What Is IT Asset Discovery? The First Step in Preventing IT Asset Loss
IT Asset Discovery helps businesses track and manage assets, preventing loss, by using active, passive, agent-based, and agentless methods, with automation enhancing security and visibility.
IT asset loss is a growing concern for many businesses. IT asset discovery is the first step in preventing these problems. It helps you identify, track, and manage every piece of technology connected to your network. From hardware like computers and servers to software and cloud-based tools, IT asset discovery ensures you always know where your assets are and who is using them.
What is IT asset discovery?
IT asset discovery is the process of identifying and tracking all the technology resources within an organization’s IT environment. This includes everything from computers, servers, and mobile devices to software applications and network infrastructure. The goal of IT asset discovery is to create a comprehensive, real-time view of all IT assets.
In simple terms, it’s about knowing what devices and software your business is using, where they are, and how they’re performing. This visibility allows organizations to manage their assets more efficiently, ensure compliance, reduce the risk of asset loss or misuse, and optimize their IT resources.
IT asset discovery typically involves scanning your network or using specialized software to find and catalog all connected devices, applications, and components. Once discovered, the information about each asset, such as its location, user, configuration, and status, is stored in an asset management system. This data can be integrated with a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) to provide a centralized location for tracking all IT assets and their relationships, improving overall asset visibility and management.
Read also: CMDB Discovery Tools: What They Are and Why Your IT Team Needs One
What assets can be discovered?
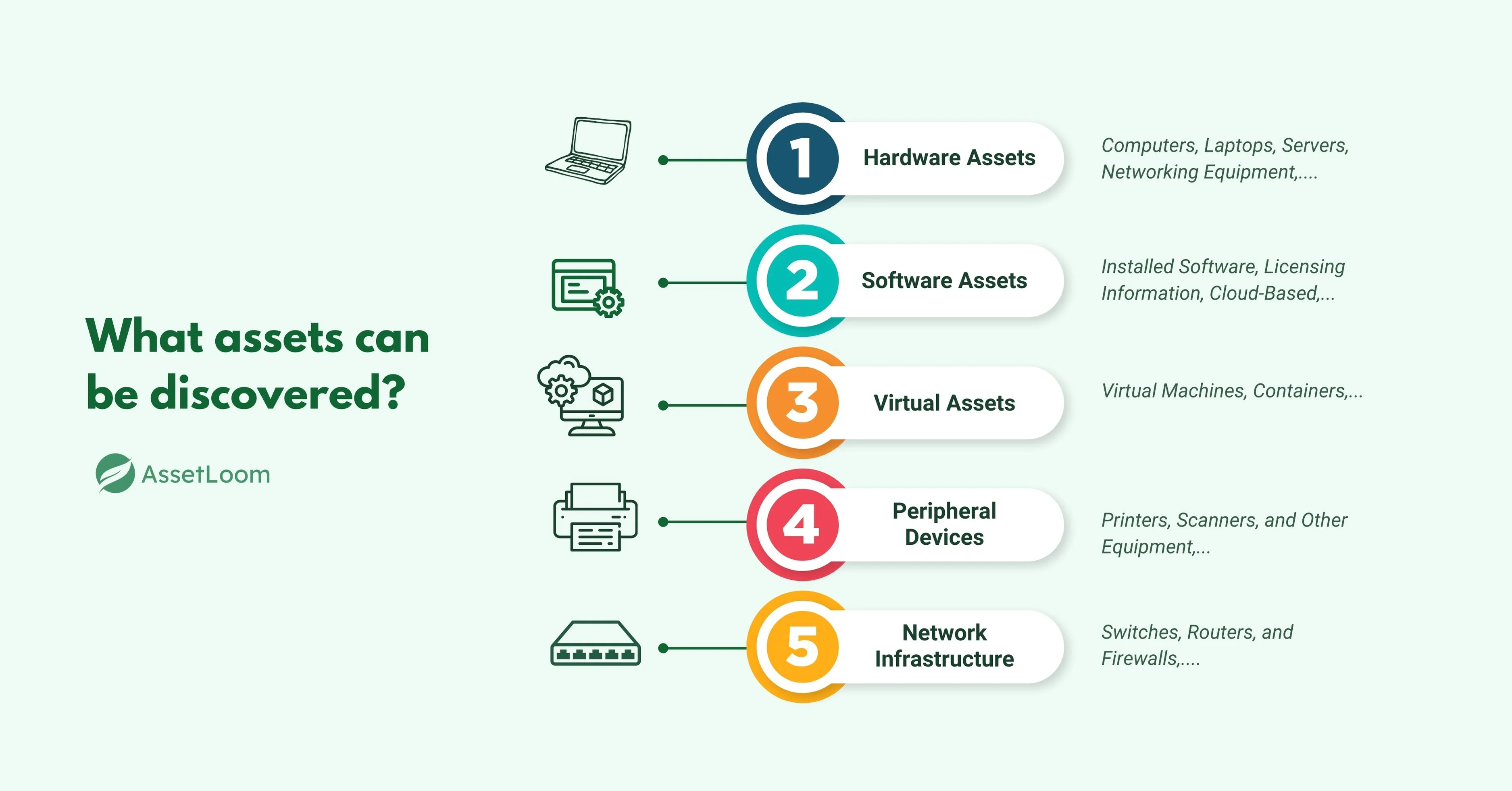
