IoT Update Management: A Crucial Guide
Learn what IoT update management is, the types and lifecycle of updates, common challenges, and best practices to keep your devices secure and reliable.
IoT devices are now part of daily business operations, from smart cameras and sensors to industrial equipment. As the number of devices grows, the risk of leaving them outdated also increases. Missed updates can lead to cyberattacks, system failures, and unexpected downtime.
For organizations with large fleets of connected devices, managing updates is no longer optional. It is a necessary step to keep systems secure, reliable, and compliant.
This guide looks at the essentials of IoT update management. You will learn about the different types of updates, how the update lifecycle works, the challenges companies often face, and the best practices that help keep devices safe and effective.
What Is IoT Update Management?
IoT update management is the process of keeping connected devices up to date with the latest firmware, operating systems, and security patches. It covers the entire cycle of planning, delivering, and verifying updates so devices remain secure, reliable, and compliant.
What makes IoT update management different from traditional IT updates is the scale and diversity of devices involved. An organization may need to update thousands of devices from different vendors, each with unique hardware limitations and connectivity challenges. Managing this effectively requires centralized oversight, secure distribution, and continuous monitoring.
In many organizations, IoT update management is closely linked to IT Hardware Asset Management, since knowing what devices you own and where they are helps determine which ones need updates and which may be at risk if left unattended.
In short, IoT update management ensures every device in a connected ecosystem is protected and performing as intended.
Types of IoT Update Management
IoT updates come in different forms, each serving a specific purpose. Here’s an easy breakdown of the main types of updates and how they keep your devices running smoothly:
- Firmware Updates: These updates improve how the device hardware works. They might fix bugs, boost performance, or even extend battery life. For example, a firmware update on a smart thermostat could make it more accurate or save energy.
- Security Patches: These are crucial updates that fix vulnerabilities in the device’s software, preventing cyberattacks and data breaches. Security patches are especially important to protect sensitive devices like cameras or smart locks from being hacked.
- Feature Updates: These updates add new capabilities or enhance existing ones. For instance, a feature update might allow a smart speaker to recognize more voice commands or connect to more devices, making it even more useful.
- Configuration Updates: Instead of changing the whole system, these updates tweak specific settings. This could mean adjusting network settings or security rules, which can optimize how a device works without a complete overhaul.
- Emergency Fixes: When a serious bug or security issue is discovered, emergency fixes are quickly rolled out. These are fast responses to urgent problems and are often applied before full testing to prevent damage or exploitation.
By understanding these update types, you can better manage and prioritize updates, ensuring that your IoT devices stay secure and perform at their best.
IoT Update Management Lifecycle
1. Assess Needs
The first step is understanding what devices are in your IoT network and what updates they need. This begins with a complete inventory of devices, ensuring you know which ones are running outdated software or have known vulnerabilities.
Once you know which devices need attention, it’s essential to prioritize updates. Devices that face security threats or are crucial to business operations should be updated first. This ensures that the most critical updates are handled before less urgent ones.
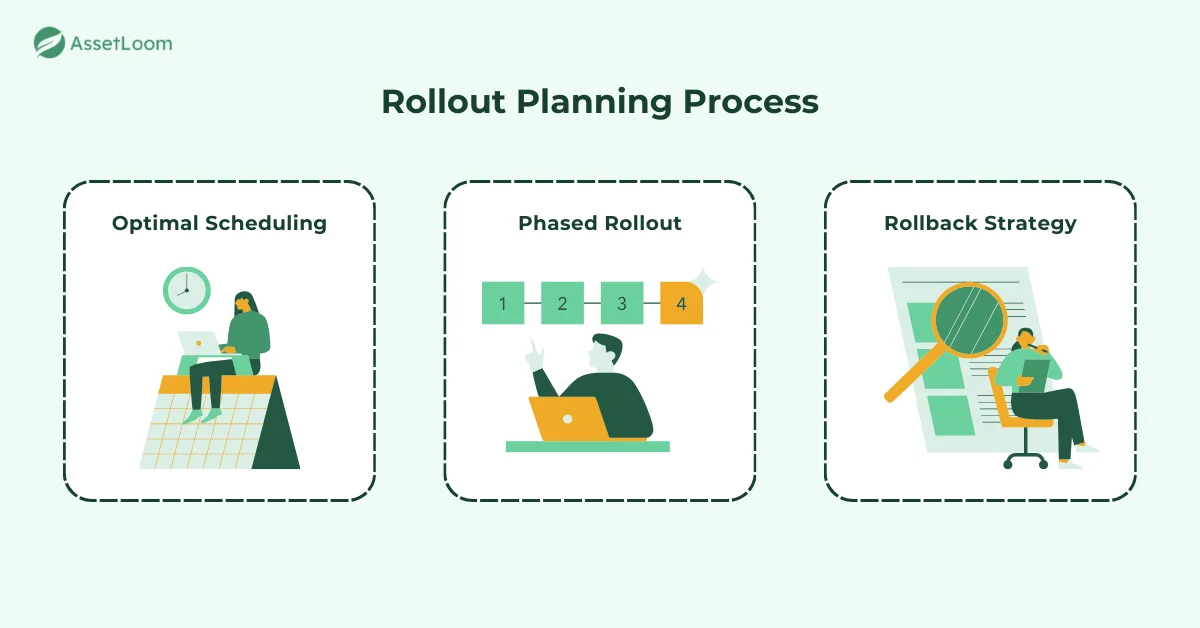
2. Plan the Rollout
Planning the rollout involves several key considerations to ensure that updates are applied effectively and without disrupting business operations. Begin by determining an optimal schedule for updates. Avoid performing updates during peak hours to prevent downtime. Scheduling updates during off-peak hours or automating them when possible can minimize disruptions.
