Cloud Security Management for Your Assets
Learn how cloud security management supports effective cloud asset management. Discover why securing cloud resources is critical.
As organizations move more of their infrastructure and data to the cloud, security management becomes a top priority. While cloud computing offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, it also introduces a complex set of challenges, especially in managing and securing cloud assets. Cloud security management is now a fundamental part of any IT strategy, ensuring that cloud-based systems remain secure, compliant, and efficient.
In this article, we will explore what cloud security management is, how it fits within cloud asset management, the challenges businesses face, and the best practices for building a strong cloud security posture.
What is Cloud Security Management?
Cloud security management refers to the process of protecting data, applications, and infrastructure involved in cloud computing. It includes implementing tools, policies, and controls to safeguard cloud assets against unauthorized access, data breaches, misconfigurations, and other security risks.
Security management in the cloud is not a one-time setup. It involves continuous monitoring, auditing, and optimization of security measures. Organizations must be proactive in identifying threats, responding to incidents, and maintaining compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Cloud Security vs. Cloud Asset Management: How They Connect
Cloud asset management involves tracking, organizing, and managing all digital assets hosted in cloud environments. These assets include virtual machines, containers, data storage, software instances, and network configurations. Without proper asset visibility and control, securing these components becomes nearly impossible.
Cloud security is deeply connected to cloud asset management in the following ways:
- Visibility and Inventory: Security begins with knowing what assets exist. Cloud asset management provides a complete inventory, which helps security teams monitor vulnerabilities and apply patches quickly.
- Configuration Management: Misconfigured cloud resources are a major security risk. Cloud asset management tools help ensure that all assets follow security configurations and best practices.
- Compliance Monitoring: Asset data feeds directly into compliance checks. Organizations can use this information to demonstrate adherence to data protection laws, such as GDPR or HIPAA.
- Incident Response: When a breach occurs, knowing what assets were involved can speed up incident resolution. Asset tracking helps teams investigate and mitigate issues faster.
Why Cloud Security Management Matters Today
Cloud environments are highly dynamic. Resources can be spun up or shut down within minutes. While this agility brings great benefits, it also increases the risk of:
- Untracked Assets: Without proper tracking, resources may be exposed without protection.
- Shadow IT: Employees may create unauthorized cloud assets that bypass corporate security policies.
- Compliance Failures: In regulated industries, a lack of proper security management can lead to fines or legal consequences.
- Increased Attack Surface: More cloud assets mean more entry points for attackers.
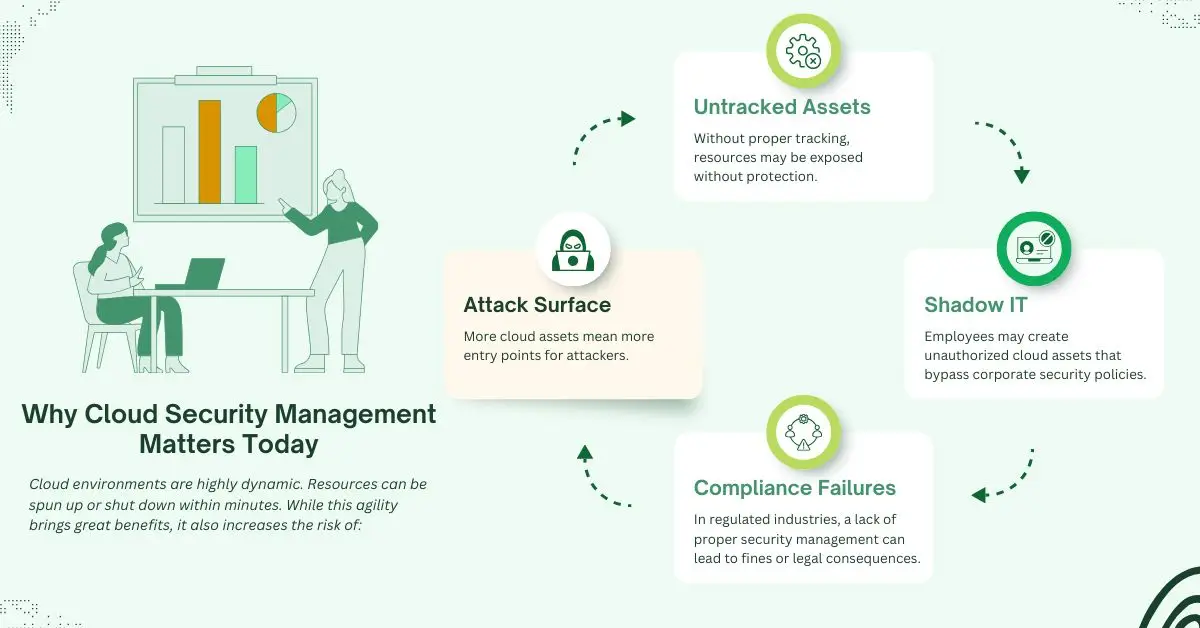
A well-structured cloud security approach helps reduce these risks and supports business continuity.
