IT Asset Disposal & E-Waste Management in 2025
Discover effective IT asset disposal and e-waste management strategies for 2025. Secure data wiping, recycling, and compliance to reduce e-waste
Do you know what happens to your old laptops, phones, and other tech once they’re no longer in use? If you’re upgrading regularly, you’ve probably got a pile of outdated devices. The real problem is disposing of them safely.
In 2025, e-waste is a growing issue. Improper disposal can harm the environment and put your data at risk. This blog will help you understand the challenges of IT asset disposal and offer practical ways to handle e-waste responsibly.
What is IT asset disposal?
IT asset disposal is the secure and environmentally responsible process of retiring outdated or unwanted IT equipment, like computers, servers, and phones. It ensures sensitive data is erased or destroyed, and the hardware is disposed of in a way that meets both legal and environmental standards.

The process involves several key steps:
- Data Security: First, all sensitive data stored on devices is securely erased or the storage media is physically destroyed. This is to prevent unauthorized access and protect business or personal information.
- Environmental Responsibility: Once data is securely removed, the hardware is recycled or responsibly disposed of. Many e-waste components can be recycled, keeping harmful materials out of landfills and helping conserve resources.
- Regulatory Compliance: Companies must ensure that their disposal process complies with data protection and environmental regulations. This avoids legal penalties and helps maintain a positive corporate image.
- Documentation: Detailed records are kept throughout the disposal process. This provides proof of compliance, secure handling, and a clear audit trail.
For example, when a company replaces old desktops, they securely erase data from the devices, send them for recycling, and provide a full report on the disposal process to ensure everything is handled responsibly and legally.
What is e-waste?
E-waste, or electronic waste, refers to discarded electronic devices that are no longer in use or have reached the end of their life cycle. This includes a wide range of tech products like computers, smartphones, televisions, printers, and even appliances like refrigerators and microwaves.
As technology evolves quickly, many electronics become obsolete or break down faster than they can be replaced, leading to a growing amount of e-waste. Improper disposal of these devices can lead to environmental and health issues, as electronics often contain harmful materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium. If not recycled properly, these materials can leak into the soil and water, causing long-term damage.
E-waste can also pose a security risk. Devices that store sensitive data, like computers and phones, can be an easy target for identity theft or data breaches if not disposed of securely.
Proper e-waste management involves recycling, reselling, or securely destroying electronics to recover valuable materials and reduce harmful environmental impacts.
How Big is the E-Waste Problem in 2025?
The global e-waste problem continues to grow at an alarming rate. In 2021, over 57.4 million metric tons (Mt) of e-waste was generated, and by 2025, there will be an estimated 347 million metric tons of unrecycled e-waste accumulated worldwide. The demand for electronic devices is increasing due to factors like rising disposable incomes, population growth, and fast-paced technological advancements. However, most of these electronics have a short lifespan and are quickly replaced, contributing to the rise in e-waste.
Shockingly, only 17.4% of e-waste is recycled properly. This means that a significant portion of it is either sent to landfills, incinerated, or improperly disposed of, releasing harmful substances like mercury, lead, and cadmium into the environment. These toxins can have long-lasting negative effects on ecosystems, wildlife, and human health.
The biggest producers of e-waste are countries like China, the US, and India, which together account for a large percentage of global e-waste generation. However, the challenge isn’t limited to large countries—e-waste is also a growing problem in smaller nations with increasing electronic consumption.
As technology continues to evolve, the volume of e-waste is expected to grow, with projections suggesting that global e-waste generation could reach 74.7 Mt by 2030, almost doubling in just 16 years. This highlights the urgent need for better e-waste management practices, recycling infrastructure, and global collaboration to tackle this issue before it gets out of control.
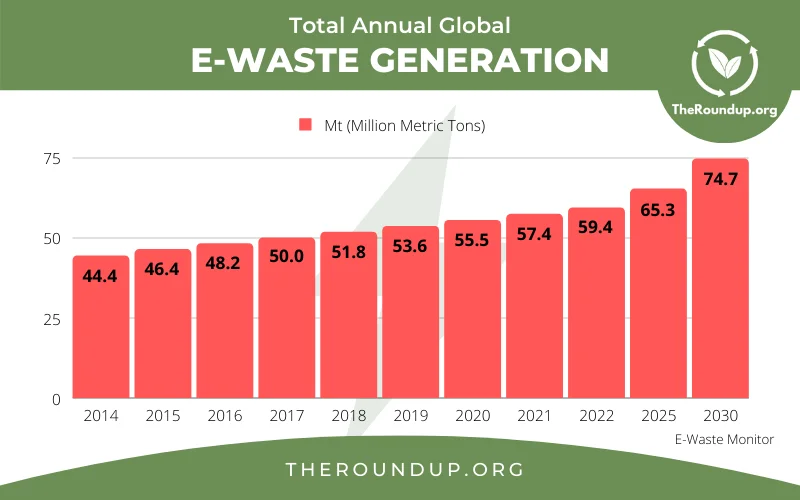
Source: https://theroundup.org/global-e-waste-statistics/
What Are the Key Regulations on E-Waste Disposal in 2025?