IT asset discovery isn’t limited to just hardware. It covers a wide range of assets that make up your IT environment, including both physical and virtual resources. Here's a breakdown of the key asset types that can be discovered:

1. Hardware Assets
- Computers and Laptops: Devices used by employees or connected to your network.
- Servers: Physical or virtual servers hosting data or applications.
- Networking Equipment: Routers, switches, firewalls, and other devices that connect systems within the network.
- Mobile Devices: Smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices used within the organization.
2. Software Assets
- Installed Software: Applications running on devices, including operating systems and productivity tools.
- Licensing Information: Software licenses that need to be tracked for compliance and renewals.
- Cloud-Based Software: Applications hosted on the cloud that are used within your IT infrastructure.
3. Virtual Assets
- Virtual Machines: Instances running on hypervisors or cloud environments.
- Containers: Virtualized environments running in containerization platforms like Docker.
4. Peripheral Devices
- Printers, Scanners, and Other Equipment: Non-computing devices that are part of your network or IT infrastructure.
5. Network Infrastructure
- Switches, Routers, and Firewalls: Core networking equipment that ensures connectivity and security.
- Storage Systems: Disk arrays, SANs, and cloud storage that support data management.
By identifying and tracking all of these assets, IT asset discovery ensures that no resource is overlooked. This comprehensive approach provides a clear view of what is being used across the organization, making it easier to manage and secure.
Active vs. passive IT asset discovery
When it comes to IT asset discovery, two main approaches are commonly used: active and passive discovery. Each method has its own strengths and is suited for different environments. Let’s take a closer look at both:
