8 Simple Ways to Do Proactive IT Asset Management
Proactive IT Asset Management keeps costs down and systems reliable with 8 simple ways to track, optimize, and manage your IT assets effectively.
If you work in IT, you probably know the feeling of chasing problems all the time. A laptop suddenly stops working, software licenses expire without warning, or no one can remember who has which device. These situations create stress, waste money, and take focus away from more important work.
This usually happens because IT assets are managed in a reactive way. Instead of planning, teams often wait until something breaks or goes missing before taking action. The result is higher costs, more downtime, and unnecessary risks.
Proactive IT Asset Management offers a better approach. It’s about staying one step ahead by keeping track of what you own, how it’s being used, and what needs to happen next. It doesn’t have to be complicated, but it does require some simple practices that make IT assets easier to manage and less of a headache.
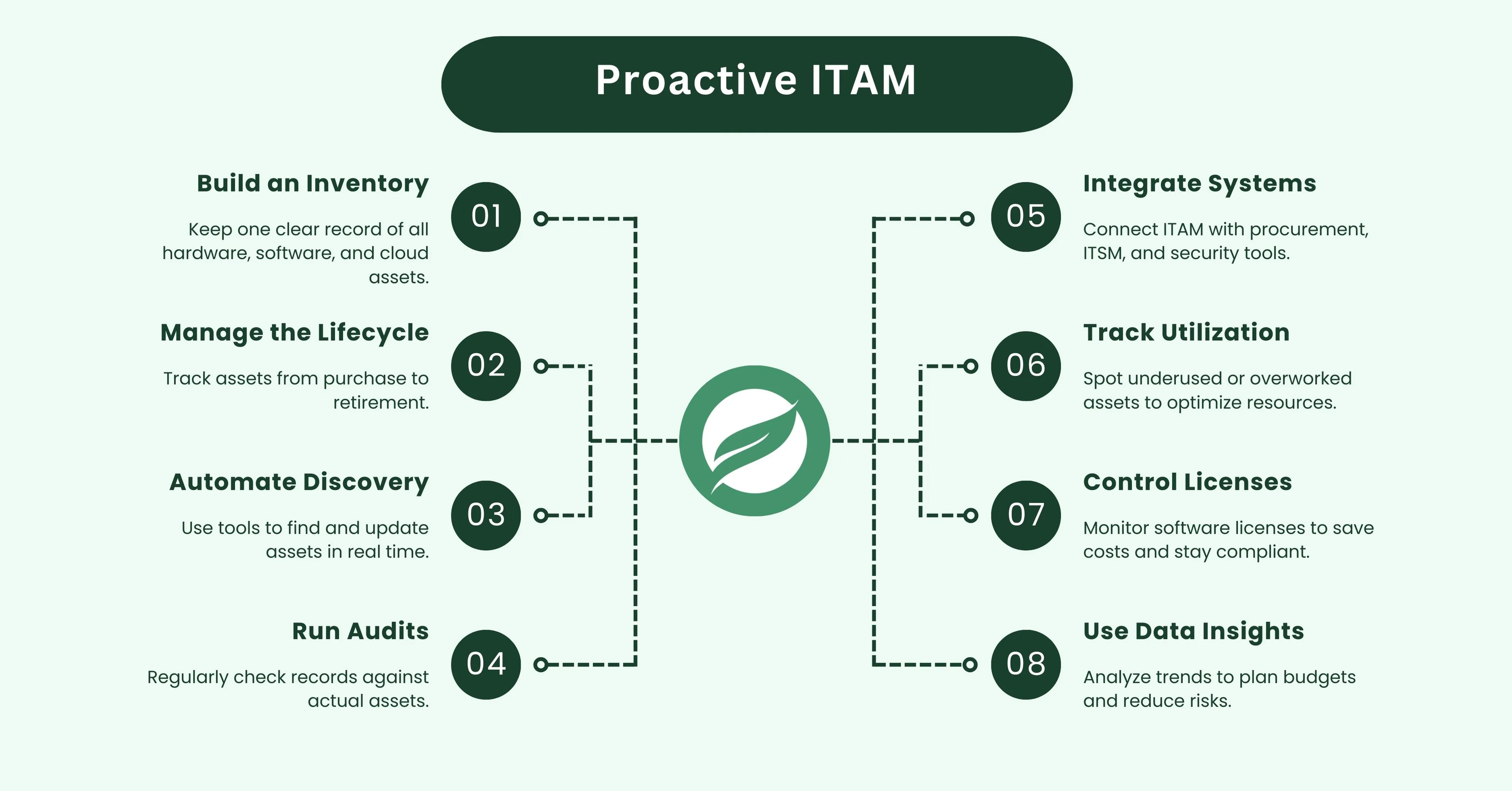
1. Establish a Comprehensive Asset Inventory
The first step in proactive IT asset management is knowing exactly what you own. Many teams run into problems because they don’t have a clear, updated list of assets. This often leads to surprise costs, forgotten licenses, or devices that get lost in the shuffle.
