IoT Device Lifecycle Management: A Quick Guide
IoT Device Lifecycle Management: Learn how to manage your IoT devices from setup to retirement, ensuring security and long-term performance.
IoT devices are becoming a central part of many businesses, but keeping track of them can quickly turn into a challenge. As more devices are added to your network, it gets harder to ensure they’re all working properly, up to date, and secure. If not managed correctly, outdated or malfunctioning devices can lead to security issues, higher costs, and unnecessary downtime.
IT Asset Lifecycle Management plays a critical role here by extending its focus to managing all IT assets, including IoT devices, throughout their entire lifecycle. IoT device lifecycle management provides a clear path to handle this. It focuses on overseeing each device from its initial setup to its eventual retirement, ensuring they perform well throughout their lifecycle.
What is IoT Device Lifecycle Management?
An IoT (Internet of Things) device is any physical object that is connected to the internet and can collect, send, or receive data. These devices are often embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to interact with their environment. Examples of IoT devices include smart thermostats, wearable fitness trackers, connected cars, and industrial machines.
IoT Device Lifecycle Management is the process of managing an IoT device from its beginning to its end. It involves overseeing everything that happens to a device throughout its life, starting when it is first introduced into a system, making sure it stays secure and functional during its use, and properly retiring or replacing it when it is no longer needed.
For example, imagine a company using smart thermostats in its offices. These thermostats are part of the IoT system, collecting data to adjust room temperatures. Lifecycle management for these devices would ensure they are set up correctly, kept up to date with the latest software, and regularly checked for any issues. When the thermostats eventually wear out or become outdated, the lifecycle management process ensures they are replaced in an organized way, with data securely wiped and old devices disposed of properly.
In simple terms, IoT Device Lifecycle Management is about taking care of devices from start to finish, so they continue to do their job effectively and do not become a burden or security risk over time.
Read also: The Role of IoT in IT Asset Management by 2025
Stages of IoT Device Lifecycle Management
IoT device lifecycle management is divided into five commonly recognized stages. Each stage involves a set of activities and best practices to ensure that devices are properly handled from their inception to retirement.
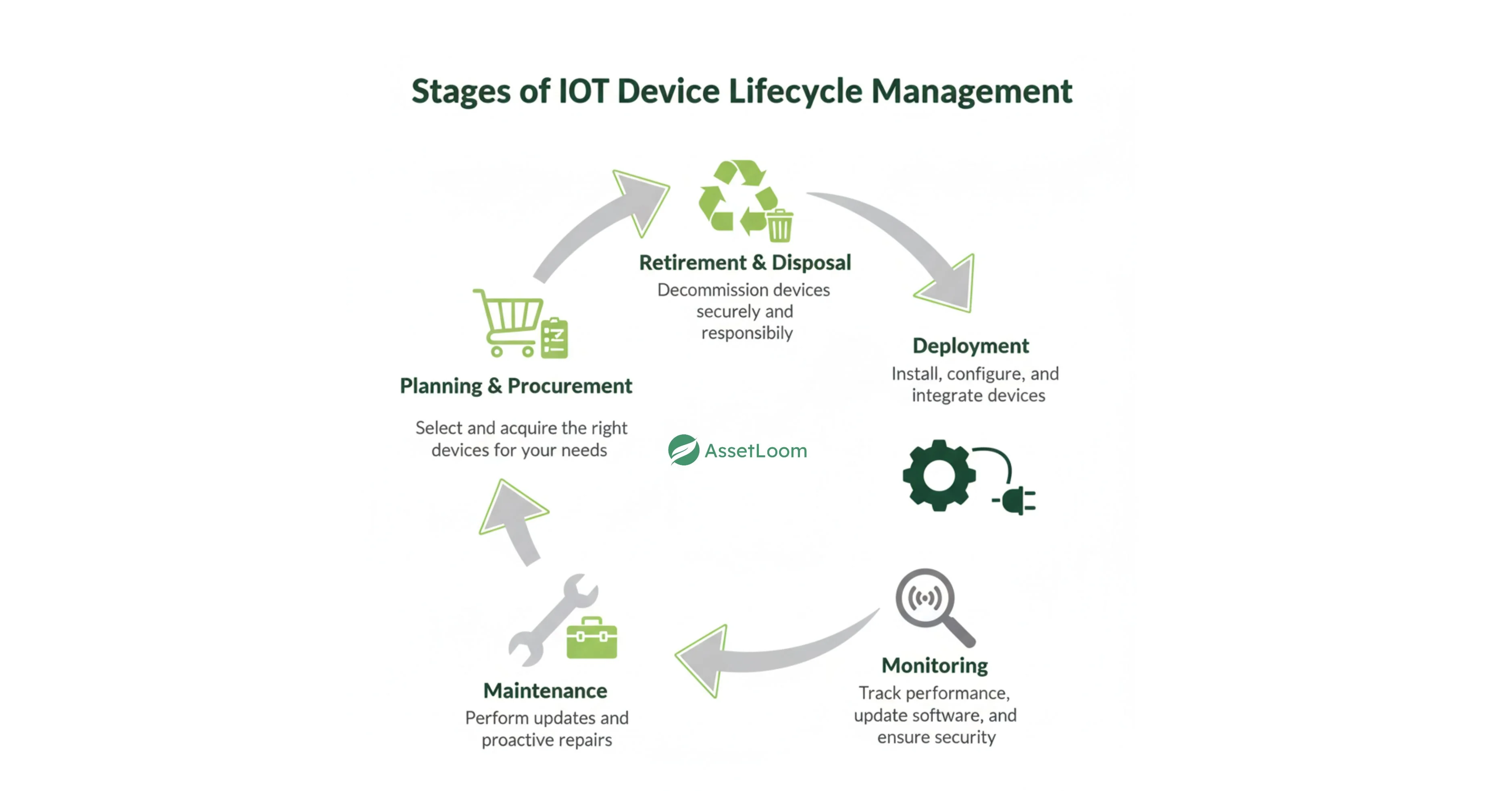