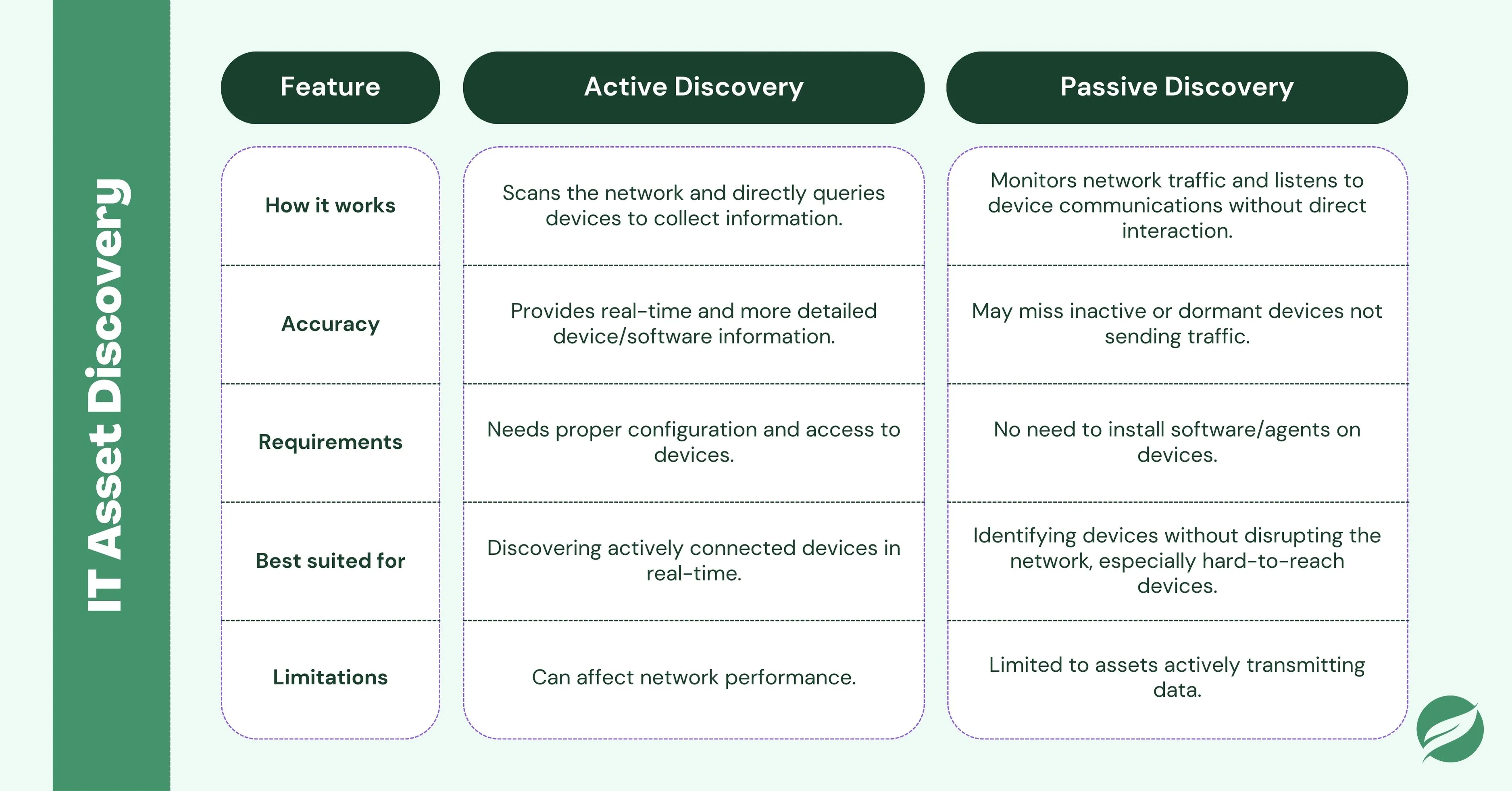
Active IT Asset Discovery
Active discovery involves scanning the network to detect and identify assets. It typically requires sending requests to devices or systems to gather information about them. This method is more intrusive, as it actively probes each device or network endpoint to collect data.
Pros:
- Provides real-time data by directly querying devices.
- Capable of identifying devices that are actively connected to the network.
- More accurate for discovering devices and software in real-time.
Cons:
- Can generate network traffic, which might affect performance.
- Requires proper configuration and access to the devices being scanned.
Passive IT Asset Discovery
Passive discovery, on the other hand, doesn’t actively scan devices. Instead, it relies on monitoring network traffic and observing device activity. It listens to the communications between devices on the network and collects information without directly interacting with them.
Pros:
- Less intrusive, with minimal impact on network performance.
- Doesn’t require installing any software or agents on the devices.
- Ideal for discovering devices that are not easily accessible or when you want to avoid interrupting the network.
Cons:
- May not capture assets that are not actively transmitting data over the network.
- It can sometimes miss devices that are dormant or inactive at the time of monitoring.
Both methods have their uses, and many organizations combine them for a more comprehensive asset discovery strategy. By using both active and passive discovery, businesses can ensure a complete inventory of all assets across their network, including those that may not always be online.
Agent-based vs. agentless IT Asset Discovery
Another key distinction in IT asset discovery is whether the process is agent-based or agentless. Both methods help businesses discover and track their IT assets, but they work in different ways and offer unique advantages and challenges.
