What Is Preventive Maintenance in IT Asset Management?
Discover what preventive maintenance means in IT asset management, why it matters, and how it helps extend the life and performance of your assets.
IT teams face constant pressure to keep systems running without interruption. But in reality, equipment fails, software crashes, and small issues often grow into costly downtime.
A single server outage can stop entire departments. Missed updates can expose security risks. Aging hardware quietly slows performance until it becomes expensive to fix.
Most of these problems don’t appear overnight. They build up slowly, unnoticed, until they disrupt something critical.
Forward-thinking IT teams are changing how they manage technology. Instead of reacting to failures, they focus on preventing them. This shift is transforming the way organizations protect and maintain their IT assets.
What Is Preventive Maintenance in IT Asset Management?
In IT asset management (ITAM), preventive maintenance means taking care of your assets before something breaks. It focuses on consistent, planned actions that reduce the risk of downtime and extend the life of every device or system.
This approach applies to all types of IT assets:
- Hardware: cleaning dust from equipment, replacing old parts, and checking battery or fan health.
- Software: updating patches, renewing licenses, and removing unused programs.
- Network devices: running firmware updates, monitoring bandwidth, and verifying backups.
Preventive maintenance is not about reacting after a failure. It’s about using schedules, data, and alerts to act early. When combined with IT asset management, it creates a reliable system that helps IT teams stay organized, prevent costly breakdowns, and keep technology performing at its best.

The Core Components of an Effective IT Preventive Maintenance Program
An effective preventive maintenance program is built on planning, consistency, and accurate data. In IT asset management, this means creating a system that helps teams maintain every device, track performance, and prevent issues before they happen.
Below are the key components that make preventive maintenance successful in an IT environment.
1. Asset Inventory and Classification
The foundation of preventive maintenance starts with knowing what assets you have. Every IT device, from laptops to routers, should be recorded in a centralized inventory. This gives visibility into what needs maintenance, how often, and who is responsible for it.
Assets should also be categorized by type, usage, and criticality. For example, a server that runs business applications needs more frequent inspections than a conference room projector. Prioritizing assets ensures that high-impact systems receive the attention they need to stay operational.
2. Scheduled Maintenance Intervals
Preventive maintenance depends on consistent scheduling. Each asset type should have a defined maintenance interval based on its workload, environment, and manufacturer’s recommendations.
For instance:
- Servers and network devices may require quarterly firmware updates and hardware checks.
- Laptops might need bi-annual battery and performance reviews.
- Printers or IoT devices could be inspected annually for wear and connectivity issues.
Setting these intervals helps IT teams stay ahead of problems, reduce emergency repairs, and plan workloads efficiently.
3. Automated Monitoring and Alerts
Automation is critical for identifying early warning signs. Monitoring tools track asset performance indicators such as temperature, storage capacity, and system uptime. When an anomaly is detected, the system automatically alerts the IT team to investigate.
For example, a spike in CPU temperature might indicate a failing cooling system, or low available storage could point to a data retention issue. Automation allows teams to act quickly, reducing the chance of downtime and avoiding costly manual checks.
4. Documentation and Maintenance Logs
Every preventive maintenance task should be properly documented. Keeping detailed records of maintenance activities helps teams track trends, validate warranty claims, and prepare for internal or vendor audits.
Maintenance logs should include information such as the date of service, actions performed, parts replaced, and technician details. Storing this data in an IT asset management system like AssetLoom allows organizations to view maintenance history, plan upcoming tasks, and measure asset performance over time.
A well-structured preventive maintenance program is not just about performing tasks on schedule. It creates a complete cycle of visibility, planning, and accountability that helps IT teams maintain stability, reduce costs, and extend the life of their assets.
Practical Examples of Preventive Maintenance in Action
Preventive maintenance becomes most valuable when it’s applied to real IT operations. These examples show how regular maintenance helps IT teams prevent downtime, extend asset life, and improve system reliability.
1. Laptop Fleet Maintenance
In many organizations, laptops are among the most used and most neglected assets. Small issues like slow performance, battery degradation, or overheating often go unnoticed until users complain.
By scheduling preventive checks every six months, IT teams can:
- Review battery health and replace weak units before failure.
- Clean cooling fans to prevent overheating and extend hardware life.
- Run diagnostics to detect slow drives or memory issues early.
This proactive approach minimizes support tickets and keeps employees productive with reliable equipment.
2. Server Infrastructure Maintenance
Servers are critical to business continuity, and even brief downtime can cause data loss or service interruptions. Preventive maintenance helps ensure consistent uptime and system health.
Regular tasks might include:
- Monitoring temperature, fan speed, and power supply efficiency.
- Performing firmware and BIOS updates on a set schedule.
- Testing backups to confirm data recovery readiness.
These steps prevent overheating, hardware failures, and configuration issues that often lead to outages.
3. Software and Patch Management
Software maintenance is just as important as hardware upkeep. Outdated applications or missed patches can expose networks to security vulnerabilities.
A preventive maintenance plan should include:
- Monthly patch reviews for operating systems and key applications.
- Automated update deployment across all workstations.
- Regular removal of unused or unsupported software.
Keeping software current not only strengthens security but also improves system performance and compliance.
4. Network Device Maintenance
Routers, switches, and access points are the invisible backbone of any IT environment. Preventive maintenance keeps them performing at peak efficiency.
Key activities include:
- Applying firmware updates to close security gaps.
- Checking signal strength and connectivity logs.
- Cleaning or replacing hardware components in high-traffic areas.
These measures help maintain stable connections, reduce latency, and avoid unexpected network disruptions.