A phased rollout is a best practice when updating IoT devices. Start with a small group of devices to test the update, making sure that everything works as expected. After testing, expand the rollout gradually, ensuring any issues that arise can be addressed before the update is deployed across the entire fleet. This approach minimizes risk and ensures that devices will continue to operate correctly.
It's also essential to have a rollback strategy in place. If something goes wrong, you should be able to quickly revert to the previous version of the software without significant downtime.
3. Deliver Updates
The next step is delivering the update. This involves securely transmitting the update to all devices. Depending on your IoT environment, this could mean using Over-the-Air (OTA) updates or remote management tools. Security is key here — updates should be encrypted during transmission and signed to verify their authenticity. This prevents the risk of malicious actors tampering with the update process.
For organizations with a large fleet of devices, managing the network bandwidth during updates is also crucial. Avoiding overloading the network and ensuring that the devices receive the updates without interruptions will improve the success rate of the updates.
4. Deploy to Devices
Once the updates are delivered, the next step is deployment. A successful deployment involves more than just installing the updates. You must verify that the devices are correctly updated and continue to perform as expected. It's wise to conduct the deployment in batches rather than all at once, as this will make it easier to identify and address any issues in smaller groups.
Real-time monitoring is essential during this stage. Tools should be in place to track the success of each device update, so any failures or issues are identified promptly. Monitoring also helps ensure that no device is left behind during the deployment process.
5. Verify Results
After deployment, verifying the update's success is crucial. You’ll need to ensure that the update has resolved the issues it was meant to fix, such as improving security or enhancing functionality. This can be done by performing basic functionality tests on the devices or using monitoring tools that check performance metrics.
Security scans should also be run to verify that the update hasn’t introduced any new vulnerabilities. Continuous monitoring will help you detect any issues that could affect business operations, such as devices failing to update properly or experiencing performance degradation.
Read also: 10 Must-Know Tips to Choose the Best Monitoring Software for Your IT Needs
6. Rollback if Needed
Not every update will go smoothly, and sometimes an update may cause issues or disrupt device performance. In these cases, having a rollback mechanism in place is essential. Rollback systems should allow the device to revert to its previous stable version quickly, minimizing downtime.
It’s also important to keep backups of the previous versions of firmware and software. These can be used to restore devices to their working state if a rollback is necessary. Ideally, the rollback process should be automated to ensure a fast and efficient recovery without requiring manual intervention.
7. Review & Report
Once the updates are complete, the final step is reviewing and documenting the entire process. This is critical not only for troubleshooting but also for compliance purposes. Regular audits of the update process help ensure that devices remain secure and that the update lifecycle is being followed consistently.
Review the success of the updates, the speed of deployment, and any issues that arose. Use this feedback to improve future update processes. Generating detailed reports also helps with compliance, as many industries require that organizations keep records of updates and system changes.
By following this lifecycle, organizations can ensure that their IoT devices are regularly updated, minimizing risks and maximizing the benefits of their IoT ecosystems. Each step helps improve device performance, enhance security, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Challenges in IoT Update Management
Managing IoT updates presents several challenges that organizations must overcome:
- Device Diversity: IoT ecosystems comprise devices from various manufacturers, each with distinct firmware, operating systems, and update requirements, which complicates update management.
- Connectivity Issues: Remote or low-bandwidth locations can delay updates or cause failures, requiring manual intervention to complete the process.