Stage 1: Planning and Conception
The planning and conception stage is the foundation of IoT device lifecycle management. It involves understanding your organization's needs and designing a strategy that aligns with those requirements. This stage ensures that the right devices are chosen based on the roles they will serve, security considerations, and budget constraints.
Key Activities:
- Needs Assessment: Evaluate the specific needs of your organization. Understand what business problems need to be solved by IoT devices, such as improving efficiency, automating processes, or collecting real-time data.
- Device Selection: Based on the needs assessment, identify which IoT devices are most suitable. Whether it’s smart sensors, wearables, or industrial devices, each device type has specific features and capabilities that must match the business objectives.
- Vendor Evaluation: Research and choose reliable vendors who provide high-quality devices. Consider factors like device reliability, security features, and after-sales support. This stage may involve negotiating contracts and setting clear terms.
- Budgeting and Resource Planning: Estimate the total cost of ownership for each device, including procurement, installation, maintenance, and potential upgrades. Allocate the budget based on priorities and expected return on investment.
Read also: Understanding IT Vendor Management
Stage 2: Procurement and Manufacturing
The procurement and manufacturing stage involves acquiring the IoT devices selected during the planning phase. This stage ensures the devices are high-quality, meet necessary specifications, and integrate well with existing systems. It is about obtaining the right devices, either purchased off-the-shelf or custom-made, that meet your needs and are ready for deployment.
Key Activities:
- Vendor Negotiation and Contracting: After selecting the devices, negotiate with vendors for pricing, delivery terms, and warranties. The contract should clearly define service expectations, support, and maintenance terms.
- Bulk Purchasing: If you need many devices, bulk purchasing can reduce costs. Be sure to factor in any discounts or special pricing agreements when planning the budget.
- Security Verification: Before purchasing, verify that the devices meet the required security standards. Check for built-in encryption, secure firmware, and compatibility with your security systems.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Test a small batch of devices before proceeding with a large order. This helps identify any issues related to performance, compatibility, or reliability early on.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Manage the delivery and storage of the devices. Ensure they arrive on time and are ready for deployment when needed.
