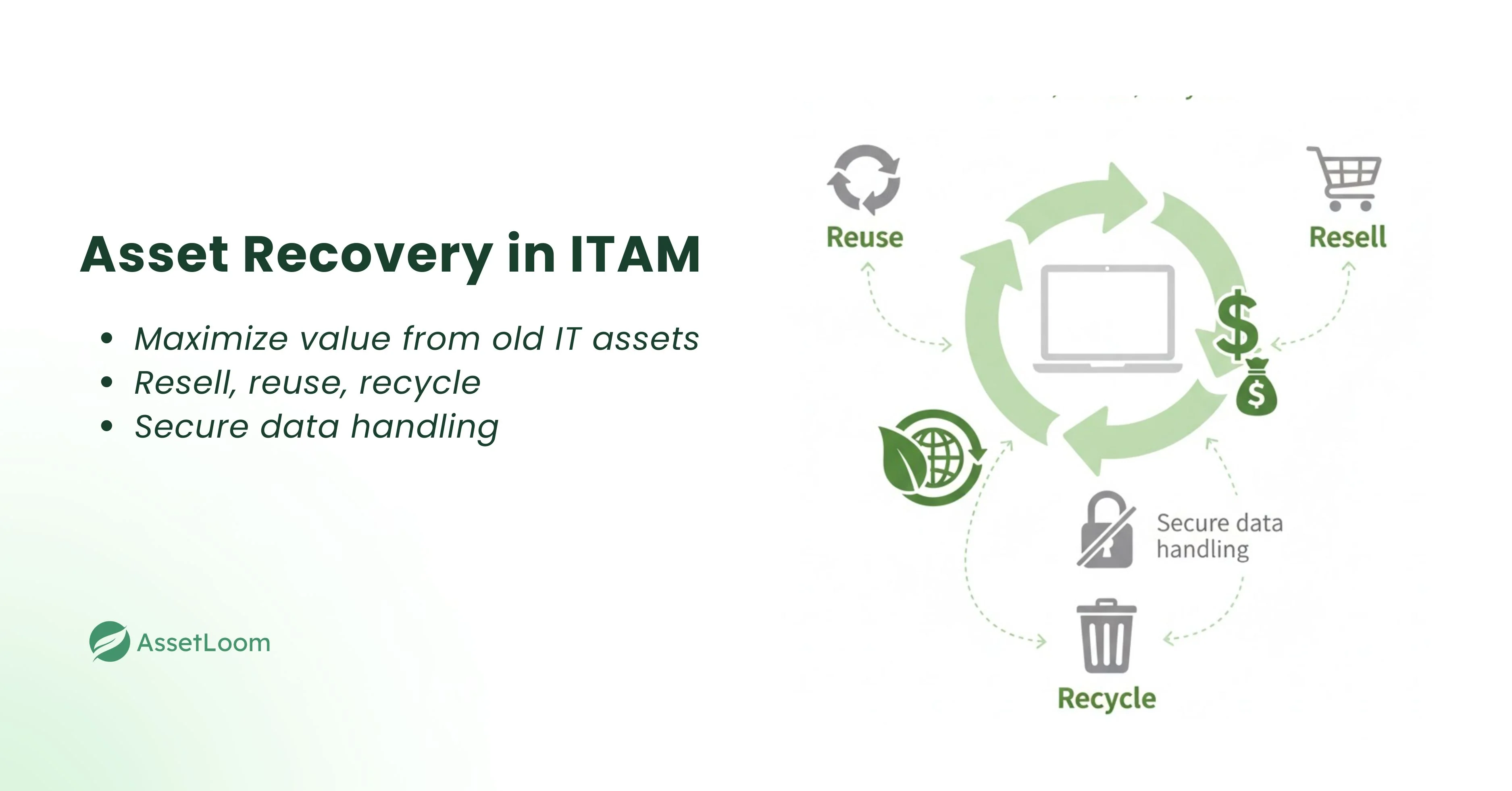
Why is Asset Recovery Important in ITAM?
