How to Track an IP Address
Learn how to track an IP address with simple steps using free online tools, command line methods like traceroute and WHOIS
An IP address is a unique number that identifies a device on a network. It helps data move between computers and servers on the internet. There are two main types: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 uses a 32-bit format, like 192.168.1.1, which limits the number of available addresses to about 4.3 billion. IPv6 uses a 128-bit format, like 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334, which provides a much larger pool of addresses. Tracking an IP address means finding details about its location, owner, or network path. This can help with troubleshooting, security checks, or investigations.
You cannot track an exact street address from an IP. Geolocation gives a general area, like a city or country. Accuracy depends on the database used and factors like VPNs, which hide real locations. Always check local laws before tracking. In places like the EU, IP addresses count as personal data under GDPR, so consent may be needed. In the US, tracking for legal reasons requires warrants, but basic lookups are allowed.
This guide explains how to track an IP address step by step. It covers tools, commands, and tips.
What Is an IP Address?
An IP address stands for Internet Protocol address. It works like a postal code for devices. When you visit a site or send an email, your device includes its IP in the data packet. The receiver uses that IP to send a response.
There are public and private IPs. Public IPs face the internet and can be tracked globally. Private IPs, like 192.168.x.x, stay inside local networks and are not visible outside. Dynamic IPs change over time, often assigned by your ISP. Static IPs stay the same and are common for servers.
How to track an IP address at home:
- On Windows: Open Command Prompt and type
ipconfig. Look for "IPv4 Address" under your network adapter. - On Mac/Linux: Open Terminal and type
ifconfigorip addr. Find the "inet" line for your interface, like en0 for Ethernet.
For public IP, use a site like whatismyipaddress.com or type curl ifconfig.me in Terminal/Command Prompt.
Why Track an IP Address?
People track IPs for several reasons:
- Security: Check suspicious logins or emails. If an email comes from an unexpected country, it might be a scam.
- Troubleshooting: See if network issues come from a specific router or ISP.
- Content personalization: Sites use IPs to show local news or prices.
- Legal investigations: Law enforcement tracks IPs for crimes, but needs warrants to get user details from ISPs.
Tracking helps block spam or find lost devices, but it has limits. VPNs or proxies mask IPs, and mobile IPs change often.
Legal Considerations When Tracking IP Addresses
Tracking an IP is not illegal in most cases, but how you use the info matters. IPs are public-facing, so looking them up is like checking a return address on mail.
- Privacy laws: In the EU, GDPR treats IPs as personal data if linked to a person. Get consent or anonymize data. In the US, the CFAA bans misuse like hacking.
- Business use: For B2B, tracking is fine if not personal. Disclose in terms of service.
- Harassment: Using IPs to stalk or dox is illegal.
For health sites, HIPAA limits tracking PHI like IPs tied to medical info. Always log actions and get legal advice if unsure.
How to Track an IP Address
You need an IP first. Common ways:
- From emails: Open the email in Gmail. Click the three dots > "Show original." Look for "Received: from" lines with IPs like [123.45.67.89]. The last one is usually the sender's.
- From websites or chats: If you run a site, server logs show visitor IPs. Tools like Google Analytics collect them. In chats like Discord, admins see IPs.
- From pings: In Command Prompt/Terminal, type
ping example.comto get the site's IP. - Shared links: Create a trackable link with tools like Grabify. Share it; when clicked, it logs the IP.
Note: Emails from big providers like Gmail often show relay IPs, not the sender's real one.
_Read more: Scheduled Asset Scan: Functionality, Tools, and Setup Challenges
Methods to Track an IP Address
Method 1: Using Online IP Lookup Tools
Free tools query databases for location, ISP, and more. Steps:
- Go to a site like iplocation.net or whatismyipaddress.com/ip-lookup.
- Enter the IP.
- Results show country, city, ISP, latitude/longitude, and sometimes a map.