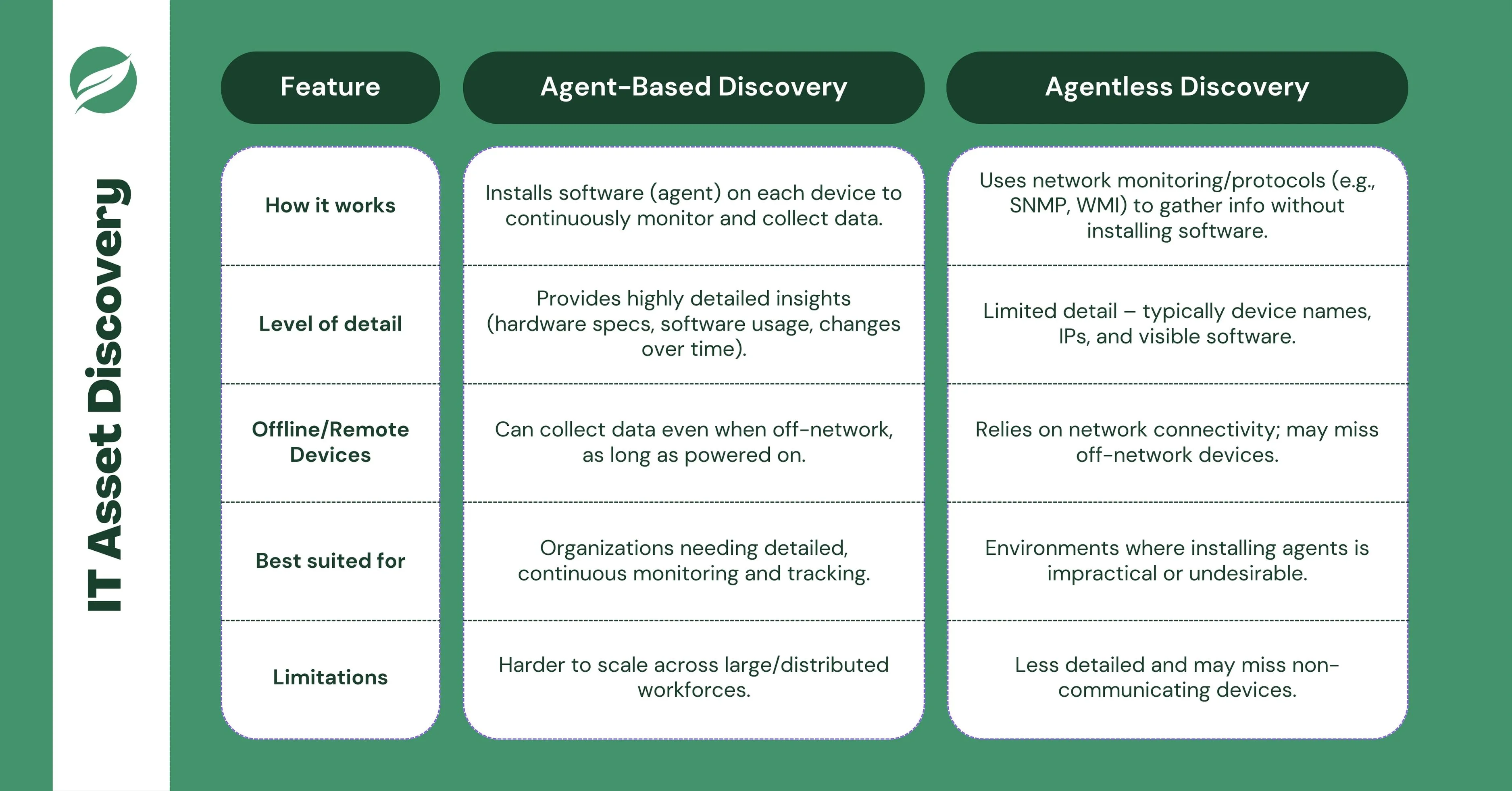
Agent-Based IT Asset Discovery
Agent-based discovery involves installing a piece of software (an agent) on each device that you want to track. The agent runs in the background, continuously monitoring and collecting data about the asset, such as its hardware specifications, software installations, and usage patterns.
How it works:
- The agent gathers detailed information, like hardware specifications, software installations, and system configurations.
- It can also track the device’s usage, health status, and any changes to the asset over time.
- Even if the device is not actively connected to the network, the agent can still gather data as long as the device is turned on.
Pros:
- Provides detailed, real-time insights into each device, including information about its configuration and software usage.