Key Components of Cloud Security Management
Effective cloud security management relies on several key components. Each plays a role in protecting the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of cloud assets.
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM ensures that only authorized users can access specific cloud assets. This includes implementing:
- Role-based access controls (RBAC)
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Least privilege access principles
Proper IAM reduces the risk of data leaks due to compromised credentials or insider threats.
2. Encryption and Data Protection
Encrypting data in transit and at rest is essential. Cloud security management includes configuring encryption settings correctly and managing encryption keys securely.
3. Continuous Monitoring
Cloud environments require ongoing visibility into activity logs, access events, and network behavior. Monitoring tools can detect unusual patterns that may indicate a breach or misconfiguration.
4. Vulnerability Management
Security teams must regularly scan cloud assets for vulnerabilities. This includes applying patches, disabling unused services, and fixing misconfigured security groups or firewalls.
5. Compliance and Governance
Organizations need to ensure that their cloud environment complies with legal and regulatory requirements. Security management includes:
- Policy enforcement
- Auditing and reporting
- Retention policies
Common Challenges in Cloud Security Management
Even with the right tools and policies, organizations still face challenges in managing cloud security. Here are some of the most common:
1. Asset Sprawl
As teams adopt more cloud services, keeping track of all assets becomes difficult. This can result in assets going unmonitored, leaving potential vulnerabilities unaddressed.
2. Lack of Standardization
Different teams may use different cloud providers or deployment models. Without a centralized approach, enforcing consistent security standards can be difficult.
3. Misconfigurations
A simple misconfiguration, such as leaving a storage bucket public, can expose sensitive data. These errors are often the result of human oversight and lack of automation.
4. Complexity of Shared Responsibility
Cloud providers and customers share responsibility for security. Providers manage physical infrastructure, but customers must secure data, users, and applications. Misunderstanding this model can lead to security gaps.
5. Limited Visibility Across Multi-Cloud Environments
Organizations that use multiple cloud providers may struggle with visibility and integration. Without a unified view of cloud assets, securing them becomes harder.
Real-World Example: Misconfigured Cloud Storage
In a widely reported case, a company exposed over 100 million customer records due to a misconfigured cloud storage bucket. The asset was left accessible without proper authentication, allowing anyone with the URL to access sensitive information.
This incident highlights the importance of combining cloud asset management with security controls. Knowing that the storage bucket existed and ensuring its configurations were secure could have prevented the breach.
Best Practices for Cloud Security Management
To build a strong cloud security strategy, organizations can adopt the following best practices:
1. Maintain an Accurate Inventory of Cloud Assets
Regularly audit your cloud environment to identify and catalog every asset. Automate asset discovery where possible to ensure real-time visibility.
Read more: Top 10 Tools for CMDB Automated Discovery
2. Automate Security Controls
Automation reduces the risk of human error. Use tools to automatically apply policies, update configurations, and monitor compliance.
3. Enforce Least Privilege Access
Only provide users and applications with the permissions they need. Periodically review access policies to remove outdated privileges.
4. Monitor and Audit Activity Logs
Enable logging for all cloud services. Regularly analyze logs to detect suspicious activity or unauthorized access.
5. Secure APIs
APIs are a common entry point for attackers. Implement API authentication, rate limiting, and logging to prevent abuse.
6. Integrate Security with DevOps
Adopt a “shift-left” approach by integrating security checks early in the development pipeline. This includes scanning infrastructure-as-code for vulnerabilities before deployment.
