Why Asset Tags Still Matter During the Disposal of IT Assets
Disposal of IT assets is made more secure and efficient with asset tags, helping prevent errors, ensure data security, and streamline the process.
Disposing of IT assets isn’t just about getting old equipment out of the way. It’s a critical process that involves security, compliance, and accountability. If any step is skipped or done carelessly, the consequences can include data exposure, audit failures, and gaps in inventory.
What Happens During the Disposal of IT Assets
Disposing of IT assets isn’t a single action. It’s a sequence of steps designed to protect data, stay compliant, and update records. Each step needs to be handled carefully to avoid gaps, especially when devices leave your building or change hands.
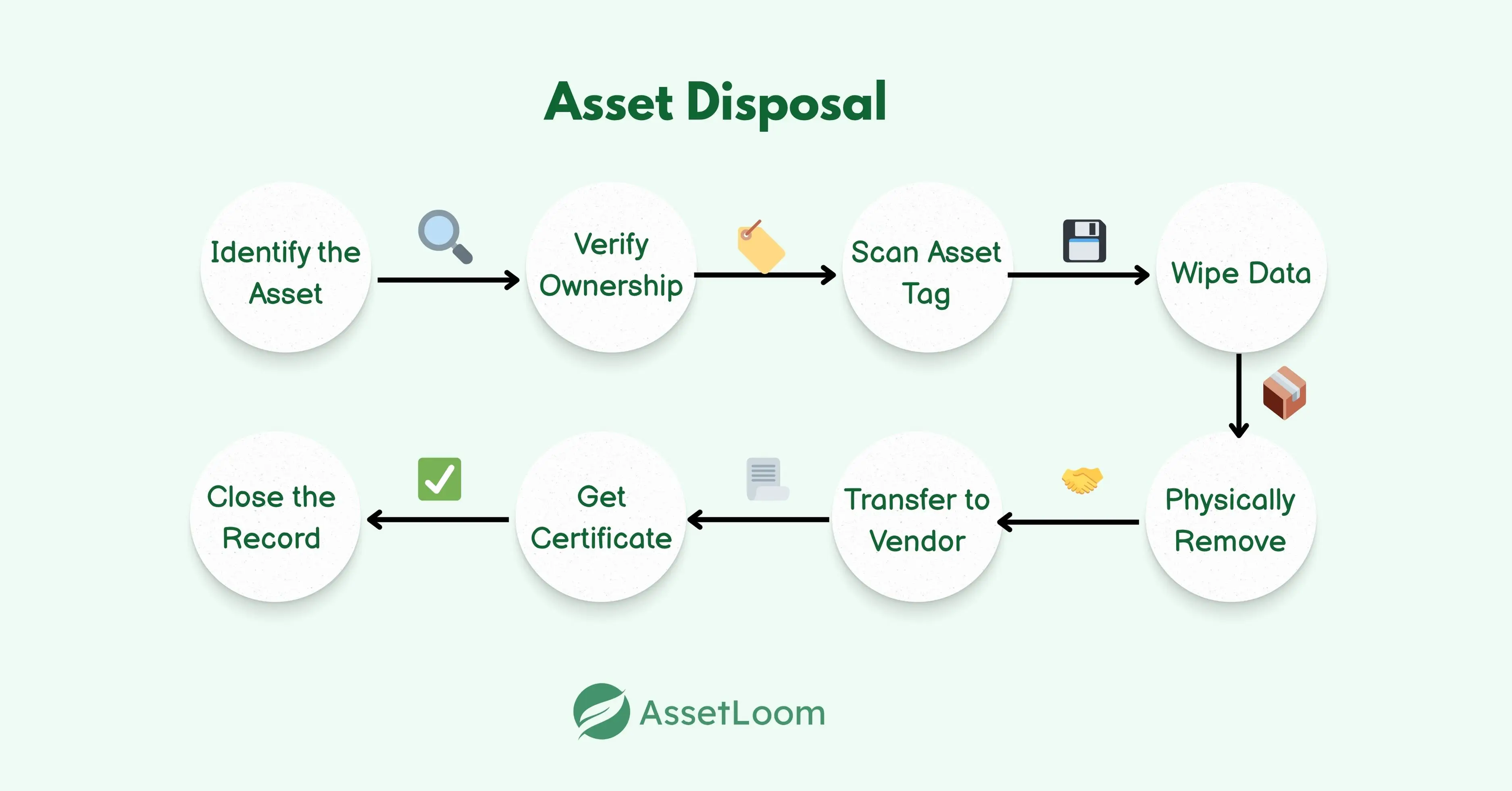
The disposal stage is where many IT teams lose visibility. Devices are sent offsite, records are closed, and tracking becomes harder. Disposal of IT assets involves more than wiping drives and recycling old hardware. It's about finishing the job with confidence. And small details—like keeping asset tags in place—make a big difference in how cleanly and securely that job gets done.