A proper inventory acts as your single source of truth for everything in your IT environment.
What should be included in the inventory?
- Hardware: laptops, desktops, servers, networking equipment
- Software: installed applications, operating systems, licensed tools
- Cloud services: SaaS subscriptions, cloud storage, virtual machines
- Mobile devices: phones, tablets, and other portable equipment
How to build and maintain the inventory
- Use automated CMDB discovery tools: scan the network to detect connected devices
- Deploy agents or scripts: collect details like manufacturer, model, location, and assigned user
- Update regularly: new devices and software should be added immediately
- Assign responsibility: someone should own the task of keeping the inventory accurate
Why this matters
- Prevents wasted spending on forgotten or unused assets
- Helps track who is responsible for each device
- Makes planning for upgrades and replacements easier
2. Manage the Full Asset Lifecycle
It’s not enough to just know what assets you have. To stay proactive, you need to manage each asset throughout its entire lifecycle. Every device and piece of software has a beginning, a middle, and an end. If you only focus on the day-to-day use, you’ll miss important steps that could save money and reduce risks.
Key stages of the asset lifecycle
- Acquisition: purchasing or subscribing to the asset
- Deployment: assigning it to a user or system
- Usage and maintenance: tracking performance, applying updates, and scheduling repairs
- Refresh or upgrade: replacing old equipment before it fails
- Disposal: securely retiring or recycling assets when they reach the end of life
Tips for effective lifecycle management
- Standardize the process so every asset goes through the same steps
- Keep clear records of purchase dates, warranty periods, and expected end-of-life dates
- Plan refresh cycles in advance to avoid sudden downtime
- Dispose of assets securely to protect sensitive data
Why this matters
- Prevents sudden failures that disrupt work
- Helps forecast budgets for replacements and upgrades
- Keeps sensitive data safe when devices are retired
Read also: 10 Reliable IT Asset Lifecycle Management Software Picks for 2025
3. Automate Asset Discovery and Updates
Keeping track of IT assets manually is time-consuming and prone to mistakes. A spreadsheet might work at first, but as your organization grows, it becomes impossible to keep everything accurate. This is where automation makes a big difference.