Stage 3: Deployment and Provisioning
The deployment and provisioning stage involves installing the IoT devices, configuring them, and integrating them into your existing systems and networks. This is when the devices are set up for full operation, ensuring they work seamlessly with other technologies in place while maintaining high security.
Key Activities:
- Device Installation and Configuration: This step involves physically installing the devices and configuring their settings. It includes tasks such as network setup, power connections, and any necessary adjustments to make sure the devices are working correctly within your infrastructure.
- Network Integration: Ensure the devices are securely connected to your network or cloud system. This includes setting up communication channels and ensuring that devices can send and receive data as intended.
- Security Setup: Establish secure access protocols and authentication methods to ensure the devices are protected from unauthorized access. Configure firewalls, encryption, and secure communication channels.
- Software Installation: Install any necessary software or firmware updates to ensure the devices are running the latest versions and are fully functional. This might include integrating the devices with centralized management systems or platforms for easier control.
Stage 4: Maintenance and Monitoring
The maintenance and monitoring stage is focused on ensuring that IoT devices remain operational, secure, and efficient over time. This stage involves ongoing tracking of device performance, applying software updates, addressing issues as they arise, and taking proactive measures to ensure devices continue to meet business needs.
Key Activities:
- Firmware and Software Updates: Regularly update the firmware and software of IoT devices to address bugs, add new features, and improve security. Keeping the devices up-to-date helps prevent vulnerabilities and ensures they stay in line with the latest technological advancements.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor device performance to detect any anomalies, failures, or degradation in functionality. This can involve tracking metrics like device uptime, data transmission speed, and battery life (if applicable).
- Security Monitoring: IoT devices are common targets for cyberattacks, so continuous security monitoring is crucial. Use security tools and platforms to check for unauthorized access, data breaches, or vulnerabilities. Regularly review and update security protocols.
- Proactive Repairs and Troubleshooting: Address any performance issues or malfunctions before they become bigger problems. Implement predictive maintenance strategies to detect potential failures early, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Collect data from the IoT devices for analysis. This data can help assess the device’s performance, spot trends, and optimize how devices are used.
Stage 5: Decommissioning and Disposal
The decommissioning and disposal stage marks the end of the IoT device lifecycle. It involves securely retiring devices that have reached the end of their useful life or are no longer needed. Proper disposal is critical to protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Key Activities:
- Data Wiping: Before removing a device from service, ensure all sensitive data is securely erased. This includes removing any personal, corporate, or operational information to prevent data breaches.
- Registry Removal: Remove the device from your organization's network registry and management systems. This ensures the device no longer has access to your systems and can no longer transmit or receive data.
- Physical Disposal: After data wiping, physically dispose of or recycle the device. If recycling, ensure that the device is handled by certified e-waste recycling programs to minimize environmental impact and comply with regulations.
- Asset Tracking and Reporting: Maintain an updated record of the devices being decommissioned and disposed of. This helps with asset tracking and can be important for audits or compliance reporting.
Best Practices for Effective IoT Device Lifecycle Management
- Plan and Standardize Early: Understand your needs and standardize devices to avoid compatibility issues.
- Prioritize Security: Implement encryption and secure features from the start and throughout the lifecycle.
- Automate Setup: Use automated provisioning tools to simplify device setup and integration.
- Monitor and Maintain Regularly: Track device performance, apply updates, and address issues promptly.
- Use Predictive Maintenance: Leverage analytics to predict and prevent device failures.
- Track Device Data: Keep records of device installation, updates, and maintenance activities.
- Securely Decommission Devices: Wipe data, remove devices from networks, and dispose of them responsibly.
- Ensure System Integration: Make sure devices integrate smoothly with your existing infrastructure.
- Optimize Lifespan: Perform regular maintenance to extend the life of devices.
- Stay Compliant: Follow data privacy laws and e-waste regulations for compliance.