What is IT Asset Disposition (ITAD)?How Asset Tags Support the Disposal of IT Assets
When assets are active, tags help track location, ownership, and maintenance. But during disposal, they do something just as important: they prevent confusion.
Once a device is ready for disposal, the risks shift. The main concern becomes making sure each item is properly wiped, documented, and removed from all systems. If you’re handling dozens or hundreds of similar devices, it’s easy for things to get mixed up. That’s where tags still help.
They confirm exactly which asset is being retired
When assets are scheduled for disposal, they often come in batches. Rows of similar-looking laptops, desktops, or switches make it hard to tell one from another. Visually, most devices look the same. But from a data and security standpoint, they are not.

Some assets may still be in use, contain sensitive information, or be flagged for reassignment. Others are truly at the end of their life. If your team cannot reliably tell them apart, there is a real risk of wiping the wrong device, retiring an active one, or missing a device that should be removed.
Example scenario:
Your team is decommissioning 15 Dell Latitude laptops. One of them still belongs to the HR department and contains payroll records. The others were used for training and are no longer needed. The HR device requires secure wiping and formal approval before it can be retired. Using asset tags, the team scans each laptop and matches it to its record. This helps them identify the HR device, process it carefully, and handle the rest through the normal disposal path.
They link physical assets to digital records
Asset tags are more than just identifiers. They create a direct link between the physical device and its digital record in your IT asset management system. This connection is particularly important during disposal because it ensures that every asset is accounted for and all relevant information stays up to date.
When a device is tagged, its number is tied to a detailed record that includes:
- Purchase date and cost
- Assigned user or department
- Device condition and warranty status
- Maintenance and repair history
- Software installed and licensing details
- Security and data classification
Example You’re preparing 20 laptops for disposal. Each one is tagged with a unique identifier that connects to the asset’s full record in the ITAM system. When your team scans a tag, they instantly access the device’s history: when it was purchased, who used it, what software licenses need to be transferred or deactivated, and any security concerns like data classification or encryption status.
This means you’re not just physically disposing of a device. You’re updating records, transferring software licenses, and ensuring compliance with data security protocols all in one step.
They help track the chain of custody during vendor handoff
Once devices are ready for disposal, they are often handed over to third-party vendors or recyclers for secure destruction, resale, or recycling. This transfer of custody requires careful tracking to ensure that every asset is handled properly and no device goes missing.
Asset tags are crucial for maintaining this chain of custody. When devices are moved from your hands to a vendor’s, the tags allow for clear tracking. Each tag is linked to a record that shows where the device is going, who is responsible for it, and when the transaction took place.
Example scenario: You send 50 desktops to a certified e-waste recycling vendor for destruction. Each desktop has an asset tag that matches its record in the ITAM system. When the vendor receives the equipment, they verify the tags against their own inventory. A certificate of destruction is issued for each device, confirming it was securely handled.
Later, if an audit reveals a missing device, you can cross-check the tag number with the vendor’s destruction certificate. This proves the device was properly disposed of and ensures no data was left exposed.
They prevent disposal mistakes
Disposal of IT assets involves multiple steps, and it’s easy to make mistakes, especially when you’re handling large numbers of devices. Mistakes during the disposal process—whether it’s sending the wrong device for destruction or failing to remove it from inventory—can lead to financial loss, data security breaches, or compliance violations.
Asset tags help prevent these mistakes by offering a reliable method to track, verify, and confirm each device before it is retired.
Example scenario: Your team is decommissioning 30 desktop computers. During the process, a technician accidentally grabs a device from the pile that was supposed to stay in use. Without asset tags, the wrong desktop would have been sent for disposal without anyone noticing. But because the device is tagged, the technician can quickly confirm the asset's status by scanning it, ensuring it is not mistakenly retired.
Asset tags provide an additional layer of validation. By scanning tags before each device is moved or processed, your team ensures that only the correct items are being retired, recycled, or destroyed.
They support final documentation and closure
After an IT asset is disposed of, the job isn’t done until all the records are updated and the process is properly closed. Asset tags help ensure everything is documented correctly.
When you scan the asset tag during disposal, it automatically updates the device’s record in your asset management system. This includes important details like the date of disposal, the reason for disposal, how the asset was disposed of (e.g., recycling, destruction, resale), and any related certificates such as data wiping or destruction.