Preventive maintenance works best when it becomes part of the daily IT workflow. With a clear schedule, reliable tracking, and proper documentation, IT teams can manage assets proactively instead of reacting to emergencies.
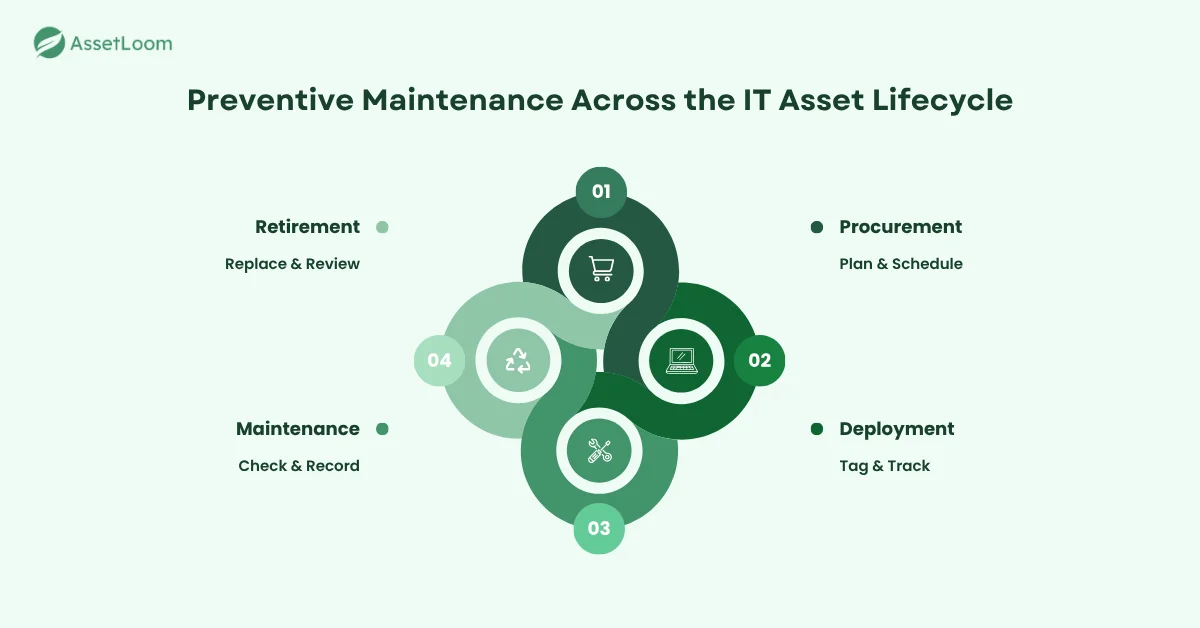
How Preventive Maintenance Fits Into IT Asset Management Workflows
Preventive maintenance works best when it’s part of the entire IT asset management process. It supports every stage of the asset lifecycle — from purchase to retirement — helping teams reduce risk and improve performance.
During procurement, IT teams review warranty terms, vendor recommendations, and maintenance requirements. This information helps set the right service schedule from the start.
When assets are deployed, they should be tagged and entered into the ITAM system with clear maintenance intervals. Servers might need quarterly checkups, while laptops may only need attention twice a year.
In the maintenance phase, preventive actions such as updates, inspections, and diagnostics keep systems running smoothly. Recording these tasks in the ITAM platform provides a clear history for audits and performance reviews.
Finally, when it’s time for retirement, maintenance records show which assets are nearing the end of their useful life. This helps teams plan replacements before breakdowns occur.
By linking preventive maintenance with every ITAM stage, organizations gain better visibility, reduce costs, and keep their technology running reliably.
Automating Preventive Maintenance
Manual tracking often leads to missed schedules and incomplete maintenance. Automation solves this by building preventive maintenance into daily IT operations.
Modern IT management tools can automatically monitor asset health, schedule recurring tasks, and send alerts when attention is needed. This helps teams take action early, before issues cause downtime.
Automation can:
- Track performance metrics such as temperature, storage, and uptime
- Send alerts when assets show early signs of failure
- Create recurring maintenance tasks for updates or inspections
- Generate reports on maintenance activity and costs
By using automation, IT teams save time, reduce human error, and maintain a consistent maintenance routine. It creates a system that keeps technology reliable, secure, and ready for business needs.
Measuring the ROI of Preventive Maintenance
The value of preventive maintenance becomes clear when you track its results over time. Measuring key metrics helps IT teams show how proactive care improves performance and reduces costs.
Here are the main areas to focus on:
- Downtime reduction: Fewer unexpected outages and faster recovery times show how preventive actions keep systems available and stable.
- Lower repair and replacement costs: Regular maintenance reduces expensive emergency fixes and extends asset life.
- Longer asset lifespan: Consistent upkeep delays the need for replacements, helping assets deliver more value over time.
- Improved productivity: With fewer equipment failures, employees experience less disruption and higher efficiency.
- Better planning and budgeting: Maintenance records help IT teams predict future costs and plan upgrades before issues arise.
Tracking these metrics turns preventive maintenance into a measurable investment, proving its role in saving time, money, and resources.
From Reactive Chaos to Proactive Control
Preventive maintenance isn’t just about fixing problems early. It’s about changing how IT teams manage technology.
Instead of reacting to failures, preventive maintenance helps teams stay one step ahead. With regular checkups, updates, and clear maintenance records, IT assets stay reliable, secure, and ready for work.
When preventive maintenance becomes part of daily IT management, everything runs more smoothly. Downtime drops, repair costs shrink, and employees can focus on their work instead of waiting for fixes.
A proactive approach turns maintenance from a chore into a strategy — one that keeps your technology stable, efficient, and built to last.

Related Blogs
Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom, right in your inbox.