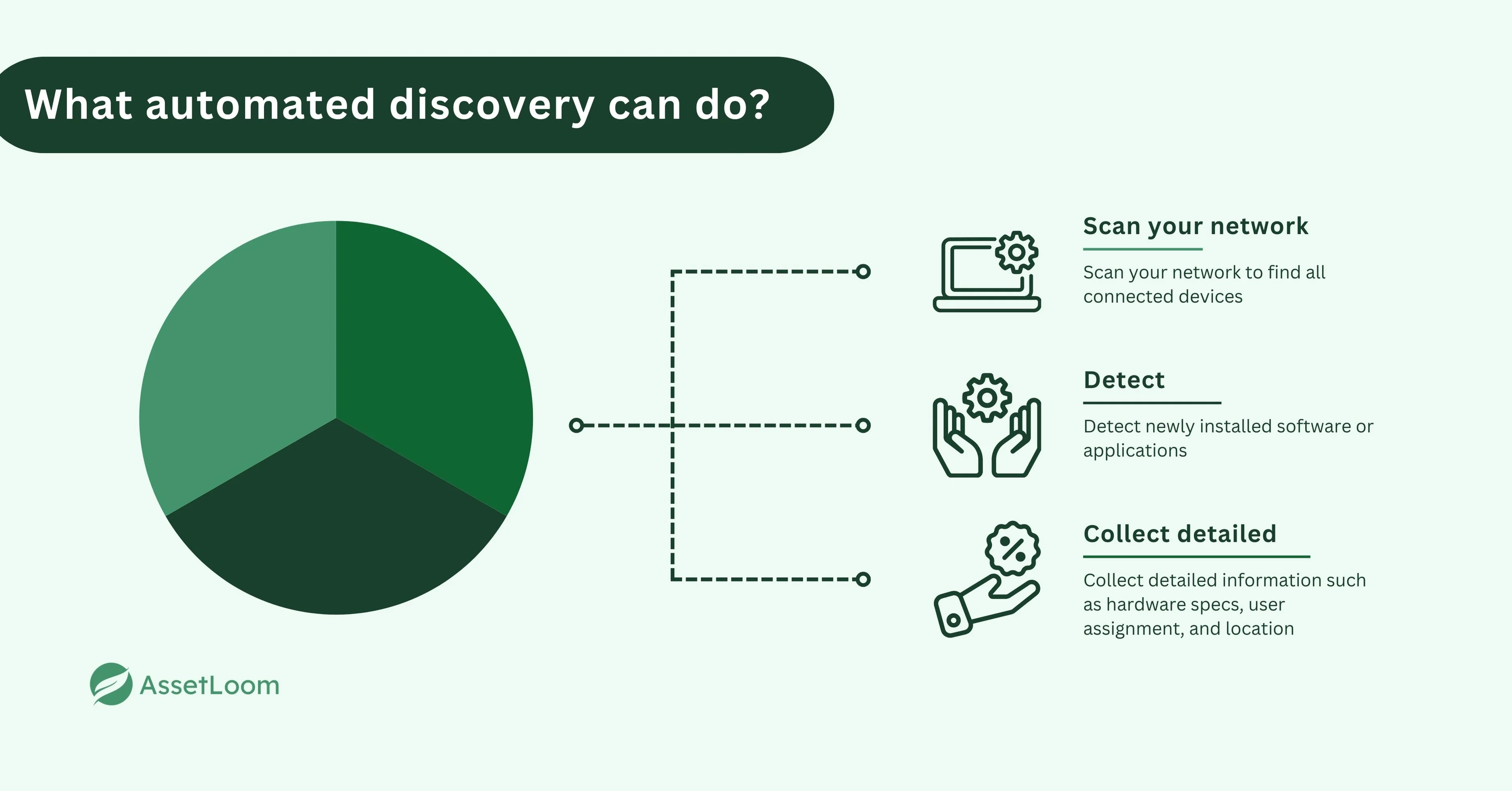
What automated discovery can do
- Scan your network to find all connected devices (Understanding Network Discovery Scan)
- Detect newly installed software or applications
- Collect detailed information such as hardware specs, user assignment, and location
- Update records in real time when changes happen
Benefits of automating updates
- Accuracy: reduces human error from manual entry
- Time savings: eliminates repetitive data collection tasks
- Real-time insights: lets you know immediately when a new device joins the network
- Compliance support: keeps records up to date for audits
Best practices
- Schedule regular automated scans to keep your inventory fresh
- Combine different methods, like agent-based discovery and network monitoring
- Reconcile automated results with physical checks during audits
Why this matters
- Ensures your inventory always reflects reality
- Helps spot unauthorized devices or shadow IT before they become a problem
- Provides IT teams with reliable data for decision-making
4. Conduct Regular Audits and Reconciliations
Even with a solid inventory and automated tools, things can still slip through the cracks. Devices may go missing, software might not be installed as recorded, or shadow IT could sneak in. Regular audits and reconciliations help catch these gaps before they become serious issues.