Popular free tools in 2025:
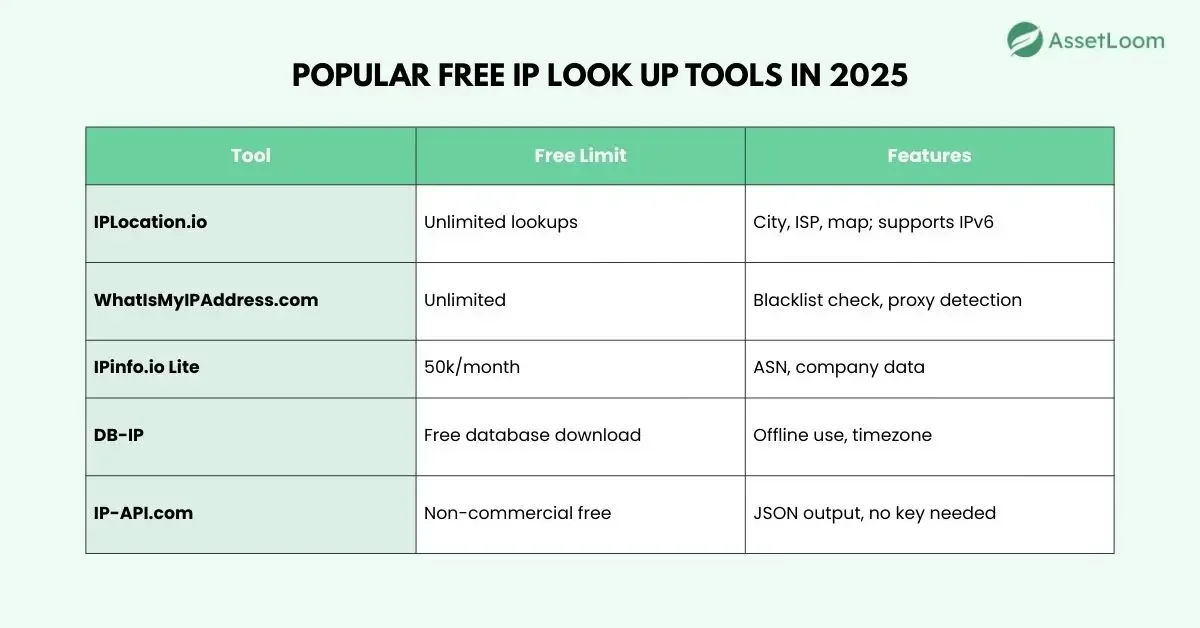
These use GeoIP databases from providers like MaxMind. Accuracy: 99% for country, 80-90% for city.
Method 2: Command Line Tools
Use built-in commands for basic tracking.
Find Your IP
- Windows:
ipconfig /all - Linux/Mac:
ip addr showorifconfig
Ping a Host
Tests reachability and gets IP.
- Type
ping google.com. Output: "Pinging google.com [142.250.191.78]".
Traceroute (Tracert on Windows)
Shows the path to an IP, hop by hop.
- Windows: Open Command Prompt, type
tracert 8.8.8.8. Lists routers and IPs along the route. - Mac/Linux: Terminal,
traceroute google.com. Same output.
Example output:
1 192.168.1.1 1 ms
2 10.0.0.1 5 ms
3 * * *
Asterisks mean timeouts. Use -n flag to skip DNS lookups for speed.
WHOIS Lookup
Gets owner info.
- Install whois on Linux/Mac:
sudo apt install whois. - Type
whois 8.8.8.8. Shows ISP, organization, country.
On Windows, use online WHOIS or PowerShell.
Method 3: Advanced Tools for Networks
For pros:
- Wireshark: Captures packets, shows IPs in traffic. Free, but needs setup.
- Nmap: an IP address scanner, scans networks for IPs. Command:
nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/24lists live hosts.
IPv4 vs. IPv6: Tracking Differences
IPv4 and IPv6 differ in format and scale, affecting tracking.
