Identifying Your Operating System (OS) Type
Learn what operating system type means, the common categories like desktop, mobile, server, and embedded systems.
Knowing your operating system (OS) type is essential in the world of IT asset management (ITAM), cybersecurity, and software deployment. Whether you manage a large network or a single computer, the process of identifying your OS type helps ensure devices are supported, secure, and compatible with necessary tools.
This article explains how an IT Asset Management tool identifies your operating system type, what information they capture, and why it matters.
What Does “Operating System Type” Mean?
An OS, or Operating System, is the main software that runs on a computer, phone, or other device. It acts like the manager of the device, controlling how the hardware (CPU, memory, storage, etc.) works and letting you run programs or apps. Without an operating system, your device wouldn’t know how to start, show you a screen, or let you do anything useful.
When we talk about identifying your operating system (OS) type, we mean finding out the exact software platform a device is running. An operating system type describes the general category of system software that runs on a device. It tells you what kind of environment the hardware is using to operate and run applications.
Common operating system types include:
- Desktop and Laptop OS, such as Windows, macOS, and most Linux distributions
- Mobile OS, such as Android and iOS
- Server OS, such as Windows Server, Ubuntu Server, or Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Embedded OS, used in devices like routers, smart TVs, or industrial machines

In IT environments, this process is usually done automatically through specialized tools rather than manual checks.
How ITAM Tools Identify Your Operating System Type
ITAM tools use a combination of automated discovery methods and direct device communication to determine OS details. These methods can vary, but the core process is similar.
1. Network Discovery
Many ITAM tools run network scans across a range of IP addresses. These scans detect active devices and gather information about them.
- Protocol checks: Tools use protocols like SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation), or SSH to request OS information directly from devices.
- Banner grabbing: Some network services send back identifying text, such as OS name and version, when queried.
This method works without installing software on each device, making it quick for large networks.
2. Agent-Based Detection
In this approach, a small program (an agent) is installed on each device. The agent regularly collects data and sends it back to the ITAM system.
The agent can directly query the operating system for:
- OS name, version, and edition
- Kernel or build number
- Last boot time
- Installed updates
Agent-based detection is highly accurate because it reads OS details straight from the source.
3. Virtualization and Cloud Integration
In virtual environments or cloud platforms, ITAM tools can integrate directly with management consoles (like VMware vCenter or AWS). These platforms already store OS details for each virtual machine, making identification straightforward.
This is particularly useful when tracking mixed environments of physical, virtual, and cloud-based systems.
4. File and Registry Inspection
On Windows systems, certain registry keys store OS version and edition information. On Linux and macOS, specific system files or commands reveal the same details.
Examples:
- Windows: Reading HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion
- Linux: Checking /etc/os-release
- macOS: Using the sw_vers command
ITAM tools use these checks either via agents or remote commands.
5. API and Endpoint Management Integration
Many organizations use mobile device management (MDM) or endpoint management tools. These systems often provide APIs that list OS types and versions.
By integrating with these APIs, ITAM tools can gather OS data without additional scans or software installation.
Information Captured When Identifying Your Operating System (OS) Type
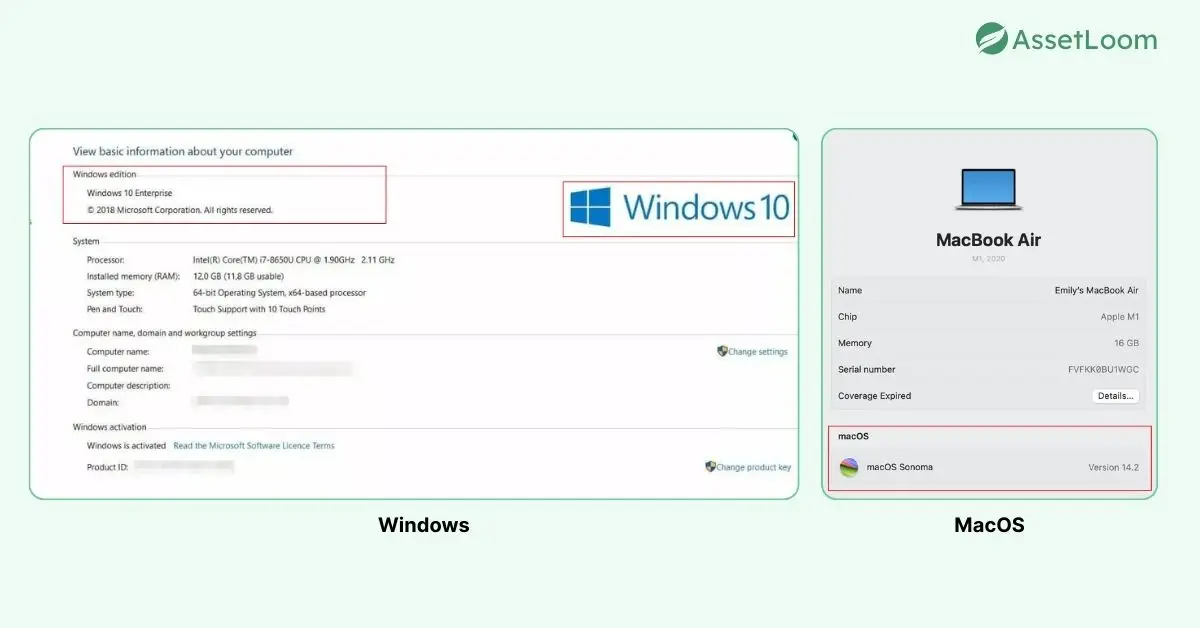
When an ITAM tool identifies your operating system type, it usually stores:
- OS Name: e.g., Microsoft Windows, Apple macOS, Ubuntu Linux
- Version and Build: Specific release numbers for precise identification
- Edition: Home, Pro, Enterprise, Server, etc.
- Architecture: 32-bit or 64-bit
- Patch Level: Latest security and feature updates installed
- License Information: Activation status, if available
Why Identifying Your Operating System (OS) Type Matters
Knowing exactly what OS is running on each device helps in many areas of IT management:
- Security Compliance: Unsupported or outdated OS versions can be a major security risk. Automatic identification allows IT teams to locate and upgrade vulnerable systems quickly.
- Patch Management: Some patches apply only to certain OS versions. Identifying your operating system type ensures updates are targeted correctly.
- Software Compatibility: Not all software runs on every OS version. Accurate identification avoids failed installations and performance issues.
- Audit and Reporting: OS type is a critical data point for compliance reports, especially in regulated industries.
- Standardization: IT teams can enforce policies to keep OS versions consistent across departments, reducing support complexity.
Best Practices for Accurate OS Identification
To make sure OS type detection is reliable, organizations can follow these guidelines:
- Use both agent-based and agentless methods for complete coverage.
- Schedule regular scans to keep OS data current.
- Integrate with cloud and virtualization platforms for full visibility.
- Verify detection results periodically to catch inconsistencies.
- Address security permissions so that OS information can be retrieved without interruptions.
Summary
Identifying your operating system (OS) type is a core task in IT asset management. It allows organizations to maintain security, compatibility, and compliance across all devices.
ITAM tools use various methods, such as network discovery, agent-based collection, file inspection, and integration with other systems, to determine OS details accurately. The information gathered helps in everything from patch management to audit preparation.

Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom. right in your inbox


