The 7Rs of Cloud Migration Strategy
The 7Rs of Cloud Migration Strategy are a set of approaches that organizations can use when moving workloads to the cloud.
When it comes to cloud migration, businesses are faced with a big decision: how to move their IT infrastructure and applications to the cloud. A cloud migration strategy allows companies to take advantage of flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. But before you dive in, it’s essential to understand the different strategies available for migrating to the cloud. These strategies are often referred to as the 7Rs of Cloud Migration Strategy. In this article, we’ll walk you through what each strategy involves, and how businesses of all sizes and technical levels can approach cloud migration.
What Is Cloud Migration?
Simply put, cloud migration is the process of moving applications, data, and other business elements from on-premise servers (physical servers) to cloud infrastructure. It’s like relocating your office or business to a more modern, efficient, and accessible space. With the cloud, your business can access computing resources such as storage, servers, and software without maintaining them in-house.
However, moving to the cloud isn’t a one-size-fits-all decision. Every business has different needs and goals, and the best way to move to the cloud depends on several factors. That’s where the cloud migration strategy comes in.
What Are the 7Rs of Cloud Migration Strategy?
The 7Rs represent seven common strategies businesses use when deciding how to migrate to the cloud. These strategies help organizations choose the best approach based on the complexity of their applications, resources, and goals.
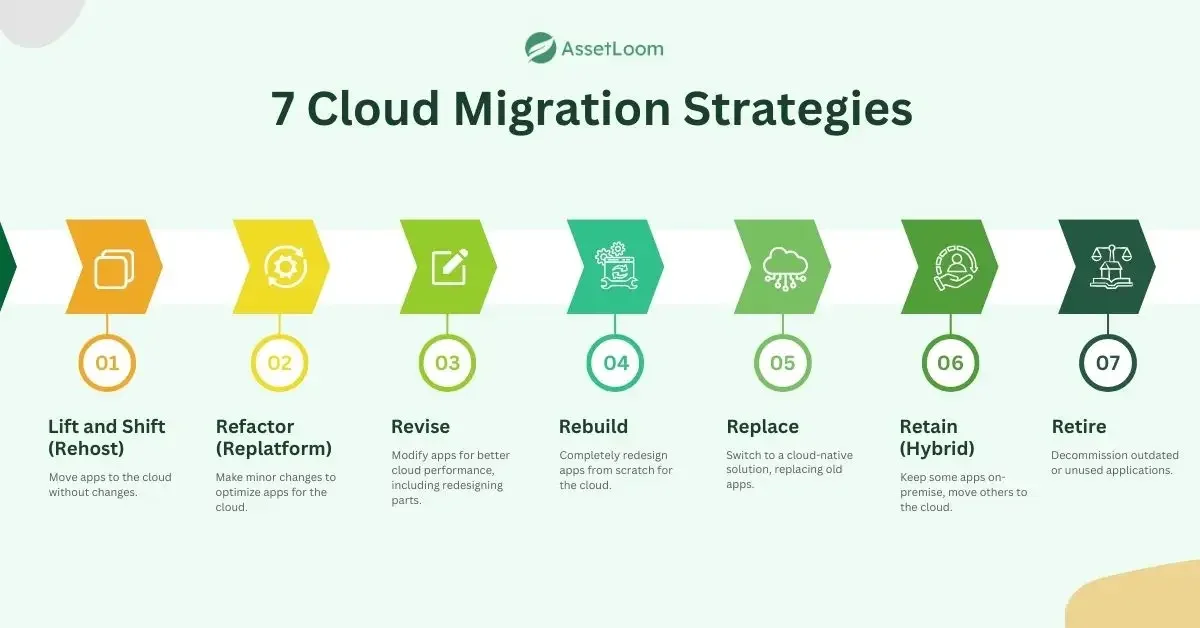
Let’s break them down.
1. Rehost (Lift and Shift)
Rehosting is the simplest and fastest approach to cloud migration. In this strategy, you essentially "lift" your existing applications from your current environment (e.g., on-premise servers) and "shift" them directly to the cloud without making any changes. This is often referred to as a Lift and Shift.
When should you use it?
- If your current infrastructure is outdated or expensive to maintain.
- If you want a quick and easy move to the cloud without much modification.
- If your apps don’t require cloud-specific features like scalability or automation.
Why it’s useful:
Rehosting is the quickest way to move your applications to the cloud without changing them. This strategy is particularly helpful for businesses that need to move their legacy systems to the cloud but don’t have the resources or time to update them. It’s a straightforward solution that allows businesses to avoid the complexity of rebuilding applications.