- Agents can monitor devices even when they’re not connected to the network, as long as they are powered on.
- Can be customized to collect specific data based on the organization's needs.
Cons:
- Requires installing and maintaining software on each device, which can be time-consuming.
- May impact system performance, especially on older or resource-constrained devices.
- Can be difficult to manage at scale, especially for organizations with large, distributed workforces.
Agentless IT Asset Discovery
Agentless discovery doesn’t require installing any software on the devices. Instead, it works by monitoring the network traffic or using network protocols (like SNMP or WMI) to gather information about devices and assets connected to the network.
How it works:
- The discovery tool "listens" to the network and looks for any data being sent between devices. From this, it collects asset information like device names, IP addresses, and software in use.
- It doesn’t require anything installed on the device itself – it just collects information from what’s actively communicating on the network.
Pros:
- No need for software installation on each device, making it easier to implement and maintain.
- Less intrusive, with minimal impact on device performance.
- Ideal for environments where installing agents is impractical or undesirable.
Cons:
- It may not provide as much detailed information compared to agent-based discovery.
- Can miss devices or assets that are not actively communicating on the network.
- Relies heavily on network connectivity and may not work effectively for remote or off-network assets.
In many cases, organizations choose a hybrid approach, using both agent-based and agentless discovery methods. This ensures they capture the most accurate data, whether the device is online, off-network, or difficult to reach with an agent.
Types of IT asset discovery
There are several types of IT asset discovery methods, each designed to address specific needs and environments. Understanding these types will help you choose the right approach based on your organization's requirements.
1. Network Discovery
Network discovery is the process of scanning the network to identify all devices connected to it. This can include computers, servers, network devices, printers, and other IT equipment. Network discovery tools can help businesses map out their entire network, giving them a visual representation of what’s connected and where.
Pros:
- Provides a comprehensive view of all devices connected to the network.
- Helps track new and unknown devices as soon as they connect to the network.
Cons:
- May not detect assets that are not actively connected to the network at the time of discovery.
- Can miss devices in remote locations or those off the network.
2. Cloud Asset Discovery
With the increasing adoption of cloud services, discovering assets in cloud environments is essential for modern IT asset management. Cloud asset discovery focuses on identifying and tracking virtual resources hosted in public or private cloud environments, such as virtual machines, cloud storage, and software as a service (SaaS) applications.
Pros:
- Crucial for businesses using hybrid or fully cloud-based infrastructure.
- Ensures visibility over cloud resources that may be harder to track through traditional discovery methods.
Cons:
- Discovery may rely on APIs or cloud-specific tools, which can have limited integration with other systems.
- Cloud environments are dynamic, and asset data can change frequently, requiring constant updates.
3. Endpoint Discovery
Endpoint discovery involves identifying and tracking devices like laptops, desktops, mobile phones, and tablets. These devices are typically used by employees and often access company networks remotely, making endpoint discovery essential for maintaining security and control over all endpoints.
Pros:
- Provides visibility into the devices that employees are using, whether they’re on-site or working remotely.
- Crucial for ensuring endpoint security, especially with the rise of remote work.
Cons:
- Devices may not always be connected to the network, leading to gaps in discovery.
- It can be challenging to manage when employees frequently switch devices or work from different locations.
4. Database and Software Discovery
This type of discovery focuses on identifying software applications, databases, and related configurations within your IT infrastructure. It ensures that all software installations, licenses, and versions are tracked, making it easier to manage compliance and optimize software usage.
Pros:
- Helps prevent unlicensed software use, ensuring compliance with vendor agreements.
- Provides valuable information for optimizing software costs and usage.
Cons:
- May not catch software that is installed but not actively running.
- It can be difficult to track software in virtual environments without the right tools.
Each of these discovery types plays a crucial role in ensuring businesses have a complete and up-to-date inventory of their IT assets. By combining them, organizations can gain comprehensive insights into both their physical and virtual environments.
IT asset discovery vs. Inventory Management
While both IT asset discovery and IT inventory management deal with tracking and managing IT resources, they serve different purposes and operate in distinct ways. Understanding the difference between the two can help organizations streamline their asset management strategies.