7. Train Teams on Cloud Security
Educate employees on secure practices and their roles in maintaining cloud security. This helps reduce accidental misconfigurations or risky behaviors.
The Role of Cloud Asset Management Platforms
Modern cloud asset management platforms can simplify security efforts by providing a centralized dashboard to track assets, enforce policies, and manage risks. These tools often include:
- Asset inventory and classification
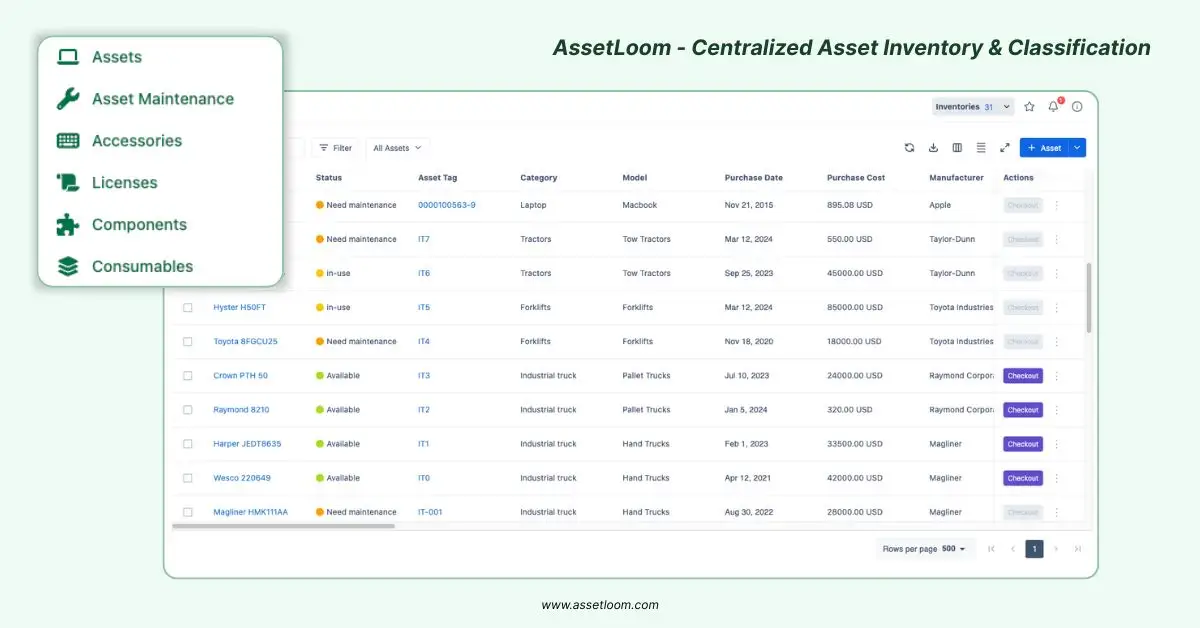
AssetLoom - Centralized Asset Inventory and Classification
- Compliance tracking
- Configuration drift detection
- Integration with security tools
Explore Top 10 Cloud Asset Management Software for Modern Businesses in 2025
By combining cloud asset management with robust security practices, organizations can reduce risk while maximizing the value of their cloud investments.
Conclusion
Cloud security management is not optional; it's a core requirement for protecting your digital infrastructure. As more assets move to the cloud, visibility, control, and security become essential. Integrating cloud security with asset management enables organizations to reduce vulnerabilities, improve compliance, and respond to incidents faster.
The connection between cloud security management and cloud asset management is clear: you can’t secure what you don’t know exists. By maintaining an accurate inventory of cloud resources and applying consistent security policies, businesses can confidently manage their cloud environments in a secure and scalable way.

Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom. right in your inbox














![Top 10 Cloud Asset Management Software for Modern Businesses [2025 Updated]](https://assetloom.com/marketing/blog/cloud-asset-management-software.png)






























![IT Asset Lifecycle Management Policy Template [Free Download]](https://assetloom.com/marketing/blog/it-asset-lifecycle-management-policy-template.webp)




