- Financial Recovery: Helps businesses recover value from old or unused assets. Reselling or repurposing old equipment offsets the cost of new purchases.
- Data Security: Ensures data is securely wiped from decommissioned assets. Protects against data breaches by safeguarding sensitive information.
- Environmental Responsibility: Reduces e-waste through recycling and proper disposal. Contributes to a sustainable environment by minimizing waste.
- Operational Efficiency: Allows businesses to reuse equipment internally. Saves money and improves operational efficiency by reducing the need for new devices.
The Role of Asset Recovery in the IT Asset Lifecycle
The IT asset lifecycle includes key phases: planning, procurement, deployment, active use, maintenance, and retirement. Asset recovery is especially important during the final phase, retirement, and beyond.
At this point, decisions need to be made about what to do with the asset:
- Reuse: If the asset is still functional, redeploy it internally to extend its life and reduce the need for new purchases.
- Resale: If the asset has residual value, sell it to a third party to recover some of the original investment.
- Recycle or Destroy: If the asset is no longer usable, dispose of it responsibly by recycling or securely destroying it to protect data and the environment.
By integrating asset recovery into the lifecycle, businesses create a closed-loop process that maximizes asset value, reduces costs, and ensures data security. It also helps businesses track assets accurately from onboarding to final disposition.
How Asset Recovery Works
Effective asset recovery is based on a standardized, repeatable process to ensure efficiency, compliance, and proper documentation. Here’s how the process typically works:
1. Identification
The first step is to identify which assets are eligible for recovery. These could include assets that are inactive, expired, unassigned, or non-compliant. Asset tracking tools help locate and verify the status of these items, ensuring that the right assets are selected for recovery.
2. Collection
Once assets are identified, they are collected from users or various locations. All relevant custody details are recorded, and the returns are logged to maintain a complete audit trail. This ensures that every asset is accounted for throughout the recovery process.
3. Inspection and Evaluation
Each asset is then assessed for its condition and functionality. The specifications, warranty status, and repair history are reviewed to determine whether the asset can be redeployed internally, resold, or if it should be disposed of.
4. Data Sanitization
Before any asset is resold or repurposed, data sanitization is performed. This involves wiping all stored data using approved methods, such as NIST 800-88 or DoD 5220.22-M. If the asset is not functional or data wiping isn’t possible, physical destruction is scheduled to ensure that no data remains on the device. Certificates of destruction are retained for compliance purposes.
5. Disposition Decision
Based on the asset’s condition, a decision is made on its disposition:
- Reuse: If the asset is still functional, it can be redeployed or reassigned for internal use.
- Resale: If the asset has residual value, it can be sold through asset recovery services to recover part of its initial cost.
- Recycling: If the asset is no longer usable, it is sent to certified e-waste partners for environmentally responsible disposal.
6. Documentation and Reporting
After the recovery process is complete, the asset’s status is updated in the ITAM system. All recovery actions, including data destruction, resale, recycling, and any compliance certificates, are logged to support audits, financial reporting, and sustainability tracking.
Asset Recovery vs. Asset Disposal: Key Differences
While both asset recovery and asset disposal occur at the end of an asset’s lifecycle, they serve different purposes and involve distinct processes. Both practices are essential in a complete IT asset lifecycle strategy, with asset recovery preferred whenever possible to improve return on investment and reduce e-waste.
Asset Recovery
Asset recovery focuses on extracting the remaining value from unused or retired IT assets. This can be done through resale, redeployment, or recycling. The goal is to maximize the asset’s residual value while ensuring proper handling and compliance with data security and environmental standards.
Asset Disposal
Asset disposal, on the other hand, is primarily concerned with the safe, compliant removal and destruction of assets that are no longer usable or valuable. Disposal focuses on getting rid of assets, with little or no effort to recover their value.
Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Asset Recovery | Asset Disposal |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Maximize residual value | Safely and compliantly eliminate unusable assets |
| Processes Involved | Resale, donation, redeployment, parts harvesting | Decommissioning, data destruction, recycling, landfill |
| Value Outcome | Recovers cost or generates revenue | Often incurs cost due to secure destruction and compliance |
| Data Handling | May include data sanitization for resale or reuse | Requires certified data destruction |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainability through reuse or responsible recycling | Varies—improper disposal can harm the environment |
| Compliance Needs | Moderate, depending on reuse method | High—must meet regulatory and privacy requirements |
Common Triggers for Asset Recovery
Asset recovery is typically triggered by specific events or conditions that make it necessary to reclaim value from IT assets. Here are some of the most common triggers:
1. End of Warranty or Lease
When assets reach the end of their warranty or lease agreements, they may no longer be covered for repair or replacement. This is a prime time to evaluate whether they can be reused, resold, or recycled.
2. Technology Upgrades
As businesses upgrade their technology to keep up with new trends or improve efficiency, older assets often become redundant. This creates an opportunity to recover value by reselling or repurposing these assets.
3. Asset Failure or Malfunction
Assets that fail or no longer perform as needed are often candidates for asset recovery. Even if they are no longer functional, certain parts may still have value through recycling or resale.
4. Employee Departures or Office Moves
When employees leave the company or when offices are relocated, assets like laptops, phones, and desktops are often returned. These assets can be evaluated for reuse within the company or sold if no longer needed.
5. End-of-Life for Equipment
When IT equipment reaches the end of its useful life, asset recovery is triggered to responsibly dispose of or recycle the assets. This prevents old equipment from sitting unused and ensures it’s managed properly for environmental compliance.
6. Non-Compliance or Underutilization
Assets that are non-compliant with company standards or are underutilized may be recovered for reuse or resale. Tracking unused or outdated assets ensures they are not wasting space or resources.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Asset recovery is often tied to sensitive data, so compliance is critical. Failing to meet regulatory standards can result in legal penalties, financial loss, and damage to your reputation. Key regulations that businesses need to follow include:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Ensures the secure deletion of personal data across its lifecycle.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Requires the secure handling and disposal of health data (PHI) in the U.S.
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act): Mandates how financial records should be handled, including proper disposal, for public companies.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): Gives California residents control over their data, including the right to delete it securely.
To maintain compliance, businesses should follow these standards:
- NIST 800-88: Provides guidelines for securely sanitizing data from IT equipment.
- ISO 27001: A standard for managing information security within organizations.
- SOC 2 Type II: Evaluates internal controls around data privacy and security.
Ensuring compliance through proper asset recovery helps businesses avoid risks and builds trust with customers.
Glossary of Related Terms
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is asset recovery in ITAM?
Asset recovery in IT Asset Management (ITAM) is the process of extracting value from old, unused, or outdated IT equipment. This can involve reselling, reusing, or recycling the assets to recover some of their original value and ensure compliance with data security and environmental regulations.
2. How does asset recovery help with data security?
During asset recovery, sensitive data is securely erased from devices using industry-standard methods, such as data wiping or physical destruction. This ensures that private information is not exposed, preventing data breaches and protecting customer and business data.
3. How do I know which assets are eligible for recovery?
Assets that are no longer needed, are out of warranty, or have become obsolete due to upgrades or replacement are eligible for recovery. This can include laptops, desktops, servers, and other IT hardware.
4. What happens if assets are not properly recovered?
If assets are not properly recovered, they may end up as e-waste, violate data protection laws, or create compliance risks. Proper asset recovery ensures that these risks are mitigated and that assets are disposed of securely and responsibly.
5. Can asset recovery help save money?
Yes, asset recovery can help businesses recover value from old assets, reducing the need to buy new equipment. It also reduces costs by allowing the reuse of equipment within the organization, or by reselling assets that still have value.
6. What are the environmental benefits of asset recovery?
Asset recovery reduces e-waste by ensuring that old equipment is either recycled or disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner. This supports sustainability initiatives and helps prevent harmful materials from ending up in landfills.
7. What legal regulations apply to asset recovery?
Asset recovery must comply with various laws and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and environmental standards like the WEEE Directive. These laws govern data protection, data destruction, and the responsible recycling of electronic waste.

Related Blogs
Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom, right in your inbox.