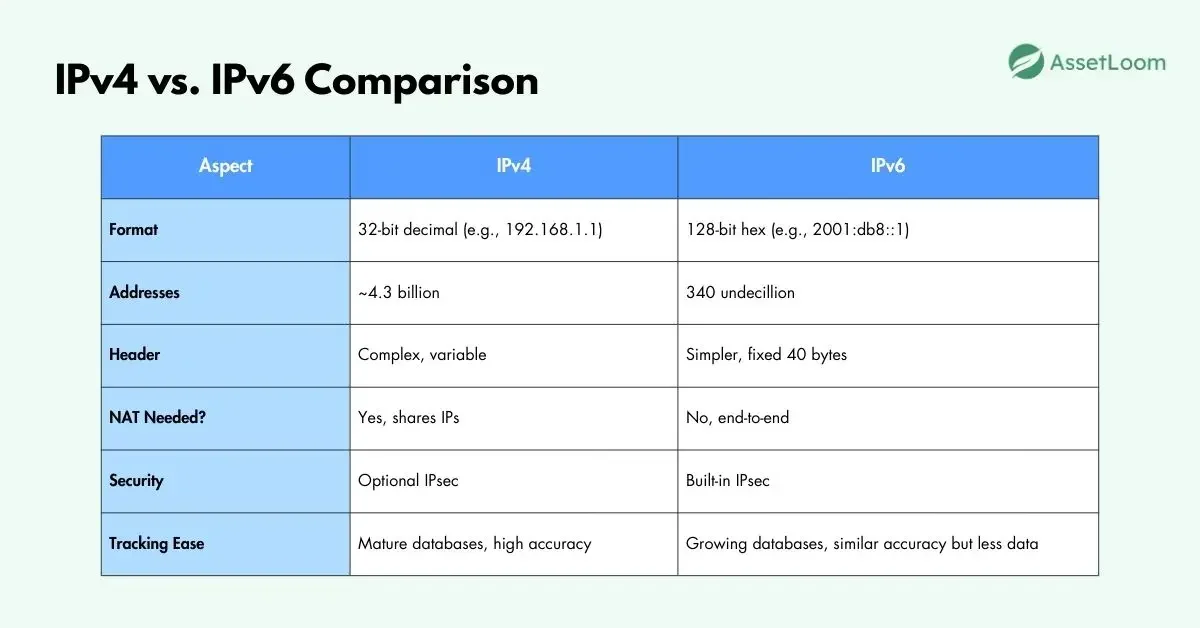
Tracking IPv6 is similar: Use the same tools, which support both. But IPv6's vast space means fewer mappings, so city-level accuracy is lower (70-80%) vs. IPv4's 90%. IPv6 avoids NAT, so IPs are more direct but privacy extensions rotate them often.
Dual-stack networks use both; tools auto-detect.
Limitations of IP Tracking
- Inaccuracy: GeoIP is approximate; VPNs show server locations.
- Dynamic IPs: Change frequently, hard to pin to one user.
- Shared IPs: Many users behind one IP (e.g., NAT, mobile carriers).
- No personal info: WHOIS shows ISP, not names without subpoenas.
- IPv6 challenges: Huge space makes exhaustive tracking impractical.
For exact user ID, contact ISP with legal process.
Read more: What is Network Scanning? 5 Best Automated Network Scanning Tools
Protecting Your IP Address from Tracking
To avoid being tracked:
- Use a VPN: Routes traffic through a server, hides real IP. Free options like ProtonVPN; paid for speed.
- Tor Browser: Bounces traffic through nodes for anonymity.
- Proxy servers: Similar to VPN but less secure.
- Mobile data: Changes IP often.
- Firewall rules: Block incoming pings.
Test by checking your IP before/after. Remember, no method is 100% foolproof against advanced tracking.
Conclusion
How to track an IP address is straightforward with free tools and commands. Start with online lookups for quick geo data, or use traceroute for paths. Understand IPv4 vs. IPv6 for modern networks. Always respect privacy laws—track ethically for security or troubleshooting.
With billions of devices online, IPs remain key to connectivity. As IPv6 grows, tracking tools will adapt. If you need more details, experiment safely in a test network.

Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom. right in your inbox