Challenges in IoT Device Lifecycle Management
Managing the lifecycle of IoT devices can come with various challenges. These include:
- Device Compatibility Issues: With a wide range of IoT devices and technologies, ensuring that devices are compatible with existing systems and networks can be complex.
- Security Risks: IoT devices are prime targets for cyberattacks. Securing devices throughout their lifecycle, from deployment to decommissioning, requires constant vigilance and updates.
- Scalability: As the number of devices grows, managing them efficiently becomes more difficult. Tracking and maintaining thousands of IoT devices can overwhelm traditional management systems.
- Data Management: The vast amount of data generated by IoT devices can be challenging to process, store, and analyze. Ensuring that data is secure and usable throughout the lifecycle is a critical task.
- Device Maintenance: IoT devices require regular updates and maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Neglecting this can lead to malfunction, downtime, and reduced device lifespan.
- End-of-Life Disposal: Properly decommissioning and disposing of IoT devices can be tricky. It’s important to follow data security practices and environmental regulations to prevent data breaches and reduce e-waste.
- Integration Complexity: IoT devices often need to integrate with other systems, such as cloud platforms and enterprise software. Ensuring smooth integration without disrupting operations can be a significant challenge.
- Cost Management: Balancing the upfront costs of IoT devices with long-term maintenance, upgrades, and replacements can strain budgets, especially when dealing with a large fleet of devices.
Overcoming these challenges requires a well-defined strategy, the right tools, and ongoing monitoring to ensure that IoT devices remain secure, functional, and cost-efficient throughout their lifecycle.
Tools and Solutions for IoT Device Lifecycle Management
To effectively manage the entire lifecycle of IoT devices, businesses can leverage a variety of tools and solutions. These tools help streamline deployment, ensure security, and monitor performance. Here are some key tools and solutions for IoT device lifecycle management:
IoT Management Platforms
These platforms provide centralized management of all IoT devices, allowing businesses to monitor, configure, and update devices remotely. Examples include:
- AWS IoT Device Management
- Microsoft Azure IoT Hub
- Google Cloud IoT Core
Asset Management Software
These tools help track devices, manage inventories, and keep detailed records of each device’s lifecycle. They also facilitate reporting, audits, and compliance. Examples include:
- ServiceNow IT Asset Management
- IBM Maximo
- AssetLoom (specific for IoT asset tracking)
Security Solutions
Security is critical throughout the IoT lifecycle. Specialized tools can help protect devices from vulnerabilities and ensure secure communications. Examples include:
- Device Defender (AWS)
- McAfee IoT Security
- Palo Alto Networks IoT Security
Monitoring and Analytics Tools
These tools allow businesses to monitor device performance in real time, detect anomalies, and perform predictive maintenance. Examples include:
- Datadog
- Prometheus
- New Relic
Over-the-Air (OTA) Update Platforms
These solutions enable businesses to remotely update the firmware and software of IoT devices without having to physically interact with them. Examples include:
- Balena
- Mender
- Particle.io
Predictive Maintenance Tools
By using data analytics and machine learning, these tools predict device failures before they occur, helping organizations minimize downtime. Examples include:
- Uptake
- Uptake
- Predix (GE Digital)
Cloud Platforms
Cloud platforms integrate IoT devices with other enterprise systems, offering scalability and ease of access. They also enable data storage and analytics. Examples include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform
E-Waste and Recycling Solutions
For secure and environmentally responsible disposal of devices, businesses can partner with certified e-waste disposal and recycling services. This ensures compliance with environmental regulations and data security standards.
By using these tools and solutions, businesses can improve efficiency, enhance security, and ensure that their IoT devices continue to operate effectively throughout their lifecycle.
Conclusion
IoT device lifecycle management is key to maximizing device value while minimizing risks. Proper planning, security, regular maintenance, and secure decommissioning are essential for ensuring devices stay functional and cost-effective.
By using the right tools and following best practices, businesses can streamline operations, extend device life, and reduce risks. Effective management leads to lower costs, improved efficiency, and a more secure IoT environment.

Related Blogs
Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom, right in your inbox.