As e-waste continues to grow, governments around the world are implementing and updating regulations to ensure safe, responsible disposal of electronic waste. These regulations aim to protect both the environment and human health, while promoting recycling and data security. Some key regulations in place for e-waste disposal in 2025 include:
WEEE Directive (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) – European Union (EU):
The WEEE Directive is one of the most comprehensive regulations globally. It requires manufacturers to take responsibility for the collection, recycling, and proper disposal of their products at the end of life. The EU aims to reduce e-waste by promoting the reuse of products and the recycling of materials.
As of 2025, the WEEE Directive mandates that a growing percentage of e-waste be collected and processed in an environmentally sound way, with specific targets for recovery and recycling rates.
RoHS Directive (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) – European Union (EU):
RoHS limits the use of certain hazardous substances, such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, in electrical and electronic equipment. This directive aims to reduce the environmental impact of e-waste by ensuring that harmful substances are not released when products are disposed of.
In 2025, these restrictions will remain in place, further limiting the environmental and health risks associated with e-waste disposal.
EPA Guidelines (Environmental Protection Agency) – United States:
The EPA sets guidelines for the disposal of electronic waste, particularly around hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, and flame retardants found in e-waste. In 2025, the agency continues to enforce these rules to ensure proper handling and disposal of harmful materials.
Additionally, the EPA encourages the recycling of e-waste through partnerships with certified recyclers, helping businesses comply with environmental standards.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Laws:
Many countries have implemented or will be strengthening EPR laws that hold manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including the collection and recycling of e-waste. These laws require manufacturers to finance or manage the recycling process, which ensures that electronics are properly disposed of.
Countries like Canada, Japan, and South Korea have already adopted strong EPR programs, and other nations are expected to follow suit in 2025 to reduce e-waste and promote recycling.
Global E-Waste Management Standards – International:
International organizations like the United Nations and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) are working toward creating global standards for e-waste management. These standards focus on the safe disposal and recycling of e-waste, with an emphasis on preventing environmental damage, improving collection systems, and enhancing the reuse of materials.
While these standards aren’t legally binding, they are becoming more influential in shaping national regulations and encouraging countries to adopt more comprehensive e-waste management practices.
National E-Waste Regulations – Country-specific:
As of 2025, 78 countries have some form of national e-waste legislation or regulation, covering about 71% of the global population. While the level of enforcement varies, more countries are introducing laws to ensure proper disposal of e-waste.
Countries like Estonia, Norway, and Iceland have among the highest recycling rates due to strong national e-waste regulations, while regions such as Africa still face challenges with enforcement and proper disposal.
Impact of Regulations in 2025
By 2025, these regulations will play a key role in improving global e-waste management. Businesses must stay compliant with local, national, and international laws, ensuring they use certified recyclers and maintain proper documentation. Failure to comply could result in hefty fines, legal action, and damage to a company’s reputation.
Ultimately, these regulations are helping to move toward a more sustainable, circular economy for electronics, where materials are reused, and the harmful effects of e-waste are minimized.
What Are the Best Practices for IT Asset Disposal?
When it comes to disposing of IT assets like computers, smartphones, and other electronic devices, following best practices is crucial for maintaining data security, complying with regulations, and protecting the environment. Here are the key best practices for responsible IT asset disposal:
Ensure Secure Data Destruction
Before disposing of any IT equipment, it's essential to securely erase all sensitive data to prevent unauthorized access. Simply deleting files is not enough. Use certified data-wiping tools (like Blancco or DBAN) that completely overwrite data, or physically destroy the storage media (e.g., hard drives or SSDs) to ensure that information cannot be recovered. This step is critical for protecting confidential company data, customer information, and personal data.
Partner with Certified E-Waste Recyclers
To ensure the proper recycling of electronic waste, partner with recyclers who are certified under standards such as R2 (Responsible Recycling) or e-Stewards. Certified recyclers follow strict guidelines for safely handling, dismantling, and recycling e-waste, ensuring that harmful materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium are properly managed and don’t end up in landfills.