Example scenario: Your team is disposing of 20 old servers. Each server has an asset tag. As the devices are processed, the team scans the tags, and the IT system updates the records with the disposal date and confirms that the device was either wiped or destroyed. The vendor also provides certificates of destruction, which are attached to each asset’s record.
Once everything is recorded, the device is marked as “disposed” or “retired” in the system, ensuring it is no longer part of your active inventory. This documentation is crucial for audits and compliance.
When and Why Tags Still Fail
While asset tags are a valuable tool for managing IT assets and ensuring a secure disposal process, they are not foolproof. There are several situations where tags can fail, leading to potential risks during the disposal process. Understanding these scenarios and the reasons behind tag failures can help mitigate risks and improve the disposal process.
1. Worn-Out or Damaged Tags
Over time, tags may become damaged, worn out, or illegible, especially if the asset has been in use for several years. This is especially true for devices that are frequently handled or stored in harsh environments. If the tag is unreadable or missing, the asset becomes difficult to track and may be overlooked during disposal.
Solution: Regularly inspect tags and replace damaged or worn ones before the disposal process begins. For high-use assets, consider using more durable tags, such as metal or laminated barcode labels, which can better withstand wear and tear.
2. Improper Tagging from the Start
Tags may fail if they were never applied correctly in the first place. For example, if the tags are placed in hard-to-reach or hidden locations on assets, they may not be scanned properly during audits or disposal. This can result in assets being missed or incorrectly documented.
Solution: Ensure tags are placed in visible, easily scannable locations when assets are first tagged. Establish standardized tagging practices that all employees follow to ensure consistency.
3. Over-Reliance on Tags for Security and Disposal
Tags can be a valuable tool, but they should not be relied on as the only method for security or disposal verification. If an organization depends solely on asset tags without proper processes to ensure secure wiping or destruction, there’s still a risk of missing critical steps in the disposal process.
Solution: Use asset tags as part of a larger disposal framework that includes data wiping protocols, vendor certifications for secure destruction, and regular compliance audits to ensure full security during disposal.
4. Human Error During Scanning or Tracking
Scanning tags during the disposal process may fail due to human error, such as incorrect scanning or skipping over assets in the disposal queue. Even with functioning tags, human mistakes can result in assets being missed or incorrectly processed.
Solution: Train staff to follow a systematic process during asset scanning and disposal. Encourage double-checking and cross-referencing with the asset management system to avoid mistakes.
5. Outdated Technology or Systems
Sometimes, the failure isn’t with the tags themselves but with outdated technology or systems used to scan or track the tags. Older barcode scanners or RFID technology may not work as efficiently, especially if tags are worn or damaged.
Solution: Ensure that scanning technology is up to date and compatible with the asset tags being used. Regularly maintain and upgrade your tracking systems to ensure smooth operation.
Useful Tagging Practices Before Disposal
Before you begin the disposal process, it’s essential to implement effective tagging practices to ensure the proper handling of each asset. Proper asset tagging before disposal can streamline the process, reduce errors, and help maintain compliance with data security and regulatory requirements.
Here are some useful tagging practices to follow:
- Ensure Accurate Tagging Information Make sure every asset is tagged with a unique identifier linked to accurate and complete asset information in your IT asset management system. This includes details such as the asset’s purchase date, assigned department, warranty status, and software licenses.
- Tag All Assets, Including External Devices Don’t forget external devices like monitors, printers, and peripherals. These should also be tagged for easy identification. Missing a peripheral can lead to incomplete disposal documentation, which may cause compliance issues.
- Label Sensitive Data Storage Devices Any device that stores sensitive or proprietary data should be clearly labeled to indicate its importance. These labels will alert your team to handle these assets with extra care, ensuring secure data wiping or destruction.
- Update Asset Records Before Disposal Before initiating disposal, ensure that all asset records are updated. This includes noting the condition of the device, marking it as “decommissioned,” and indicating the reason for disposal (e.g., end-of-life, upgrade). Having up-to-date records ensures accuracy during disposal.
- Document and Track Disposal Approvals Require proper approvals for asset disposal. Ensure that these approvals are documented and linked to the asset’s digital record, so that there is a clear trail of who authorized each device’s disposal.
By following these tagging practices before disposal, you ensure that assets are properly tracked, that data security is prioritized, and that the disposal process is compliant with both internal and external regulations.
Final Thoughts
Disposing of IT assets requires careful attention to security, compliance, and proper documentation. Asset tags are essential for tracking, verifying, and securely disposing of equipment. While they play a critical role, it's important to integrate them with solid processes, regular audits, and secure data destruction practices.

Related Blogs
Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom. right in your inbox