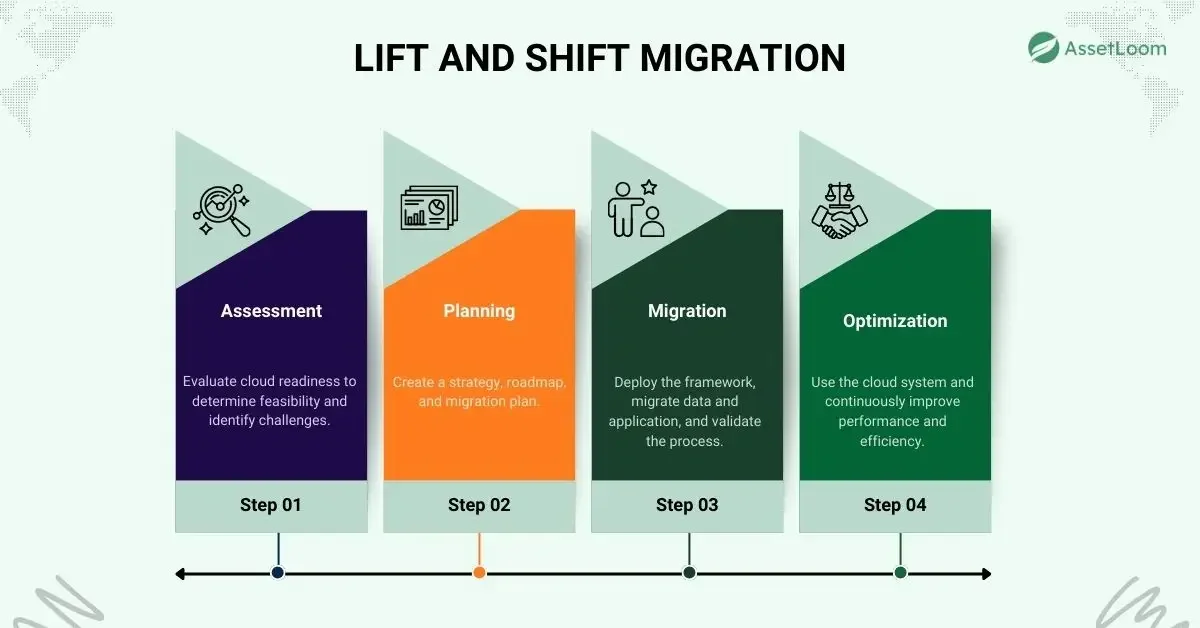
Though it doesn't fully leverage cloud-native features, it provides a fast, easy way to reduce infrastructure costs and get your apps running in the cloud quickly. Rehosting helps businesses immediately move to a more scalable, cost-efficient environment without a lengthy migration process.
2. Refactor (Replatform)
Refactoring, or replatforming, involves making minor changes to your applications so they can perform better on the cloud. This could include modifying the underlying infrastructure, like moving from traditional databases to cloud databases. However, you don’t completely redesign the application.
When should you use it?
- If you need to take advantage of cloud features (like automated scaling or cloud databases) but don’t want to rebuild everything.
- If your current app can be improved with minor tweaks for cloud performance.
Why it’s useful:
Refactoring allows businesses to take advantage of some cloud benefits without a complete overhaul of their applications. By making small adjustments, like migrating to a cloud-friendly database or using cloud-native services, businesses can improve the performance and scalability of their existing systems.
This approach strikes a balance between simplicity and efficiency, giving businesses more flexibility in how they use the cloud. While it requires more time and resources than rehosting, refactoring provides a way to optimize applications without starting from scratch, making it a good option for businesses looking for a moderate-level upgrade.
3. Revise
In this strategy, you don’t just make a few tweaks but significantly update or modify the application to better align with cloud requirements. It’s more than just replatforming but doesn’t require a complete rebuild either. You might change parts of the application’s code, structure, or design to fit cloud environments.
When should you use it?
- If you need a more extensive optimization than just replatforming but don’t want to completely rewrite the app.
- If your app needs more than small fixes to perform well in the cloud.
Why it’s useful:
Revise goes beyond replatforming by enabling businesses to modernize their applications more comprehensively for the cloud. Instead of just tweaking the infrastructure, you make deeper changes to the application’s design, performance, and structure. This strategy helps you ensure that your apps can run efficiently in the cloud while meeting business needs for speed, scalability, and flexibility. It’s an ideal solution for businesses that want to improve the cloud-readiness of their apps but aren’t ready for a full rebuild.
4. Rebuild
Rebuilding means completely redesigning and rebuilding your application from scratch for the cloud. You’ll take advantage of cloud-native technologies like microservices, serverless computing, and cloud-based databases to optimize your application’s performance, scalability, and security.
When should you use it?
- If your legacy system is outdated or too complex to rehost or refactor.
- If you want to fully harness the power of the cloud by adopting modern architecture like microservices or serverless computing.