- Security Risks During Updates: Unsecured update transmission can leave devices vulnerable to attacks. Encryption and authentication are essential to secure the update process.
- Scaling Across a Large Fleet: Updating thousands of devices across multiple locations is time-consuming and difficult without automated tools, increasing the risk of missed or inconsistent updates.
- Limited Device Resources: Many IoT devices have limited processing power, making large updates challenging. Smaller, optimized update packages are needed to address this.
- Downtime and Business Continuity: Some updates require devices to go offline or reboot, which can disrupt critical business operations. Planning is needed to minimize downtime.
- Compliance and Documentation: Regulated industries require detailed tracking of updates for compliance purposes. Failure to do so can lead to legal issues.
- User Disruption: Updates can change device behavior or interfaces, causing confusion or mistakes among users. Balancing security and user experience is key.
Best Practices for IoT Update Management
To manage IoT updates effectively, organizations need to follow best practices that ensure updates are secure, efficient, and cause minimal disruption. Here are some strategies to implement:
Automate the Update Process
Automating updates is one of the best ways to reduce manual effort and human error. By using Over-the-Air (OTA) updates or remote management tools, updates can be pushed to devices seamlessly, ensuring that every device in the fleet stays current without requiring constant attention.
Rollout Updates in Phases
Rather than deploying updates to all devices at once, start with a small group of test devices. This allows you to evaluate the success of the update and catch any issues early. Once the pilot group has been updated successfully, gradually roll out to the rest of the fleet, which minimizes the risk of widespread problems.
Monitor Updates in Real-Time
Real-time monitoring during and after updates is essential for catching issues as soon as they arise. By tracking device performance and update success, you can quickly address failures or other problems, ensuring that devices continue functioning smoothly post-update.
Prioritize Critical Updates
Security patches and firmware updates that address known vulnerabilities should always take priority. By applying these updates first, organizations can protect devices from threats and ensure that security gaps are closed before tackling less urgent updates.
Have a Rollback Plan in Place
Despite careful planning, some updates may cause issues. It’s crucial to have a rollback plan to quickly restore devices to their previous stable version. This ensures minimal disruption if something goes wrong, allowing for quick recovery without significant downtime or loss of data.
Maintain Detailed Records
Keeping thorough documentation of all updates is essential, especially for compliance and auditing purposes. Record the devices updated, the type of update applied, and any issues encountered. This documentation helps maintain transparency and ensures that your update process meets regulatory standards.
Test Updates Before Full Deployment
Before applying updates across the entire fleet, always test them on a small batch of devices. This ensures that the update doesn’t interfere with device functionality or cause unexpected disruptions. It’s a critical step in ensuring updates don’t break essential features or processes.
Minimize User Disruption
Some updates may change how users interact with IoT devices. To minimize disruption, schedule updates during off-peak hours and notify users about upcoming changes. This helps to reduce confusion and ensure that any changes to functionality are smoothly adopted.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can streamline the IoT update process, improve security, and ensure their devices continue to function optimally with minimal downtime or risk.
The Future of IoT Update Management
As IoT devices evolve, so will the strategies and technologies for managing updates. Here are the key trends shaping the future of IoT update management:
- AI-Driven Updates: AI tools will automate and optimize update processes, predicting which devices need updates and prioritizing security patches based on real-time threat intelligence.
- Self-Healing Devices: Devices will be capable of automatically detecting and applying updates or fixing issues without manual intervention, reducing the workload for IT teams.
- Predictive Maintenance and Updates: Devices will not only notify organizations of needed maintenance but also predict when updates are necessary to avoid performance or security issues.
- Edge Computing and Localized Updates: Updates will increasingly be delivered directly to devices at the network edge, reducing latency and bandwidth strain while improving update speed.
- Standardization of Update Protocols: The adoption of universal standards for IoT updates will allow for more seamless and secure update management across diverse devices and manufacturers.
- Regulatory Pressures and Compliance: As IoT security regulations tighten globally, organizations will need to ensure their update processes comply with stricter requirements.
- Blockchain for Secure Updates: Blockchain technology could provide an immutable record of updates for IT asset management, ensuring transparency and security, particularly in high-risk sectors like healthcare and finance.

Conclusion
IoT update management is essential for maintaining device security, performance, and compliance. As IoT devices become more integral to business operations, efficient and secure update processes will be crucial.
By implementing best practices and embracing emerging technologies, organizations can tackle the challenges of IoT updates and keep devices secure and reliable. In the future, automation, predictive maintenance, and standardized protocols will make managing updates easier and more effective, ensuring devices continue to add value without compromise.

Related Blogs
Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom. right in your inbox