What to audit
- Hardware: check that all devices listed in your system physically exist and are in use
- Software: verify that licenses match installations
- Cloud accounts: ensure subscriptions are active, used, and assigned correctly
- User assignments: confirm each asset is linked to the right employee or department
How to run effective audits
- Schedule audits at regular intervals (quarterly or biannually works for many organizations)
- Compare physical inventory with digital records
- Involve both IT staff and end users to validate accuracy
- Document discrepancies and resolve them quickly
Benefits of reconciliation
- Improves the reliability of your IT asset records
- Identifies unused or missing assets that can be reassigned or retired
- Helps meet compliance and security requirements
- Builds trust in your IT data across the organization
Why this matters
- Prevents wasted money on assets that aren’t being used
- Reduces the risk of non-compliance during official audits
- Keeps your asset data accurate and actionable
5. Integrate ITAM with Other Systems
IT Asset Management works best when it doesn’t stand alone. Many problems happen because ITAM isn’t connected with other business systems, which leads to duplicate work and missing information. Integrating ITAM with the right tools creates a complete and consistent view of your assets.
Systems to connect with ITAM
- Procurement: so that every new purchase is automatically added to your inventory
- IT Service Management (ITSM): to link assets with support tickets and incidents
- Configuration Management Database (CMDB): to map relationships between assets and services
- Security tools: to track vulnerabilities and apply patches faster
Benefits of integration
- Less manual work: asset details flow automatically across systems
- Better visibility: IT teams can see how assets connect to services and users
- Stronger compliance: asset records stay consistent across departments
- Faster support: service desk agents can quickly see which asset is linked to a ticket
Best practices
- Start with the systems most closely tied to assets, like procurement and ITSM
- Use APIs or built-in connectors for seamless data sharing
- Keep integration rules clear to avoid data duplication
Why this matters
- Eliminates silos and ensures asset data is reliable everywhere
- Improves collaboration between IT, finance, and security teams
- Creates a smoother experience for both IT staff and end users
6. Monitor and Optimize Asset Utilization
Owning IT assets is one thing, but making sure they are used effectively is another. Many organizations waste money on devices and software that sit idle, while other assets are overworked and break down sooner than expected. Monitoring usage helps you spot these patterns and make smarter decisions.
What to monitor
- Hardware usage: which laptops, servers, or printers are underutilized or overused
- Software usage: track logins and activity levels for licensed applications
- Cloud subscriptions: check if all accounts are active and necessary
- Storage and network performance: ensure resources are allocated properly
Ways to optimize utilization
- Reassign unused devices to teams that need them
- Retire or recycle old equipment that no one uses
- Cancel or downgrade software licenses that are rarely accessed
- Upgrade or add resources where demand is consistently high
Benefits of utilization tracking
- Cost savings: stop paying for assets that provide no value
- Improved performance: reduce strain on overused equipment
- Smarter planning: align resources with actual business needs
Why this matters
- Ensures every dollar spent on IT assets delivers value
- Reduces downtime caused by overloaded or neglected devices
- Supports better long-term budgeting and planning
7. Implement Proactive License Management
Software licenses can easily become one of the biggest hidden costs for IT. Paying for unused licenses, missing renewal dates, or falling out of compliance can all hurt your budget and create legal risks. Proactive license management helps you stay in control.
What to track
- Number of purchased licenses vs. number actually in use
- Renewal dates for each license or subscription
- License terms and restrictions (per user, per device, concurrent use, etc.)