Why it’s useful:
Rebuilding is the most time-intensive option but also the most rewarding in terms of cloud optimization. This strategy allows businesses to fully leverage cloud-native technologies such as microservices, serverless computing, and containerization, which can greatly improve performance, scalability, and security.
By starting from scratch, you can design an app specifically for the cloud, ensuring that it benefits from everything the cloud has to offer. Rebuilding gives businesses the opportunity to modernize their entire infrastructure, future-proofing their applications for long-term success. It’s the best option for businesses that need to make the most of the cloud’s capabilities and are willing to invest in a more extensive transformation.
Considerations:
- It’s time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- The most expensive option, as it requires significant effort to redesign the application.
5. Replace
Sometimes, instead of migrating an old application, the best option is to replace it with a new, cloud-native solution. This could mean moving from a traditional on-premise software solution to a SaaS (Software as a Service) product.
When should you use it?
- If your existing app is outdated, expensive to maintain, or no longer meets your business needs.
- If a cloud-based solution exists that offers better functionality or performance.
Why it’s useful:
Replacing legacy applications with new, cloud-native solutions is an efficient way to modernize your business operations without having to maintain outdated systems. SaaS (Software as a Service) solutions, for example, come with built-in cloud features like scalability, security, and easy updates, allowing businesses to focus more on their core operations rather than IT management.
Replacing old software with modern, cloud-based alternatives can lead to improved efficiency, better integration with other tools, and reduced overhead costs. It’s a great option when legacy applications are no longer meeting business needs or are too costly to maintain.
6. Retain (Hybrid)
In a retain strategy, you keep certain applications on-premise, especially if they have special needs like compliance, enterprise cloud security, or performance requirements. This can be part of a hybrid cloud strategy, where some workloads are in the cloud and others stay on physical servers.
When should you use it?
- If certain applications or data can’t be moved due to legal, regulatory, or performance reasons.
- If you need to maintain control over specific assets or processes.
Why it’s useful:
Retaining certain applications on-premise or in a private cloud can be beneficial for businesses that have specialized security, compliance, or performance needs. Some apps may handle sensitive data that needs to stay within the organization’s infrastructure due to legal or regulatory requirements.
A hybrid approach allows businesses to take advantage of the cloud for certain workloads while maintaining control over others. This flexibility ensures that businesses can meet industry regulations and privacy standards while still benefiting from the scalability and cost-effectiveness of the cloud. Hybrid models are ideal for businesses with diverse IT requirements that need a balanced solution.
Learn more: Cloud Compliance.
7. Retire
In some cases, the best option is to retire old applications that are no longer useful or needed. This can be the easiest strategy, as you simply shut down old systems and move on.
When should you use it?
- If certain applications are redundant or have become obsolete.
- If your business no longer needs certain apps due to newer technologies or business shifts.
Why it’s useful:
Retiring old systems that are no longer needed can save businesses a lot of time, effort, and money. If certain applications are outdated, redundant, or irrelevant to current business operations, decommissioning them reduces complexity and simplifies the IT environment. Retirement also helps businesses avoid the ongoing costs associated with maintaining legacy systems. By eliminating unnecessary or obsolete applications, businesses can focus their resources on more productive and efficient technologies, ultimately improving operational efficiency and reducing technical debt.
How AssetLoom Helps During the Cloud Migration Process
AssetLoom plays an important role in the cloud migration process by providing a detailed inventory of all your IT assets. This includes hardware, software, and network assets, ensuring that everything is accounted for before migration. With this information, IT teams can easily map out the relationships and dependencies between different applications and services, helping them identify which components need to be migrated together.
Explore** **Top 5 IT Asset Management Cloud Software for 2025.
Having this clear visibility is crucial for effective planning. It helps avoid any disruptions during migration by ensuring all critical parts of your infrastructure are moved at the right time. AssetLoom makes it easier to develop a solid cloud migration strategy that reduces risks and ensures a smoother transition to the cloud.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cloud Migration Strategy
When planning your cloud migration strategy, it’s essential to understand your current infrastructure, goals, and the complexity of your applications. The 7Rs provide a roadmap for choosing the right approach, whether you’re looking for a quick migration, a complete redesign, or even retiring outdated systems.
- Lift and Shift is fast and easy but doesn’t fully leverage cloud features.
- Replatform makes small adjustments to gain more cloud benefits without a major redesign.
- Revise takes things a step further with deeper changes to improve cloud compatibility.
- Rebuild completely modernizes your app for cloud performance.
- Replace involves switching to a new cloud-native solution.
- Retain is ideal for apps that must stay on-premise for specific reasons.
- Retire is the best option for obsolete or redundant systems.
Choosing the right strategy will depend on your business needs, budget, and time. Cloud migration is a big step, but understanding these 7Rs will help make the process smoother and more effective for your organization.

Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom. right in your inbox