Recycling and Refurbishment
If the device is still functional, consider refurbishing it for reuse or donating it to a charitable organization. Many devices can be repurposed or resold, extending their useful life and reducing e-waste. If the device is not reusable, ensure that it is sent to a recycling facility where valuable materials, such as metals and plastics, can be recovered and reused in the production of new electronics.
Adhere to Legal and Environmental Regulations
IT asset disposal must comply with local, national, and international regulations, such as the WEEE Directive in the EU or EPA guidelines in the US. These regulations ensure that e-waste is processed in an environmentally responsible manner and that any data destruction practices meet the required standards for security and compliance. It's also essential to maintain documentation for regulatory and audit purposes, proving that proper disposal protocols were followed.
Maintain Documentation and Chain of Custody
Proper documentation is a crucial part of the disposal process. Keep detailed records of every IT asset disposed of, including serial numbers, the disposal method, and the recycler or donation recipient. This creates an audit trail that can be used to prove compliance with environmental and data protection laws. It also ensures that the devices were disposed of in a secure and ethical manner.
Use IT Asset Management (ITAM) Systems
Implementing an IT asset management (ITAM) system can help you track the entire lifecycle of your IT equipment—from acquisition to disposal. ITAM software helps ensure that assets are properly managed, data is securely wiped, and devices are disposed of responsibly. It also helps businesses plan for the replacement and recycling of equipment, minimizing waste and maximizing the value of their technology investments.
Consider Environmental Impact
Always prioritize eco-friendly disposal methods. Electronics contain valuable resources that can be recycled, such as metals, plastics, and glass, which can be reused in the manufacturing of new products. Proper disposal reduces the environmental impact of e-waste by preventing toxic chemicals from leaching into the environment and conserving valuable materials.
How Can IT Asset Management Help Reduce E-Waste?
IT Asset Management (ITAM) plays a crucial role in reducing e-waste by helping organizations manage the lifecycle of their technology more efficiently.
Track and Optimize Asset Lifecycles
Tracking and optimizing asset lifecycles helps reduce e-waste. Here’s how IT Asset Management (ITAM) systems make it possible:
- Real-Time Tracking: Monitor the status and condition of each asset, allowing for informed decisions about repairs, upgrades, or replacements.
- Timely Maintenance: Keep track of maintenance schedules to extend the life of equipment and prevent premature disposal.
- Informed Replacement Decisions: Determine whether to continue using, repair, or upgrade equipment based on its remaining useful life.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Ensure assets are used effectively, preventing overuse or underutilization, and extending their lifespan.
Proper Disposal and Recycling
IT Asset Management (ITAM) helps ensure that when assets reach the end of their life, they are disposed of responsibly and sustainably. Here’s how ITAM systems contribute to proper disposal and recycling:
- Track End-of-Life Assets: ITAM systems help businesses identify assets that are no longer functional or needed, making it easier to separate them from active equipment for proper disposal.
- Certified Recycling Partnerships: ITAM ensures that old equipment is sent to certified e-waste recyclers, reducing the environmental impact by ensuring that hazardous materials are handled safely.
- Recycling Documentation: ITAM systems can maintain records of the disposal process, ensuring that assets are disposed of in compliance with regulations and that valuable materials are recycled.
- Reduce Landfill Waste: By tracking when assets can be recycled or repurposed, ITAM minimizes the chances of devices being sent to landfills unnecessarily.
Promote Refurbishment and Resale
IT Asset Management (ITAM) systems can help businesses identify opportunities to extend the life of their equipment through refurbishment or resale. Here's how ITAM helps:
- Identify Usable Assets: ITAM tracks the condition of devices and identifies equipment that is still in good working condition but may no longer be needed, allowing for refurbishment or resale.
- Maximize Asset Value: Instead of disposing of equipment prematurely, businesses can refurbish and resell or donate items, helping them retain value and reduce the need for new purchases.
- Donate or Resell: ITAM systems facilitate the donation of functional equipment to charities or schools, contributing to community support and reducing e-waste.
- Extend Product Life: By tracking asset usage, ITAM can help businesses decide whether to refurbish devices instead of discarding them, reducing the volume of e-waste.
Data Security and Compliance
Ensuring that IT assets are disposed of securely and in compliance with regulations is a critical part of reducing e-waste. IT Asset Management (ITAM) systems help manage data destruction and ensure that businesses meet legal requirements for disposal:
- Secure Data Wiping: ITAM systems track the secure erasure of sensitive data from devices before they are recycled or disposed of, preventing data breaches.