- Vendor agreements and support contracts
How to manage licenses proactively
- Maintain a central record of all licenses and agreements
- Set reminders for renewal and cancellation dates
- Regularly audit license usage to identify unused or duplicate subscriptions
- Reclaim and reassign licenses from employees who no longer need them
Benefits of proactive license management
- Avoid penalties: stay compliant during vendor audits
- Save money: stop paying for licenses no one uses
- Simplify renewals: no more last-minute surprises
- Better planning: forecast future software needs more accurately
Why this matters
- Reduces wasted spending on unused or unnecessary software
- Prevents compliance issues that could lead to costly fines
- Keeps your software environment organized and predictable
8. Leverage Data for Better Decision-Making
IT asset management is not just about keeping lists. The data you collect can give you valuable insights that help shape smarter strategies. By looking at trends and patterns, you can predict future needs, reduce waste, and make better investment choices.
Types of data to analyze
- Asset performance: track repair frequency, downtime, and failure rates
- Cost data: compare purchase costs, maintenance expenses, and total cost of ownership
- Usage trends: see which devices and software are heavily used vs. rarely touched
- Lifecycle information: forecast when assets will need upgrades or replacements
How to use the data
- Identify assets that cost more to maintain than replace
- Negotiate better contracts with vendors using accurate usage data
- Plan budgets with real numbers instead of guesswork
- Spot risks early, such as security vulnerabilities on outdated systems
Benefits of data-driven ITAM
- Smarter planning: align IT spending with actual business needs
- Cost control: stop overspending on assets with poor return on investment
- Risk reduction: address issues before they impact operations
Why this matters
- Turns ITAM into more than record-keeping
- Gives decision-makers clear insights to guide strategy
- Helps IT become a proactive partner in business growth
Summary
Proactive IT Asset Management is about staying one step ahead so you can reduce surprises, save money, and keep IT operations running smoothly. The practices we covered are simple, but when done consistently, they make a big difference.
Here’s a quick recap of the 8 simple ways:
| # | Practice | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Establish a Comprehensive Asset Inventory | Keep a single, updated record of all hardware, software, cloud, and mobile assets |
| 2 | Manage the Full Asset Lifecycle | Track assets from purchase to disposal to avoid surprises and plan ahead |
| 3 | Automate Asset Discovery and Updates | Use tools to reduce errors and keep records current in real time |
| 4 | Conduct Regular Audits and Reconciliations | Cross-check records with reality to find missing or unused assets |
| 5 | Integrate ITAM with Other Systems | Connect ITAM with procurement, ITSM, CMDB, and security tools |
| 6 | Monitor and Optimize Asset Utilization | Spot underused or overworked assets and reallocate resources wisely |
| 7 | Implement Proactive License Management | Stay compliant, cut wasted costs, and avoid renewal surprises |
| 8 | Leverage Data for Better Decision-Making | Use insights from asset data to plan budgets, reduce risks, and improve strategy |
Conclusion
IT asset problems don’t have to catch you off guard. By taking a proactive approach, you can prevent common headaches like missing devices, expired licenses, and sudden equipment failures.
The eight practices we’ve covered are straightforward but powerful. They help you stay organized, reduce costs, and keep your IT environment reliable. When your assets are managed proactively, your team spends less time firefighting and more time focusing on the work that really matters.

Related Blogs
Hardware Management
How Construction Equipment Management Software Cuts Costs?

ITAM in General
Fixing Inventory Sync Issues Between ITAM and ITSM Tools

ITAM in General
The Hidden Costs of a Stolen Work Laptop & How to Prevent Them

Subscribe for Expert Tips and Updates
Receive the latest news from AssetLoom. right in your inbox


































![Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) Policy Best Practices [FREE TEMPLATE]](https://assetloom.com/marketing/blog/bring-your-own-device-policy-best-practices.webp)