IT Asset Discovery
IT asset discovery focuses on identifying and tracking all devices, software, and network components in real-time. It involves scanning the network, devices, or cloud environments to automatically detect and gather detailed information about every asset in use. This process helps businesses maintain visibility into their IT infrastructure and ensure that nothing is overlooked or forgotten.
Key Features of IT Asset Discovery:
- Real-Time Data Collection: Provides continuous updates on the status, location, and condition of assets.
- Automation: Tools scan networks and devices without requiring manual input or constant oversight.
- Comprehensive Visibility: Discovers a wide range of assets, from physical devices to virtual resources.
- Integration with CMDB: Can feed data directly into a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) for better centralized management.
**Purpose: **The primary goal of IT asset discovery is to provide a comprehensive, real-time inventory of all assets within the organization to enhance visibility, security, and operational efficiency.
Inventory Management
Inventory management, on the other hand, is more focused on tracking the physical and financial aspects of assets. This process involves organizing and managing the storage, movement, and usage of items like hardware, software, and other IT equipment. While it includes tracking asset locations and quantities, it may not provide real-time updates or granular details about each asset.
Key Features of Inventory Management:
- Static Records: Keeps track of physical assets and their status, but often lacks real-time data.
- Manual Updates: Requires regular checks and manual entries to ensure the data is up-to-date.
- Physical Tracking: Focuses on the movement and storage of physical assets, such as hardware.
- Limited Scope: May not include virtual assets or provide insights into the broader IT environment.
**Purpose: **Inventory management is primarily concerned with managing stock levels, ensuring assets are available when needed, and controlling costs. It often deals with the broader logistical aspects of asset tracking.
Read also: Best IT Inventory Tracking Strategies for Small & Large Businesses
Key Differences:
- Real-Time vs. Static: IT asset discovery provides real-time updates on assets, whereas inventory management relies on periodic manual updates.
- Automation vs. Manual: Discovery tools automatically detect and update asset information, while inventory management often requires human input.
- Scope: IT asset discovery covers a wider range of assets, including virtual assets, software, and network components. Inventory management is more focused on physical assets and their movement.
- Use Case: IT asset discovery is used to maintain accurate, up-to-date visibility of all assets for security, optimization, and compliance. Inventory management is used to control and track physical assets, ensuring they are available and properly managed.
How They Complement Each Other
While IT asset discovery provides the granular details and real-time visibility needed to manage assets effectively, inventory management helps ensure those assets are properly tracked, stored, and utilized. Together, they offer a comprehensive solution for managing both the physical and virtual elements of IT assets.
IT asset discovery use cases and benefits
IT asset discovery is a vital tool for businesses looking to manage their IT infrastructure more effectively. It provides numerous use cases and benefits that help organizations ensure efficiency, security, and compliance. Let's take a look at some common use cases and the key benefits of implementing IT asset discovery.
Security and Risk Management
IT asset discovery plays a key role in identifying security risks. By continuously tracking all assets, organizations can ensure that no unauthorized devices or software are connected to the network. It helps detect rogue devices, outdated software, or missing security patches, which are often exploited by cybercriminals. Example: If an employee connects a personal device to the network, the discovery tool will flag it, allowing IT teams to take action and prevent potential vulnerabilities.
Software License Compliance
Keeping track of software licenses is critical for maintaining compliance with vendors. IT asset discovery helps organizations ensure that they aren’t using more software licenses than they’re entitled to, and it can also flag instances where software may be running without a valid license. Example: Discovery tools can automatically scan for unlicensed or expired software and provide alerts before the software is used in violation of terms.
Audit and Reporting
IT asset discovery simplifies audits by providing an up-to-date list of all assets within the network. This makes it easier for organizations to comply with internal and external auditing requirements. Example: When an external auditor requests a list of assets, the IT asset discovery system can generate reports that are accurate and up to date, ensuring that the business is prepared for any audits.
Lifecycle Management
From procurement to retirement, IT asset discovery tracks the entire lifecycle of IT assets. It helps organizations manage asset depreciation, plan for upgrades, and ensure that assets are properly disposed of when they reach the end of their useful life. Example: Discovery tools can alert teams when an asset is approaching the end of its useful life, helping them plan for replacement before it affects operations.