- Compliance with Regulations: ITAM ensures that asset disposal complies with data protection laws and environmental regulations, such as GDPR, WEEE, and EPA guidelines, protecting businesses from legal risks.
- Documentation for Audits: ITAM provides detailed records of the disposal process, including how data was wiped and where the equipment was sent, creating an audit trail for compliance purposes.
- Data Destruction Verification: ITAM systems can integrate with certified data destruction services to ensure proper documentation and verification of data destruction, assuring that data is not recoverable.
Environmental Impact Reduction
IT Asset Management (ITAM) systems play a significant role in reducing the environmental impact of e-waste. Here’s how:
- Track and Reduce E-Waste: ITAM helps businesses track the disposal of IT assets, ensuring that only truly obsolete or unusable equipment is disposed of, preventing premature disposal of still-functional devices.
- Promote Sustainable Practices: ITAM encourages the use of sustainable disposal methods, such as recycling and repurposing, reducing the amount of e-waste that ends up in landfills.
- Resource Recovery: By ensuring that equipment is recycled, ITAM helps recover valuable raw materials like metals, plastics, and glass, which can be reused in the production of new devices, reducing the need for mining and conserving natural resources.
- Eco-Friendly Partnerships: ITAM ensures that businesses work with certified e-waste recyclers who follow strict environmental standards, preventing the release of toxic chemicals into the environment.
Maximizing Asset Utilization
IT Asset Management (ITAM) systems help businesses get the most out of their IT assets, reducing waste and extending the life of equipment. Here’s how ITAM can help maximize asset utilization:
- Optimize Asset Usage: ITAM provides insights into how assets are being used across the organization, ensuring that equipment is being fully utilized and not underused or overused.
- Avoid Unnecessary Purchases: By tracking asset performance and usage, ITAM helps businesses identify when existing equipment can still meet needs, reducing unnecessary purchases and minimizing e-waste.
- Asset Sharing and Reallocation: ITAM systems help businesses identify underutilized assets that can be reassigned or shared across departments, ensuring that equipment serves its purpose and reduces the need for additional purchases.
- Maximize Return on Investment (ROI): By ensuring that assets are fully utilized, businesses can maximize the ROI of their IT investments, while delaying replacements and reducing waste.
AssetLoom helps businesses manage their IT assets efficiently, enabling better decision-making, optimized usage, and responsible disposal. With its comprehensive IT Asset Management (ITAM) system, AssetLoom tracks the entire lifecycle of assets, from acquisition to disposal, ensuring that businesses can maximize the lifespan of their equipment and minimize unnecessary e-waste. The platform offers data-driven insights that help businesses make informed choices about asset maintenance, upgrades, and secure disposal, all while staying compliant with regulations. By integrating with certified recycling and data destruction services, AssetLoom ensures that end-of-life assets are disposed of in an environmentally friendly and secure manner, ultimately reducing e-waste and promoting sustainability.
What Does the Future Hold for IT Asset Disposal & E-Waste Management?
The future of IT asset disposal and e-waste management is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, stronger environmental awareness, and stricter regulations. As e-waste continues to grow, recycling methods will become more efficient, with new technologies allowing for better recovery of valuable materials, such as rare metals. AI and automation will play a larger role in sorting and dismantling e-waste, making the process faster and more precise, while reducing reliance on manual labor.
Governments worldwide are likely to implement stricter regulations, holding manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products. This means businesses will need to ensure their disposal practices are more sustainable. As these regulations tighten, global standards for e-waste management will become more aligned, ensuring that companies meet environmental and data security requirements.
Data destruction methods will also improve, offering more secure and effective ways to wipe information from old devices, reducing the risk of data breaches. As consumers become more aware of the environmental and security issues surrounding e-waste, they’ll likely participate more in recycling programs, pushing businesses to provide easier ways to dispose of old electronics.
Overall, the future of e-waste management looks promising, with a focus on creating a more sustainable digital economy, reducing waste, and ensuring secure disposal of IT assets.
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, the importance of responsible IT asset disposal and e-waste management becomes ever more critical. By adopting best practices such as secure data destruction, proper recycling, and optimizing asset lifecycles, businesses can significantly reduce their environmental impact and protect sensitive information. The future of e-waste management holds exciting possibilities, with innovations in automation, AI, and sustainable practices paving the way for a more efficient, eco-friendly approach. As regulations tighten and consumer awareness grows, businesses will need to stay proactive in managing their IT assets to ensure compliance, security, and sustainability. Embracing these changes not only helps reduce e-waste but also contributes to a cleaner, more responsible digital world.

Related Blogs
Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom. right in your inbox