Network Optimization and Troubleshooting
IT asset discovery helps identify network bottlenecks and inefficiencies. By knowing exactly what devices are connected to the network, IT teams can optimize performance and troubleshoot problems more effectively. Example: If a network issue arises, discovery tools can quickly pinpoint which devices are connected, making it easier to identify faulty or outdated equipment that may be causing the problem.
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
During mergers and acquisitions, organizations need to assess and integrate IT assets from both sides. IT asset discovery helps provide a complete inventory of both organizations' assets, ensuring smooth integration and avoiding surprises down the road. Example: When two companies merge, asset discovery tools can help identify duplicate software licenses or unregistered hardware that may need to be addressed.
How does IT asset discovery work?
IT asset discovery involves scanning and identifying all devices, software, and components in an organization’s IT environment. While the exact process can vary depending on the discovery method used, the general workflow typically follows these steps:
1. Scanning the Network or Devices
- The first step in IT asset discovery is scanning the network to identify devices that are connected or communicating. This can be done through network protocols, direct queries, or monitoring network traffic.
- Active discovery typically involves sending requests (like pings) to devices to gather information, while passive discovery listens to network traffic to detect devices without actively interacting with them.
- For devices that are off the network, agent-based discovery involves installing small software agents on each device to collect information even when not connected to the network.
2. Identifying and Categorizing Assets
- Once devices and software are discovered, the next step is to identify what they are. This includes determining the type of device (e.g., computer, server, printer), the operating system, software versions, hardware specifications, and any other relevant details.
- Information such as serial numbers, IP addresses, and MAC addresses are typically collected. For software, license numbers, version details, and installation status are tracked.
3. Storing and Organizing the Data
- After assets are identified, the collected data is stored in an asset management system or Configuration Management Database (CMDB). This central database serves as a single source of truth for all asset information, making it easy to access and update data as needed.
- The CMDB can link related assets together, showing how devices and software interact within the infrastructure. For example, it might link a laptop with the software installed on it and the user who is responsible for it.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Updates
- IT asset discovery isn’t a one-time event. It requires continuous monitoring to ensure that the data remains current. Automated tools can regularly scan the network or devices to detect new assets, decommissioned assets, or changes in existing assets (such as software updates or configuration changes).
- For example, if a new device is added to the network or if an existing device is moved, the discovery tool will automatically update the asset list to reflect these changes.
5. Reporting and Alerts
- Once assets are discovered and organized, the system can generate detailed reports on asset status, usage, and compliance. These reports are crucial for audits, planning, and decision-making.
- Additionally, alerts can be set up to notify IT teams when critical changes occur, such as when an unauthorized device is connected, a software license is nearing expiration, or an asset reaches its end of life.
6. Integration with Other Systems
- For effective IT management, IT asset discovery tools often integrate with other business systems like network management tools, IT service management (ITSM) systems, or security software.
- These integrations allow for seamless data flow across platforms, providing a holistic view of the organization’s assets. For instance, data from the discovery tool can be used to trigger workflows in an ITSM system when an asset needs repair or replacement.
Automate IT asset discovery with AssetLoom Asset Management
Automating IT asset discovery with AssetLoom helps businesses streamline asset tracking, reduce manual work, and keep their IT environment up-to-date. Here's how it works:
- **Automatic Network Scanning: **AssetLoom scans your network to detect all connected devices and software in real time, ensuring accurate, up-to-date asset tracking.
- **Agent-Based and Agentless Discovery: **Choose between agent-based or agentless discovery, allowing for flexible, non-intrusive monitoring of devices on or off the network.
- **Real-Time Updates and Alerts: **New assets are automatically detected, and any changes are instantly reflected in your asset inventory. Alerts notify you of critical updates, such as unauthorized devices or license expirations.
- **Centralized Data Management: **Asset information is stored in one platform, simplifying access, integration with other systems, and cross-functional collaboration.
- **Custom Reporting: **Generate detailed reports for asset lifecycle management, compliance tracking, and audit preparation.
By automating asset discovery, AssetLoom helps businesses stay organized, compliant, and efficient, while also reducing the risk of asset loss.

Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom. right in your inbox















![Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) Policy Best Practices [FREE TEMPLATE]](https://assetloom.com/marketing/blog/bring-your-own-device-policy-best-practices.webp)